In the middle Devonian period, some more advanced bony fishes appeared. Part or all of their bones ossify into hard bone. The outer layer of the skull is made up of a large number of bone fragments joined together in a complex pattern, covering the top and sides of the head and back over the gills. The gill arch is composed of a series of bone chains connected by joints; the entire gill is covered by a single piece of bone - the operculum. Therefore, they form a single water outlet of the gill at the posterior mobile edge of the opercular bone. Their blowholes are greatly reduced or even disappear. In most teleost fishes, the jaws are connected to the skull in a lingual joint by the lingual bone.
The vertebrae of these bony fishes have a spool-shaped central bone called a vertebra; the vertebrae are interconnected and form a movable backbone that supports the body. The spines extending upward from the vertebral body are called medullary spines; the spines extending downward from the vertebral bodies at the tail are called vein spines. The sides of the thoracic vertebrae are associated with the ribs.
The "extra" fins have degenerated and disappeared; all functional fins are supported internally by bony rays.
The scales covering the outside of the body are completely ossified. The scales of primitive bony fishes are thicker, usually diamond-shaped, and can be divided into two types: one is the tooth scales represented by early lobe-finned fishes, and the other is the hard scales represented by early ray-finned fishes. scale. As bony fishes evolved, the thickness of their scales gradually decreased, and eventually, progressive bony fishes had only a thin layer of bony scales.
Primitive bony fishes had functional lungs, but the lungs of most later bony fishes were converted into swim bladders that helped control buoyancy.
In 1990, researcher Yu Xiaobo from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered the squid in the western suburbs of Qujing, Yunnan. At that time, it was identified as a primitive meat that lived in the early Devonian period more than 400 million years ago. Fin fish. Lobe-finned fishes are a branch of the bony fish family, and the other branch of bony fishes are ray-finned fishes.
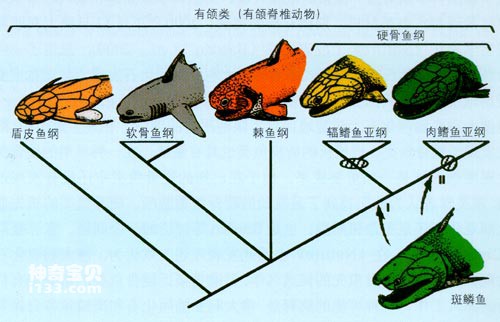
The evolutionary position of the spotted fish
In April 1999, researcher Zhu Min from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered through further research on the grouper fish that the grouper fish may not only be the most primitive lobe-finned fish, but also the most primitive representative of all bony fishes. Many of the non-teleost fish characteristics retained in the genus Ophiosaurus fill the morphological gap between teleosts and non-teleost fishes.
In the middle of the Devonian period, bony fishes differentiated into two major branches that followed different evolutionary paths: ray-finned fishes (subclass) and lobe-finned fishes (subclass).
Overall, no group of water-dwelling animals on Earth has achieved such evolutionary success as bony fishes. Even the most highly developed aquatic invertebrates, such as the various molluscs and the ammonites that developed so complexly during the Mesozoic Era, are far from the bony fishes that have such an important role in aquatic life. degree of adaptation. Bony fishes have occupied a variety of ecological niches in all waters on the planet, from small streams to large rivers, from small ponds deep in continents to various lakes, from shallow bays to various depths in the vast oceans. The waters are filled with bony fish roaming everywhere. There are also great differences in body size among various species of bony fish. Some small fish will never grow more than 1 centimeter, while tuna can grow to very large sizes. The body shapes and ecological adaptation types of teleost fishes also vary widely, each with its own merits. Moreover, the number of bony fish species and individuals far exceeds that of many other vertebrates combined. Therefore, bony fish are the real conquerors of water on earth.
animal tags: tuna
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.