Locusts are a pest that causes serious damage to crops and vegetation. The following methods are usually used to eliminate locusts:
1. Chemical control: Use pesticides to spray or fumigate areas where locusts gather. This method is effective, but it may also have negative effects on the environment and human health and should be used with caution.
2. Biological control: Use natural enemies or parasites to control the number of locusts. For example, natural enemy insects or birds can be introduced to prey on locusts, or parasitic insects can be used to parasitize locusts to limit their reproduction.
3. Mechanical control: Use mechanical equipment (such as insect traps, nets, traps, etc.) to collect and kill locusts. This method is suitable for small-scale locust outbreaks, but may not be effective for large-scale outbreaks.
4. Ecological control: Reduce the habitat and food source of locusts by changing the structure and function of the ecosystem. For example, by changing the farming method of farmland and increasing vegetation coverage, the damage of locusts can be reduced.
5. Integrated pest and disease control: Comprehensively use chemical, biological, mechanical and other means to take targeted comprehensive control measures to achieve the best control effect.
In actual operations, appropriate prevention and control measures should be taken based on the type, number, distribution range of locusts, local environmental conditions and agricultural production conditions to minimize the damage caused by locusts to crops.
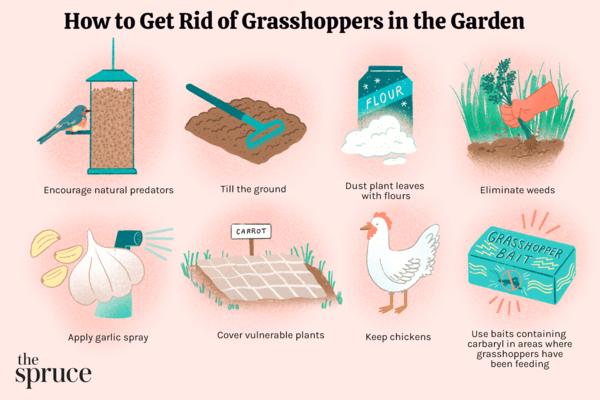
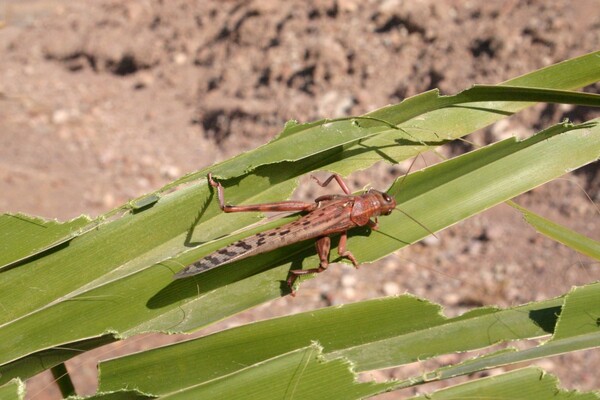
Locusts are a type of insects, mainly including insects such as Acrididae and Trichodoridae. Both their larvae and adults feed on plants and are an important agricultural pest. The characteristics and habits of locusts are as follows:
Appearance characteristics: Locusts are large in size, with an oblong body, two pairs of short wings, and well-developed hind legs suitable for jumping. The larvae and adults are similar in appearance, but the larvae are smaller.
Life habits: Locusts mostly live in arid and grassland environments and like to gather together to form large groups. They are usually active at night or in the early morning and mostly stationary during the day.
Strong reproductive capacity: Locusts reproduce very quickly. A pair of adults can lay up to hundreds of eggs. After hatching, the larvae can grow into adults in a short time and form a new group.
Wide diet: Locusts feed on a variety of plants, including crops, grassland vegetation, etc., causing serious damage to agriculture and ecosystems.
Strong migration ability: Some locusts have the ability to migrate over long distances, causing the spread of pests across borders.
Few natural enemies: Locusts have relatively few natural enemies, including birds, spiders, parasites, etc., but it is difficult to effectively control locusts.
Since locusts are large in number, reproduce rapidly, and have a certain ability to migrate, once they break out, they are likely to cause serious agricultural disasters. Therefore, timely and effective measures need to be taken to prevent and control locusts to reduce losses to agricultural production.
Locusts, also known as "grasshoppers", are a general term for a class of insects, mainly including insects of the family Tetrigoniidae and Acrididae. They are a typical herbivorous insect that feeds on various plants, including crops and wild plants, and are considered one of the important pests in agricultural production.

The characteristics of locusts mainly include:
Appearance characteristics: Adults are large and slender, usually with two pairs of wings and long hind legs suitable for jumping. Larvae are similar in appearance to adults, but smaller in size.
Strong reproductive capacity: Locusts reproduce quickly, a pair of adults can lay hundreds of eggs, and the larvae grow rapidly after hatching, and can become highly fertile adults in a short period of time.
Group behavior: Locusts often form large groups, hundreds of millions, causing great damage to crops and vegetation.
Migration ability: Some locusts have strong migration ability and can migrate long distances, causing the spread of pests across borders.
Diet is wide: Locusts feed on all kinds of plants, including gramineous crops, vegetables, grassland vegetation, etc., which has a serious impact on agricultural production and the ecological environment.
Locusts have caused serious disasters many times in history, causing serious damage to human agricultural production and the ecological environment. In order to prevent and control locusts, comprehensive measures such as chemical control, biological control, and mechanical control are usually taken to reduce their harm to crops.

Locusts have both beneficial and harmful sides, depending on their numbers and behavior.
The beneficial insect side:
Role in natural ecological balance: In nature, a moderate amount of locusts is part of the ecological balance. They can serve as a link in the food chain and provide food for other animals.
Soil improvement: In a certain amount, locust excrement can improve soil texture and promote plant growth.
Herbage: Locusts can control the overgrowth of plants within a moderate range and help maintain the health of vegetation.
Pest side:
Pest side:
Large-scale crop damage: When the number of locusts is too large, they will form a large group, devour crops and wild vegetation on a large scale, causing serious agricultural and ecological disasters.
Economic losses: Locust disasters will cause a large number of crop failures, affect farmers' income, and cause significant losses to the agricultural economy.
Ecosystem impact: Large-scale locust breeding and devouring behavior will destroy the balance of the ecosystem and affect the survival of wild animals and plants.
Therefore, the degree of benefit or harm of locusts depends on their number and environmental conditions. A moderate number of locusts can be part of the ecosystem and have certain benefits; but too many locusts will become serious pests and cause serious harm to agriculture and the ecological environment. In order to maintain ecological balance and protect agricultural production, effective prevention and control measures need to be taken to manage locusts.
animal tags: locust
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.