Molluscs are a category with a very large number and variety of invertebrates. There are 120,000 modern species and fossil species that have been discovered, making them the second largest category in the animal kingdom after arthropods. Molluscs have strong adaptability and are therefore widely distributed. There are a large number of members on land, fresh water and salt water, such as snails, river mussels, conch, squid, etc. are all familiar representatives to us.

snails
Although various types of molluscs have different shapes and habits, their basic characteristics are very similar. Their bodies are soft and most are not segmented. They are generally divided into four parts: head, feet, visceral mass and mantle. The mantle usually secretes a hard shell of calcium to protect the outside of the body. Because the shape of the mantle varies from species to species, the shapes of the hard shells of different species of molluscs also vary. However, except for most adult gastropods, their shells are bilaterally symmetrical, that is, bilaterally symmetrical. It is based on these differences in the structure of hard shells and soft bodies that scientists divide molluscs into 10 classes, which are monoplaque, polyplacoid, non-plate, gastropod, digopoda, bivalves, and rhinoplastids. Class cephalopods, class cephalopods, class stilts and snails.
Monoplacophytes are characterized by a shell shaped like a hat or spoon. They appeared as early as the early Cambrian period and have continued to multiply until modern times. The modern Xinkasa clam is the representative.
The polyplacoid body is symmetrical on both sides and oval in shape, and the back shell is composed of 8 bone plates. They appeared in the late Cambrian period and have continued into modern times.
Alabasters have no bony plates or shells, and their bodies are symmetrical on both sides like worms. However, their bodies are covered with a horny skin with calcium needle-like spines, which can also play a certain protective role. There are no fossil representatives of the class Anaplasma, and there are modern living ones such as Aplysia.
The gastropod class is a mollusc that we are all familiar with. Snails, snails, conches, etc. are all members of this class. Their soft bodies and shells twist during ontogeny, resulting in a single-helical shell shape. Gastropods also appeared as early as the early Cape of Good Hope, and have continued to multiply until modern times. They are distributed on land, oceans, and freshwater.

Nautilus
The shell of Digopod is like a slender tube, open at both ends and symmetrical on both sides. The Carniopoda appeared from the Ordovician period and has continued to modern times. Representative animals include hornbills and so on.
The Bivalvia class is also a familiar mollusk. River mussels, sea fans, clams and most of the shells we can pick up at the beach belong to the Bivalvia class. They are characterized by a two-valved shell with a hinged structure between the two shell valves; their soft body lacks an obvious head and has fleshy feet on its ventral side. From the Cambrian to modern times, bivalves have always been distributed in the oceans and freshwaters of the earth.
The shells of Rhythmia also look like they have two valves, but there is no hinge structure. Their shells are actually single shells in the form of "pseudo-bivalve". They are extinct ancient creatures that only lived from the Cambrian to the Ordovician. Representatives include Hyalalte shells and so on.

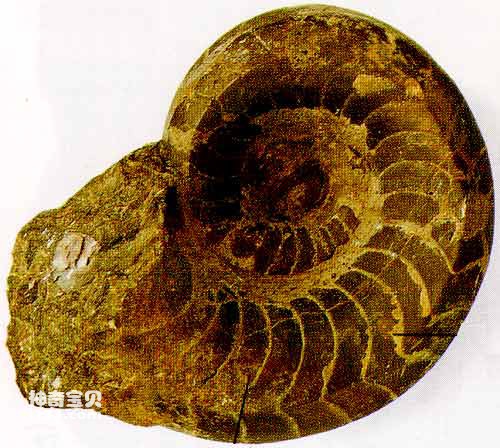
Ammonites
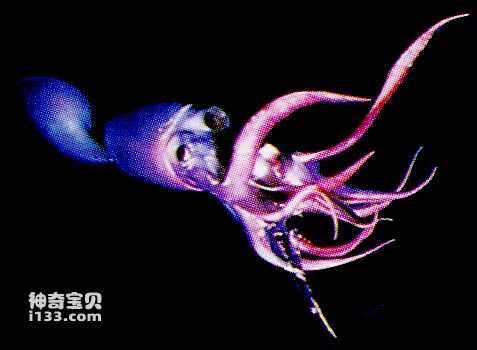
Cephalopoda is the most well-developed and advanced class in the phylum Mollusca, including nautiloids, baculites, ammonites, belemnites, and modern octopuses and cuttlefish that once flourished in large numbers and were of great significance during geological history. They are all carnivores in the ocean and are good at crawling on the bottom or swimming in the water. Cephalopods are symmetrical on both sides, with a very obvious head in front of the body, large well-developed eyes on both sides, a mouth in the center, and horny jaws in the mouth; a ring around the mouth can be used to hunt other animals. Animal wrist. Some cephalopods have outer shells, some have inner shells, and some have no shells. Cephalopods also have a long evolutionary history, from the Cambrian to modern times.
Bambooliths are a type of ancient molluscs with radial symmetry and single cone-shaped shells. They are distributed from the Ordovician to the Devonian, and are represented by Bambooliths.
Glossus is also a type of ancient mollusk with a single cone-shaped shell, but they are bilaterally symmetrical. They are distributed from the Cape of Good Hope to the Ordovician, and representatives include Glossus and others.
animal tags: Snail mussel conch squid nautilus ammonite
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.