Traumatic insemination is a unique and aggressive mating behavior observed in certain species of bed bugs, particularly Cimex lectularius. Unlike most insects, where males deposit sperm into the female reproductive tract, male bed bugs use their sharp reproductive organ, often referred to as the "intromittent organ" or "spermalege," to pierce the female's abdomen directly. This method of insemination raises intriguing questions about its evolutionary advantages and implications for reproductive strategies.
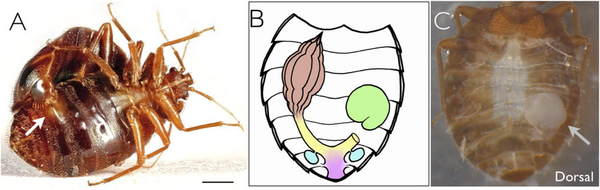
Piercing the Abdomen: During mating, the male bed bug thrusts its specialized genitalia into the female’s body wall, bypassing the traditional reproductive pathway. This method allows for immediate sperm transfer but can cause significant injury to the female.
Sperm Placement: The sperm is deposited into the female's body cavity, where it can still travel to the ovaries to fertilize the eggs. This unusual strategy, while dangerous for the female, ensures that the male's genetic material is introduced effectively.
Traumatic insemination offers several potential benefits that may explain its evolution:
Increased Mating Success: By circumventing the female's reproductive tract, males can achieve higher rates of fertilization, especially in environments where competition for mates is intense.
Sperm Competition: This method may also enhance the male's chances in sperm competition, as the direct injection of sperm can lead to a higher fertilization rate compared to traditional mating methods.
While this method may benefit male bed bugs, it has significant repercussions for females:
Injury and Stress: The act of traumatic insemination can cause physical harm, leading to stress and potentially affecting the female's reproductive success and longevity.
Evolutionary Countermeasures: Some female bed bugs have developed adaptations, such as thicker abdominal walls or specific mating behaviors, to mitigate the risks associated with traumatic insemination.
The behavior surrounding traumatic insemination also highlights interesting social dynamics:
Mating Strategies: Males may engage in aggressive courtship behaviors to subdue females, indicating a highly competitive mating environment.
Multiple Mating: Females often mate with multiple males, which may lead to sperm competition and influence reproductive strategies on both sides.
Traumatic insemination is a striking example of how mating strategies can diverge dramatically from the norm. While it allows male bed bugs to achieve higher rates of reproductive success, it comes at a considerable cost to females. Understanding this behavior sheds light on the complexities of sexual selection and the evolutionary pressures that shape reproductive strategies in the animal kingdom.
Q1: What is traumatic insemination?
A1: Traumatic insemination is a mating behavior in which male bed bugs pierce the female's abdomen with their reproductive organ to inject sperm directly into her body cavity.
Q2: Why has this behavior evolved?
A2: It likely evolved to increase mating success and enhance sperm competition in environments where competition for mates is high.
Q3: How does this affect female bed bugs?
A3: This method can cause injury and stress to females, impacting their reproductive success and overall health.
Traumatic insemination exemplifies the extraordinary diversity of reproductive strategies in nature, highlighting the interplay between aggression and reproduction in the evolutionary narrative of bed bugs.
animal tags: Bed-Bugs
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.