Weevils, particularly those in the family Curculionidae, exhibit some of the most intriguing mating behaviors in the insect world. One of the most striking features of male weevils is the presence of hundreds of tiny spines at the tip of their reproductive organs. This article delves into the significance of these spines during mating, their evolutionary advantages, and what they reveal about the complex world of insect reproduction.
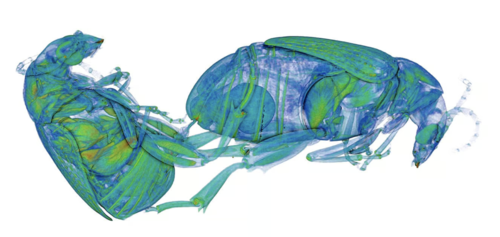
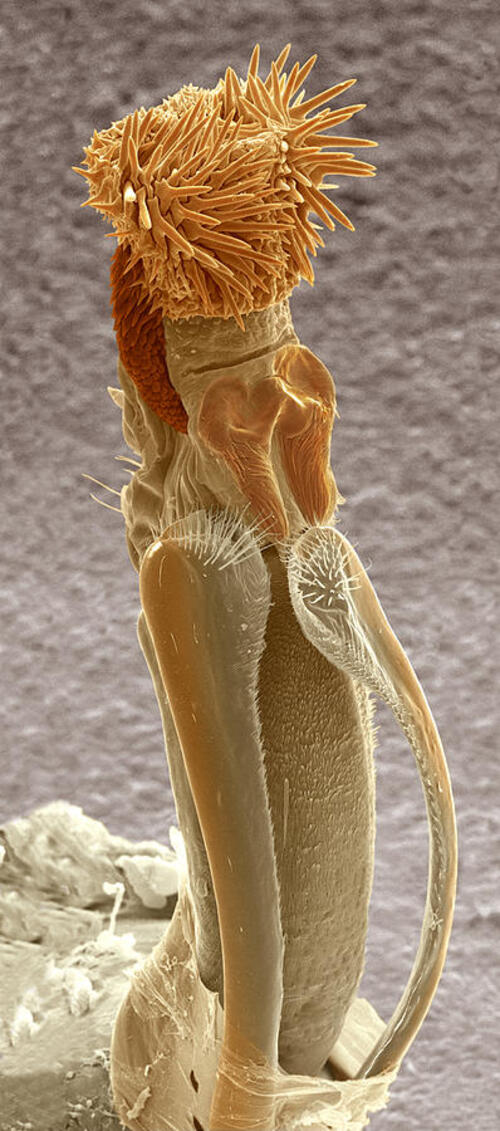
The male weevil's genitalia is not only designed for sperm transfer but is also equipped with a unique adaptation: hundreds of tiny spines or barbs.
Structure and Function: These spines are thought to serve multiple purposes, including gripping the female during mating, ensuring a secure connection, and potentially aiding in the transfer of sperm more effectively.
Variability Among Species: Different species of weevils exhibit variations in the size and arrangement of these spines, which can influence mating success and species recognition.
The mating behavior of male weevils is a fascinating spectacle that involves several steps:
Courtship Rituals: Before mating, males engage in elaborate courtship displays that may include pheromone production and physical gestures to attract females.
Spine Interaction: During copulation, the spines on the male’s genitalia play a crucial role. They help anchor the male to the female, reducing the likelihood of separation and increasing the chances of successful sperm transfer.
The evolution of spiny genitalia in male weevils offers several advantages that enhance reproductive success:
Sperm Competition: In species where females mate with multiple males, the spines can help ensure that a male’s sperm is preferentially used for fertilization, giving him a competitive edge.
Increased Copulation Duration: The presence of spines can lead to longer mating durations, allowing for more sperm to be transferred and increasing the male's chances of fathering offspring.
While the spines provide advantages to males, they can also impact female weevils:
Physical Trauma: The use of spines can cause physical injury to females during mating, leading to potential fitness costs. Some females may develop adaptations to mitigate these risks.
Mate Selection: Female weevils may choose mates based on the characteristics of the male's spiny genitalia, indicating a potential role of sexual selection in their evolution.
The mating behavior of male weevils, particularly the role of their spiny genitalia, provides a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of insect reproduction. These adaptations not only enhance the male's chances of successful mating but also reflect the ongoing evolutionary arms race between the sexes.
As researchers continue to explore these intricate behaviors, we gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary pressures that shape mating strategies in the insect world. The spiny genitalia of male weevils exemplifies the remarkable diversity of reproductive adaptations found in nature.
Q1: Why do male weevils have spines on their genitalia?
A1: The spines help secure the male to the female during mating, ensuring effective sperm transfer and enhancing reproductive success.
Q2: How does spine morphology vary among weevil species?
A2: Different weevil species exhibit variations in spine size and arrangement, which can affect mating success and species recognition.
Q3: What impact do these spines have on female weevils?
A3: The spines can cause physical injury to females during mating, leading to potential fitness costs and influencing female mate choice.
By exploring the unique mating behavior of male weevils and the role of their spiny genitalia, we gain valuable insights into the intricate world of insect reproduction and the evolutionary strategies that drive it.
animal tags: Weevils
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.