Qiao Tuo and others from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently reported online in the magazine "Alcheringa" about the lungfish from the Lower Devonian Yujiang Formation in Guangxi, my country - Kassel's Beakfish (Cathlorhynchus zengi), providing conclusive evidence for the discovery of fossils of the family Dipnorhynchidae outside Australia.
Lungfish is one of the only three remaining lobe-finned fishes (lungfishes, coelacanths, and tetrapods). It is also a famous "living fossil". The study of lungfish began in the history of evolutionary biology. played an important role. There are only 3 genera and 6 species of living lungfish, but lungfish were very prosperous in the Devonian Period. From 1811 to the present, about 80 genera and nearly 250 species of fossil lungfish have been discovered, of which 49 genera were found in the Devonian strata. middle. Typical lungfish are very specialized, with unique features such as palatal tooth plates; quadratic palatine and endocranial healing; and two pairs of nostrils opening on the ventral side of the brain to adapt to crushing feeding and life at the interface between land and water. . The earliest representatives of lungfish are Diabolepis, which was found in the Lohokovian strata of the Early Devonian in Yunnan, and Uranolophus and Webster's Beakfish, which were found in the Braggian strata of North America and Europe. Westollrhynchus). The bones behind the head of these primitive lungfishes are still similar to those of other early lobe-finned fishes, but the teeth and skulls have been specialized in the morphology of typical lungfishes.
The family Lungfish is the original Devonian lungfish, and its typical representatives include Dipnorhynchus, Cathlorhynchus and Speonesydrion. In the past, these three genera of lungfish were only reported in Australia and were considered endemic to Australia. Although Zhang Miman and others once classified Erikia from the Amesian strata in Yunnan, my country, into the family Lungfish, this classification has been controversial because its tooth plate has not been found. The Kassel's Beakfish reported by Qiao Tuo and others this time is a well-preserved mandibular tooth plate specimen provided by Zeng Guangchun, a fossil enthusiast in Guangxi. This specimen is very similar to the type species of the genus Cassirus in the dentition, dentition and ventral symphysis, and can undoubtedly be assigned to the genus Cassirus and becomes the family of the family Lungfish outside Australia. Definitive evidence found. The article also conducted a phylogenetic analysis of the Devonian lungfish, confirming the conclusion that Erica belongs to the family Lungfish. Lungfish fossil evidence shows that my country's South China Plate and the Australian Plate had close paleogeographic connections during the Early Devonian Amesian, confirming the hypothesis that southern my country is the center of the origin and evolution of lobe-finned fishes.
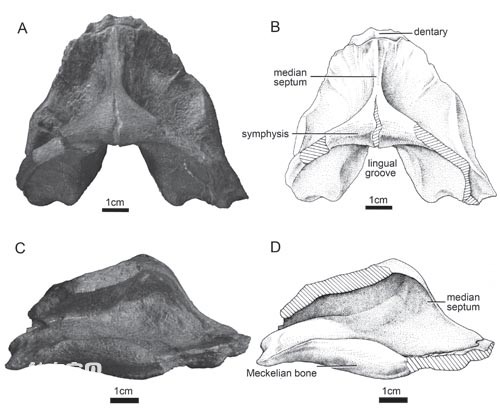
Figure 1 Specimens of Kassel's Beakfish
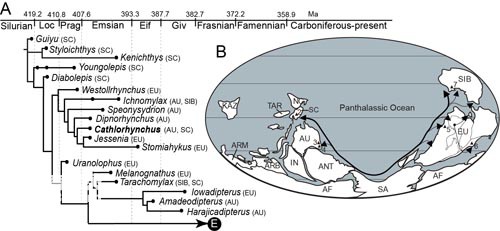
Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary routes of early Devonian lungfishes
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.