In 1985, paleoanthropologist Lin Yipu discovered some ancient mammal fossils in the fissure accumulation of the Jellyfish Mountain quarry in Shanghuang Town, Liyang County (now Liyang City). After returning to Beijing, he provided these fossils to Qi Tao, an expert on Tertiary mammals at the institute. Qitao identified that some of the teeth were similar to the teeth of ancient mouse deer found in Inner Mongolia, and thus concluded that the animals with these teeth should have lived in the Early Tertiary Period (between 65 million and 24 million years ago). Subsequently, Qi Tao and other researchers went to the site to investigate and published preliminary research reports, reporting on the fossils of animals such as Lenodontus leucodon and Rabbit luhei in Luohe, and based on this, they estimated the age of mammals in the Tertiary period of the Yellow River. It is determined to be the Ildin Manha period-early Shalamulun period of the middle Eocene, about 45 million years ago.

Jellyfish Hill Quarry
Qitao continued to conduct field work in Shanghuang in the following years, unearthed a large number of fossils, and named them Shanghuang Fauna. Some of the tiny teeth are particularly noteworthy because they resemble primates in some ways, but retain many very primitive, even insectivore-like features.

Ancient Mouse Deer
Qitao’s research attracted the attention of American colleagues. Beginning in 1992, renowned vertebrate paleontologist Ms. Mary Dawson of the Carnegie Museum of Natural History (and paleoprimatologist Christopher Beard) worked with Dr. Zitao of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology. Wang Banyue, Li Chuankui, and Guo Jianwei formed a joint research team to conduct further field investigations in the Shanghuang area and related areas, and conducted in-depth research on the primate-rich Shanghuang fauna and related fauna.
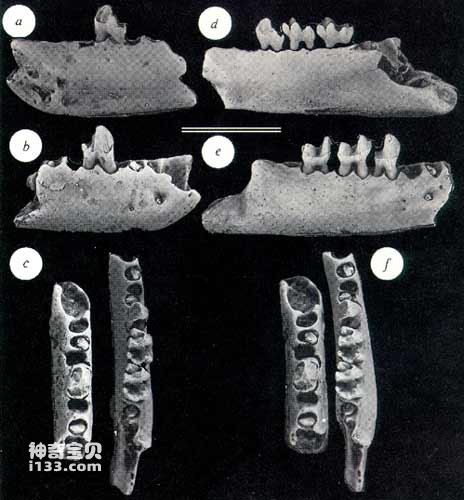
Sinensis fossil
Subsequent work discovered at least 4 species of higher primates! One of them was named Aurotus sinensis, and the other three needed further excavation and research because the data were insufficient at that time.
The fossil material of E. sinensis is only a right mandibular fragment with three teeth and some scattered teeth. However, its age is the middle Eocene epoch 45 million years ago, which is much higher than that of the higher spiritual beings of Fayoum. Primates are nearly 10 million years earlier; it suggests to people that the origin of higher primates is more likely to be in the East, in China. The so-called "dawn ape" means "the dawn of the anthropoid suborder".
animal tags: Sinensis fossil primate
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.