Many animals can see colors like humans, but some are color blind. Whether an animal can see colors depends on whether they have color receptors in the retina of their eyes. Cones are responsible for perceiving colors like red, green, and blue, while rods are more sensitive to light than cones and are responsible for visual perception in low-light environments. This is why we can't see colors clearly in the dark. Humans have three types of cones, red, blue, and green, which allow us to see the full spectrum of colors, an ability known as trichromatic vision.
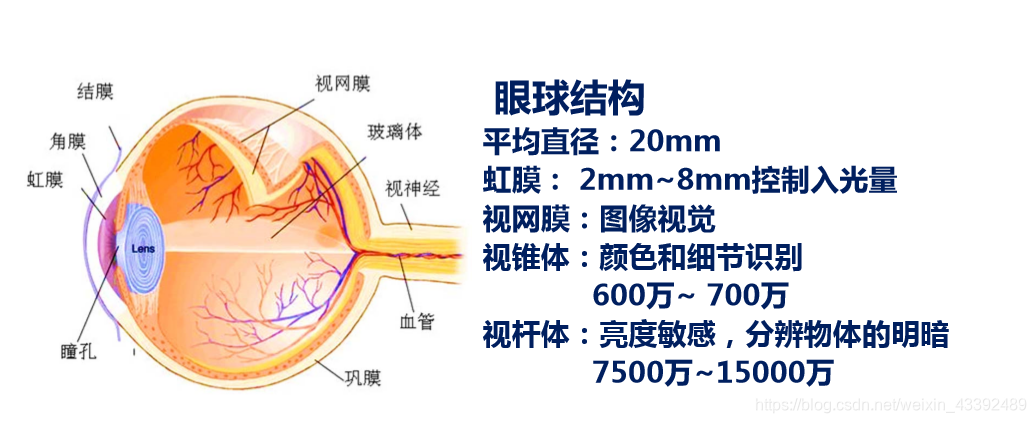
However, some animals have fewer cones or more rods, which limits their ability to perceive colors and also affects their night vision. This article will explore some color-blind animals and why they can't see the full spectrum of colors. Let's take a closer look!
Although color-blind animals can't see bright colors like humans, they have other ways of perceiving the world around them. Here are some common color-blind animals.
Whales have better night vision, probably because they have more rods.

Whales are monochromatic, meaning they have only one type of cone. Therefore, they see the world in different shades of gray. However, they are able to distinguish between light and dark.
In addition, whales can see better in the dark, probably because they have more rods. They also use echolocation to navigate their environment and find prey. Meanwhile, whales have a tapetum lucidum, which reflects light through the retina, helping them see better in the dark.
Dogs rely on other senses, such as smell and hearing, to make up for their limited vision.

Like most mammals, dogs are dichromats, meaning they have only two types of cone cells. Dogs primarily see shades of gray, blue, and yellow, and have trouble distinguishing between red and green, making their color vision similar to that of humans who are red-green color blind. Dogs are also insensitive to changes in brightness, meaning the colors they see are not as vivid as our own.
Dogs rely on other senses, such as smell and hearing, to make up for their lack of vision. They also have more rods and a reflective layer, which allows them to see more clearly in low-light conditions.
Cats are dichromats, similar to humans who are color blind.

Like dogs, cats are dichromats, possessing two types of cone cells, making them similar to humans who are color blind. They are able to distinguish between different shades of blue, yellow, and red. Additionally, they are also able to distinguish between red and green light. However, cats are better at distinguishing blue and violet, and less able to perceive colors closer to the red spectrum, such as pink and violet. For example, pink may look like green, and violet like another shade of blue.
To compensate for their lack of color perception, cats have a reflective layer that reflects light back to the retina, which allows them to see more clearly in low-light conditions.
Owls are more sensitive to light than humans.

Owls are unique animals that have some very interesting characteristics. Owls are nocturnal, have excellent hearing, and are able to turn their heads 270 degrees. Owls have unusually large eyes compared to their skulls. Another interesting feature is that owls cannot move their eyes, and they need to turn their heads to see around. However, owls have very poor color vision.

Owls are more sensitive to light than humans due to their greater number of rods. Additionally, they have fewer cones, meaning they cannot see the colors we can, and are therefore considered color blind. In other words, the world of owls is black and white. However, despite their poor color vision, they do not rely on echolocation like most color blind animals, but instead use their excellent night vision to hunt in complete darkness.
Raccoons have a reflective layer in their eyes that reflects light, helping them see more clearly in low light conditions.

Raccoons (Procyon lotor) are another nocturnal color blind animal that lives primarily in the humid forests of North America. Raccoons have poor long-sightedness and are considered color blind. However, their eyes are better at recognizing green light, and their eyes reflect red light in the dark.
To compensate for their lack of color vision, raccoons have a photoreflector, a structure that reflects light off the retina, helping them see better in low-light conditions. Like most color-blind animals, raccoons rely on their keen senses of smell, touch, and hearing to effectively navigate and hunt in their habitat.
By understanding the characteristics of these color-blind animals, we can see that despite their limitations in color perception, they use their other senses and the unique abilities they have evolved to survive in their world just fine.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.