The so-called food chain refers to the food relationship between the weak and the strong and the interdependence between living things. As the saying goes, "big fish eat small fish, small fish eat shrimps, and shrimps eat the mud bottom" vividly and vividly metaphors this interdependent food chain relationship. .
The first link in the Southern Ocean food chain is phytoplankton, mainly diatoms, as is the case in other oceans around the world. Phytoplankton can perform photosynthesis and convert carbon dioxide and water into organic matter under sunlight, that is, convert solar energy into chemical energy and store it. Phytoplankton are primary producers that feed other consumers.
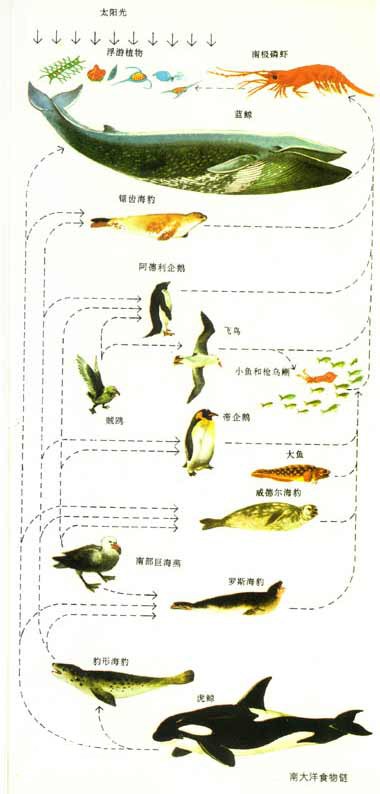
The food chain of the Southern Ocean
Another link in the food chain is zooplankton, mainly krill in the Southern Ocean, which feed on phytoplankton. Zooplankton, in turn, are food for other organisms at higher trophic levels, such as seals, penguins and whales.
The last link in the food chain is human development and utilization of marine biological resources. Over the years, people have exploited krill, fish, seals and whales in the Southern Ocean to varying degrees.
The food chain in the Southern Ocean is quite fragile because Antarctic krill is a key link in the food chain. In the marine pasture of the Southern Ocean, there are lush phytoplankton, more than 90% of which are diatoms. They are the food for an astonishing number of Antarctic krill. In turn, the krill maintain a small but astonishing number of high-level organisms. Animal life such as seals, penguins and whales etc. Once the krill link is interrupted, the entire food chain in the Southern Ocean is destroyed.
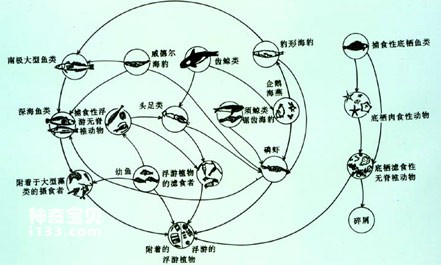
Food chain in floating ice area
The reason why the Southern Ocean is dense and rich in life is mainly because the water from the northern warm ocean current is rich in nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which forms an upwelling and flows to the surface, promoting the growth of phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are extremely abundant in upwelling areas and in coastal waters of the Antarctic continent. People can see them "dying" seawater or ice floes dark green or brown. Abundant phytoplankton provide abundant food for zooplankton, which in turn support other higher animals.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.