Solid fossils are fossils formed by preserving all or part of the paleontological remains themselves (especially the hard parts).

mosquito in amber
Under particularly suitable circumstances that can avoid air oxidation and bacterial corrosion, the remains of some organisms can be preserved relatively intact without significant changes. For example, some mammoths that lived in the Quaternary Period 25,000 years ago and were preserved in the permafrost found in Siberia not only have their skeletons intact, but also their skin, body hair, flesh, and even the food in their stomachs. The complete fossil of a woolly rhinoceros discovered in Staluny, Poland, that fell into an asphalt lake 10,000 years ago, is the most complete vertebrate fossil known so far. The coal seams formed in the Fushun Coal Mine in China from the Eocene to the Oligocene (about 56 million years ago to 23 million years ago) contain a large amount of amber, which often contains well-preserved insect fossils such as mosquitoes, bees, and spider fossils. .
However, the remains of such organisms that have not undergone significant fossilization or have only some slight changes are rarely found. The vast majority of biological fossils only retain their hard parts, and they have undergone varying degrees of fossilization. The so-called "fossilization" means that as sediments turn into rocks during diagenesis, the biological remains buried in the sediments have undergone physical and chemical transformations, but still retain their biological appearance and some biological features. The role of structure. Fossilization generally includes several methods and processes such as mineral filling, alternation and distillation.
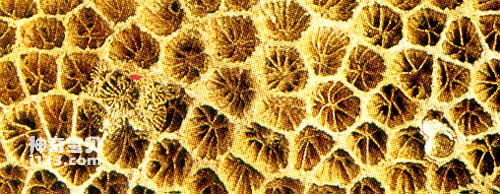
coral fossil
For example, there are more or less gaps between the hard structures of invertebrates, such as the partitions of corals, the grooves of sponges, the chambers of foraminifera, the porous and loose inner layers of some shells, and the lining of vertebrates. skeleton. Especially in the limb bones of vertebrates, the hollow part is left after the organic matter in the medulla decomposes and disappears. After being buried under the ground for a long time, the minerals (mainly calcium carbonate) dissolved in the groundwater often pass through the pores. Recrystallization results in a denser, solid, and heavier solid fossil. This effect is the mineral filling effect.

petrified wood
The process in which the constituent materials of biological hardware are gradually dissolved during burial and then gradually supplemented and replaced by foreign minerals is called alternation. In this process, if the dissolution and alternation speeds are equal and the molecules are exchanged, the original fine structure can be preserved. For example, the formation of petrified wood, often found around the world, is the result of the replacement of wood fibers in ancient trees with silica, but fine structures such as growth rings and cell outlines are still preserved. And if the alternation speed is lower than the dissolution speed, the subtle structure of the biological hardware will also be destroyed, and ultimately only the external form of the original object will remain. Common alternating materials include silica, calcite, dolomite, pyrite, etc. The corresponding processes can be called silicification, calcite, dolomitization and pyritization.
Distillation refers to the process in which unstable components decompose and volatile substances first evaporate and disappear after ancient biological remains are buried, and finally only a carbonaceous film is left and preserved. This process is also called charring. For example, the skeleton of graptolite is composed of chitin. After distillation under burial conditions, elements such as hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen evaporate, leaving only a carbonaceous film. For another example, the main component of plant leaves is carbohydrates. After distillation, only carbonaceous material is often preserved as fossils.
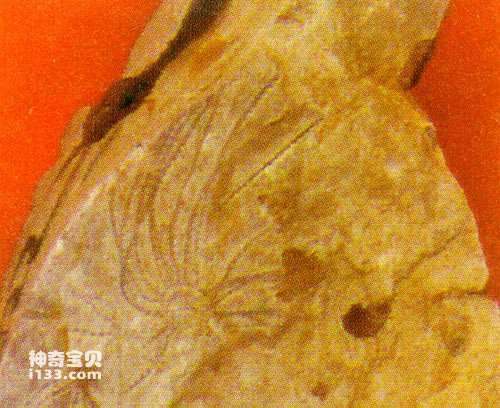

graptolite

Fossil leaves
Solid fossils preserve all or part of the remains of paleontological organisms, so generally they can provide scientists with the most detailed information on the body shape and structure of paleontological organisms, and are therefore the most important materials in paleontological research.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.