According to the World Fish Database as of February 2022, there are about 34,800 named fish species in the world, accounting for more than half of all vertebrates, and about 250 new fish species are discovered every year. The oldest known fish species is Haikouichthys ercaicunensis, which was found in the Chengjiang Fauna in Yunnan and dates back to the Cambrian period about 520 million years ago.
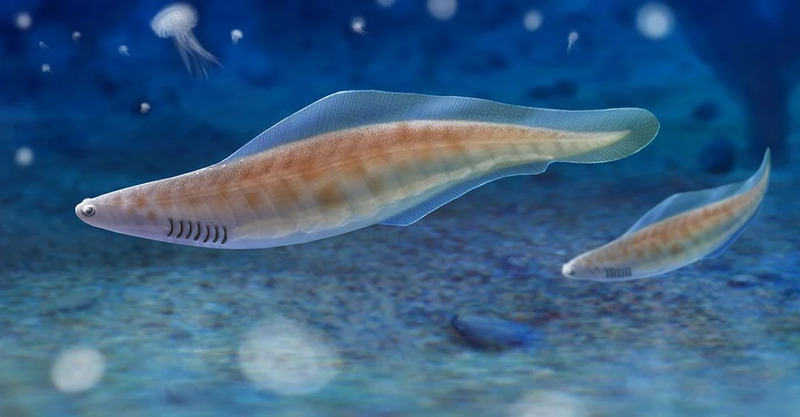

Fish mainly live in water and are distributed in marine and freshwater environments, of which about two-thirds live in the ocean and the rest live in freshwater. So, do you know which prehistoric fish still survive today? Including frilled sharks, coelacanths, lampreys, golden arowana, sturgeons, Senegalese bipinnatus, Da's sturgeon, alligator gar, giant arapaima and great white sharks. These ancient fish still exist today, let us learn about them together.
1. Frilled Shark (380 million years ago)
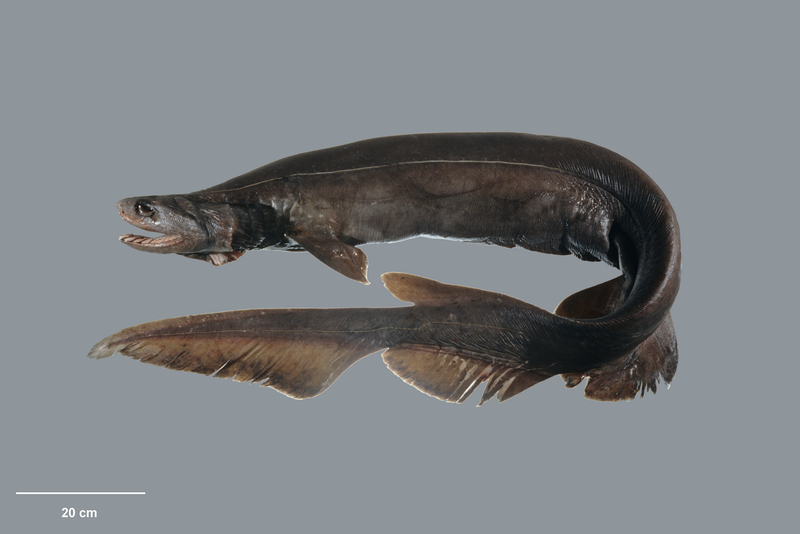

The frilled shark (also known as the pseudo-eel shark, scientific name: Chlamydoselachus anguineus) is a primitive shark, known as a "living fossil" for its ancient characteristics. Its body shape is similar to that of an eel, up to 2 meters long, with dorsal fin, caudal fin and anal fin located on the back of the body. It has six gill slits on both sides, and the gill septa are elongated and wrinkled, and these wrinkles cover each other, hence the name frilled shark.
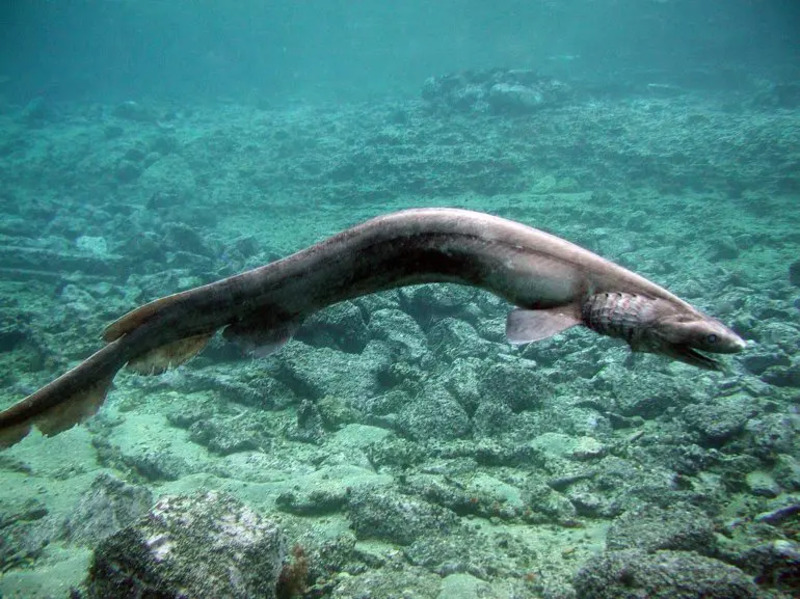

The frilled shark mainly inhabits deep sea areas with a depth of 600 to 1,000 meters. Its distribution range is almost all over the world, but its distribution is very scattered. Compared with other sharks, frilled sharks have six pairs of gill slits, probably because they live in a deep-sea environment with low oxygen, so more gill slits are needed to improve gas exchange efficiency.
2. Coelacanth (377 million years ago)
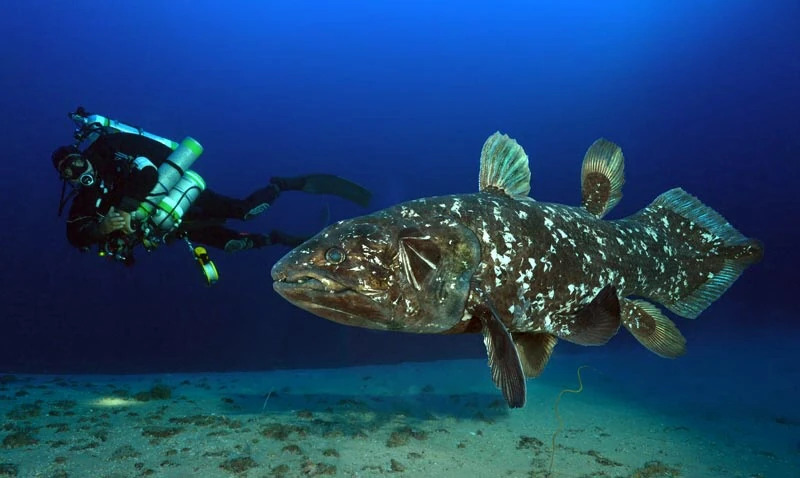

Coelacanth (scientific name: Coelacanthiformes) belongs to the order Coelacanthiformes of the class Lobe-finned fish. This fish first appeared in the fossil record of the middle Devonian period. It was once thought to have been extinct 65 million years ago. However, since 1938, traces of coelacanth have been gradually discovered by humans, so it is known as the "living fossil of the dinosaur era."
The coelacanth is larger than most fossil species, with a spindle-shaped body and covered with thick scales. The scales on the sides of the body can be up to 5 cm long and have small spines on the surface. If you touch it carelessly, you may get hurt. The coelacanth has a very long lifespan, perhaps close to a century, and its growth rate is extremely slow.
3. Lamprey (360 million years ago)
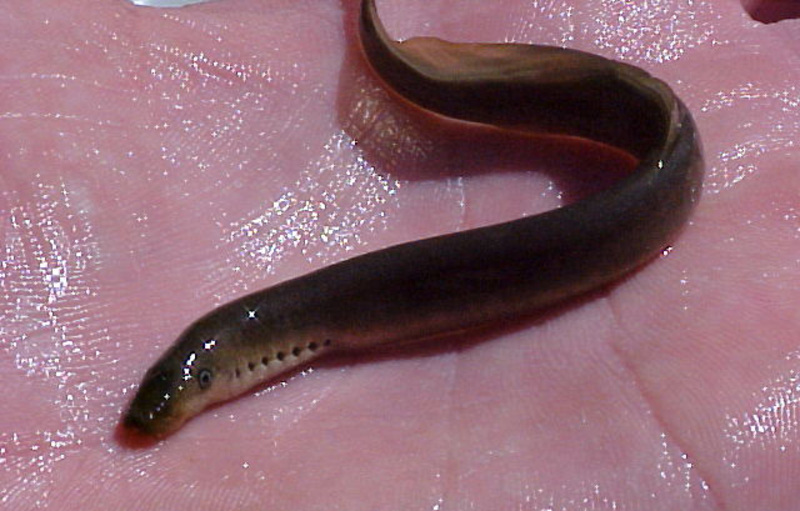

Lamprey (scientific name: Petromyzontidae), also known as lamprey or seven-star, is an ancient creature of the order Lampreys of the class Cyclostomidae. It is a transitional form of evolution from invertebrates to fish and is the most primitive type of fish-like animal.
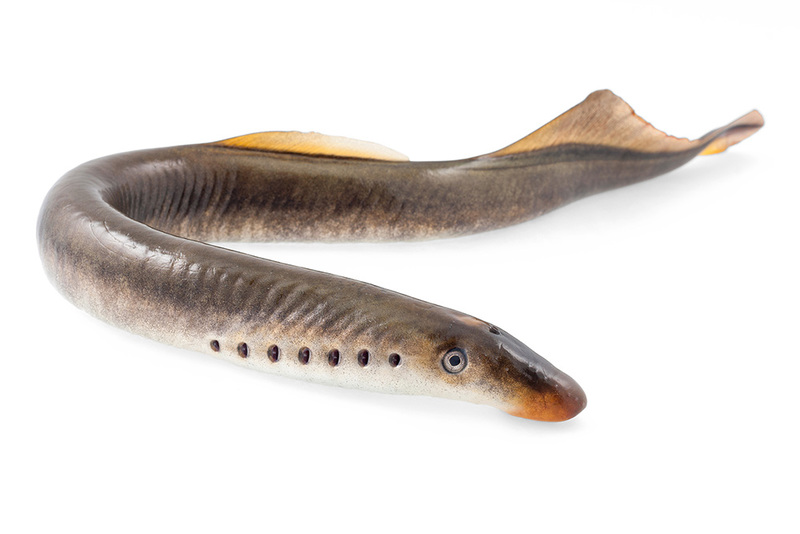

Lamprey is a cyclostomum creature without a lower jaw. Its mouth is full of sharp teeth, a feature unique to the ancestors of ancient fish. Its gills are bag-shaped and remain in their original state, with seven gill openings on each side, arranged behind the eyes. Its mouth is funnel-shaped, with circles of teeth distributed inside, forming a round suction cup that can be attached to larger fish. In 2014, the American horror movie "The Man-eating Eel" was based on the lamprey.
4. AsianDragonfish (355 million years ago)
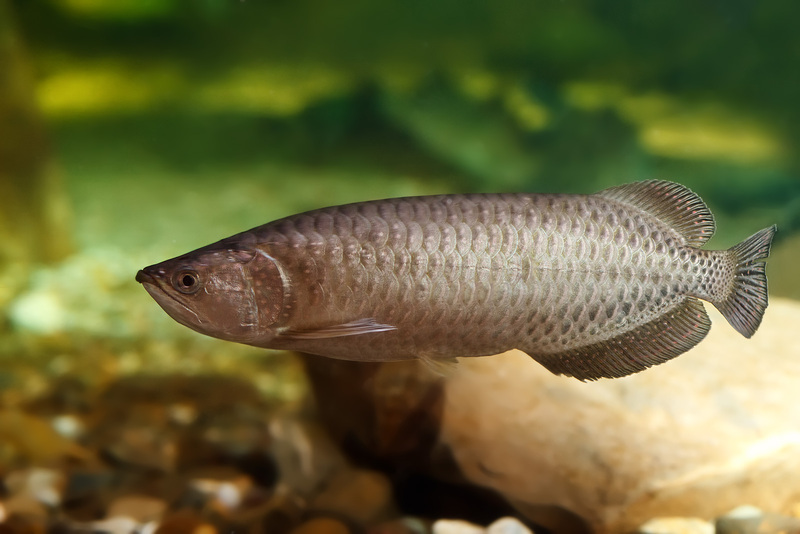

The Asian dragonfish (scientific name: Scleropages formosus) is an ancient primitive freshwater fish belonging to the genus Osteoglossidae. In Taiwan, it is called the red dragon, Hong Kong people call it the dragon spitting pearl, and in Malaysia it is called the golden dragonfish. Adult dragonfish are usually between 40 and 50 cm long and can live for decades. It has a ferocious character and mainly feeds on live fish, shrimp, aquatic insects and frogs. The Chinese community regards it as a high-end ornamental fish and believes that it can bring good luck and wealth.
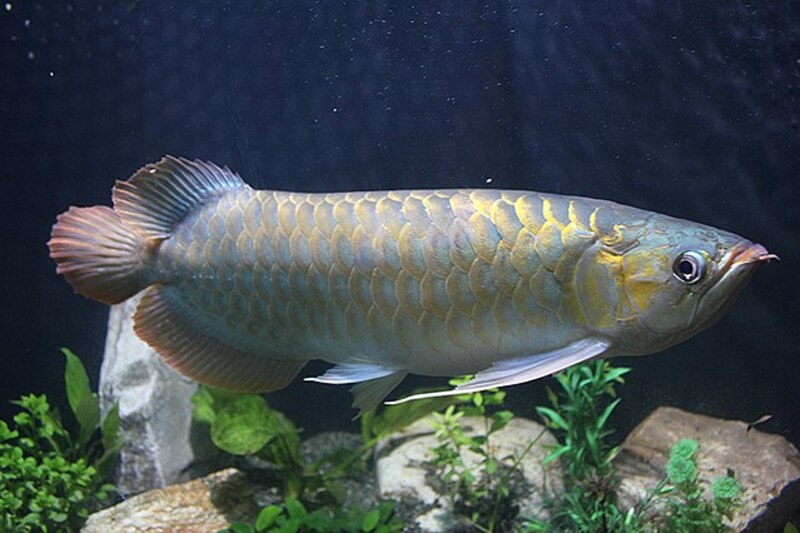

Since the mid-20th century, Asian dragon fish has gradually been developed as an ornamental fish. Due to its armor-like shining metallic scales, bright colors and majestic posture, it has gradually become a highly watched species, and its value has soared, becoming one of the most expensive ornamental fish. Dating back to the Archean Carboniferous period, dragon fish has belonged to the Osteoglossidae family and has existed as early as that era.
5. Sturgeon (150 million years ago)
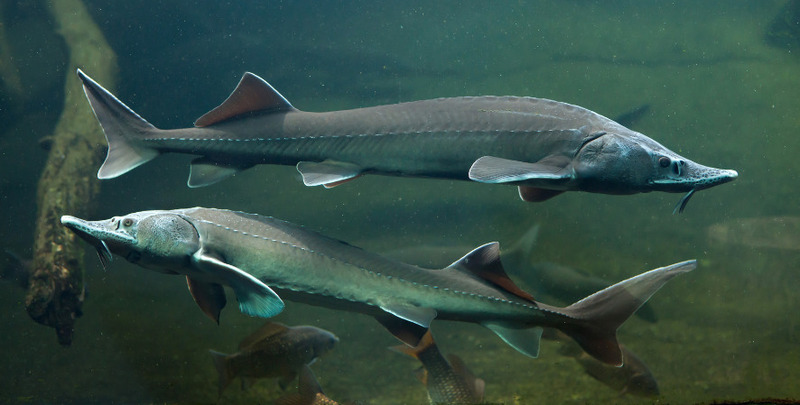

Sturgeon refers to the general term for fish of the order Acipenseriformes (scientific name: Acipenseriformes) of the class Actinopterygii. Acipenseriformes is an ancient fish species distributed in the northern part of the Northern Hemisphere. Many species are migratory fish and have high economic value. Sturgeons originated in the Mesozoic Era 150 million years ago. As a rare ancient fish, they are between cartilaginous fish and bony fish. The skeleton of sturgeons is generally less ossified, with an unossified elastic notochord as the axis, no vertebrae, and the cartilaginous shell of the skull is mostly unossified.
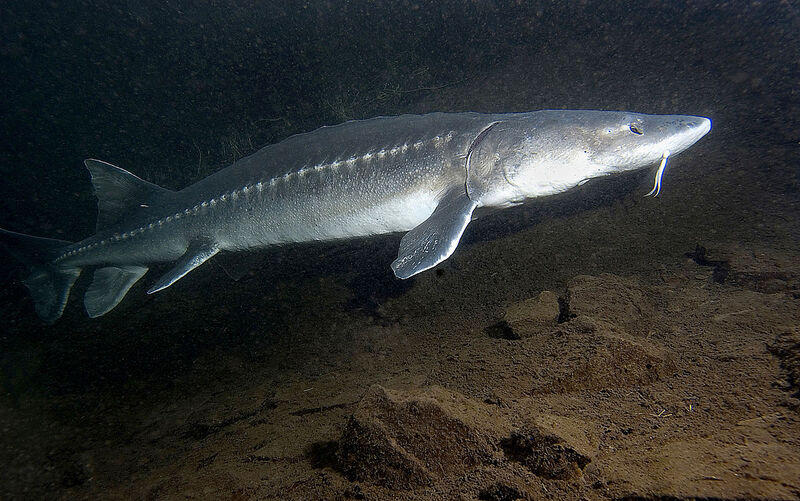

In Chinese waters, fish of the order Acipenserformes include: sturgeons and Acipenser schrenckii in the Heilongjiang, Wusuli, and Songhua River systems; Acipenser dabryanus, Acipenser sinensis, and Sturgeon in the Yangtze River system; and naked sturgeons, sturgeons, and Siberian sturgeons in Xinjiang.
6. Polypterus senegalus (145 million years ago)
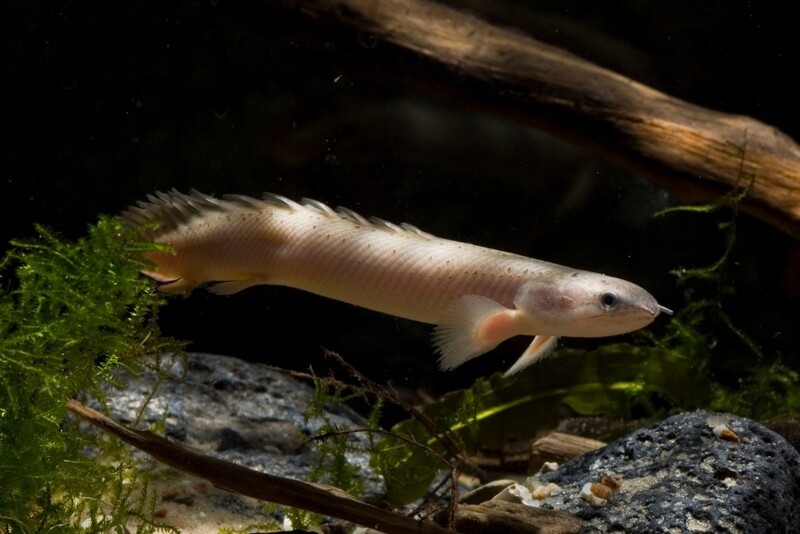

Polypterus senegalus (scientific name: Polypterus senegalus), commonly known as polypterus, also known as golden dinosaur or nine-segment dragon, is an ancient freshwater fish belonging to the order Polypteridae, family Polypteridae, and genus Polypterus, mainly distributed in Africa. Golden dinosaurs are widely found in freshwater streams and lakes in East Africa, West Africa, and Central Africa, and are relatively abundant. Its unique structure makes it an important species for studying fish evolution, and its peculiar appearance also makes it an ideal ornamental fish. The history of the Senegal polypterus can be traced back to the Cretaceous period.
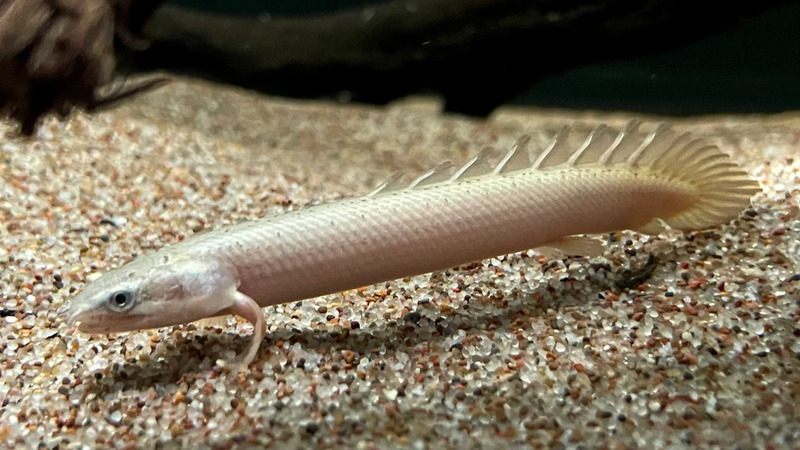

This fish usually lives in still waters such as swamps or lagoons. It is a carnivorous fish that mainly feeds on frogs, fish, insects, and crustaceans. It can breathe air, which enables it to survive in environments with low oxygen concentrations. The young fish have external gills in the early stages.
7. Huso dauricus (130 million years ago)
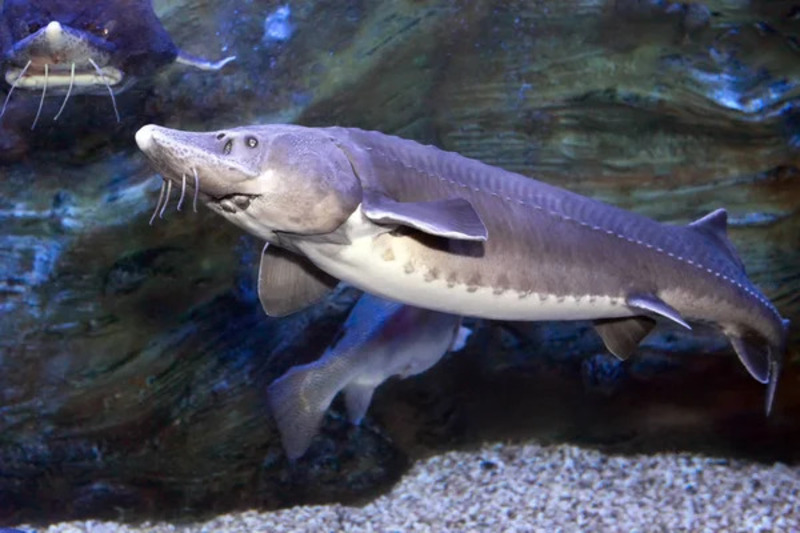

Huso dauricus (scientific name: Huso dauricus), also known as sturgeon, East Asian sturgeon, sturgeon or sturgeon, was called sturgeon, yellow croaker or cowfish in ancient times. It is a large benthic freshwater fish of the genus Huso of the family Acipenser. Huso dauricus belongs to the cartilaginous fish, and its origin can be traced back to the Cretaceous period about 130 million years ago. It is a rare fish species only found in the Heilongjiang River Basin.

Huso dauricus has a very long lifespan, up to 100 years. It is mainly distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Heilongjiang River in Northeast Asia, including the Ussuri River, the lower reaches of the Songhua River and the lower reaches of the Nenjiang River, and usually lives on gravel and sandy bottoms. The maximum body length of the Dabryan sturgeon can reach 5.6 meters and the weight can reach 1 ton. It is one of the largest freshwater fish in existence. It has a ferocious personality and mainly preys on other fish. It has a huge appetite and will even bite its own kind when hungry.
8. Alligator gar (more than 100 million years ago)
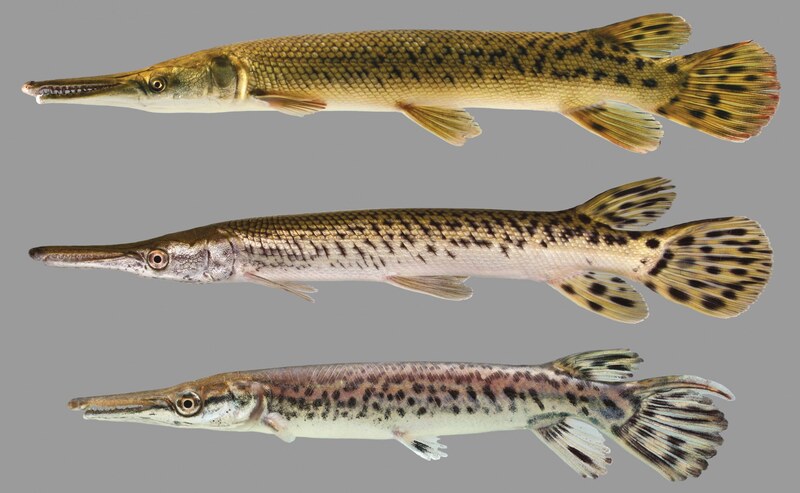

The Fu crocodile (scientific name: Atractosteus spatula), also known as the alligator gar and the big gar, is named the hammer bone gar in Taiwan, commonly known as the crocodile rocket, and is a very ancient ray-finned fish. The Fu crocodile is the largest fish in the order of the gar and one of the largest freshwater fish in North America. It can reach a length of 2.4 to 3.0 meters and weigh about 91 to 159 kilograms. It has survived on Earth for more than 100 million years.
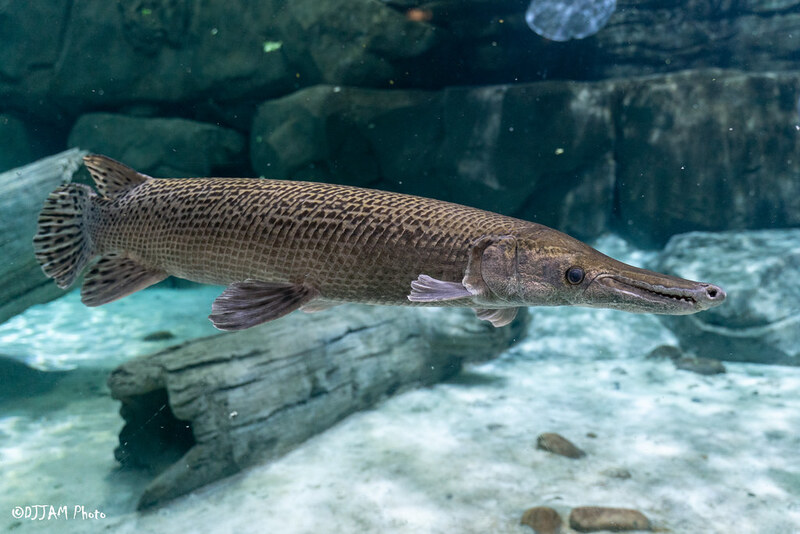

The body of the crocodile is long and cylindrical, covered with dense blue-gray diamond-shaped scales and dark black stripes. Its snout is protruding, and its upper and lower jaws are covered with sharp teeth. It looks like a crocodile's mouth, hence the name. The crocodile can breathe in a low-oxygen environment by swallowing air and storing it in its swim bladder, which allows it to survive for up to two hours out of water. Its lifespan is generally 26 to 50 years, and can be up to 75 years.
9. Arapaima (100 million years ago)
Arapaima gigas, also known as walrus fish or warship dragon, is mainly distributed in rivers in South America, especially in the slow-flowing sections of the Amazon River. A mature Arapaima can be over 2.5 meters long and weigh about 100 kilograms (the largest individual caught so far weighs 230 kilograms). It can reach a maximum length of 4.5 to 6 meters, making it one of the largest freshwater fish in the world.
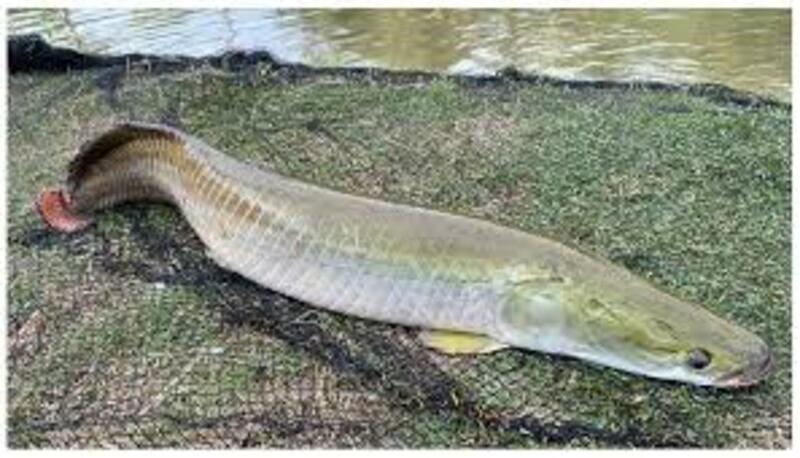

This fish lives in freshwater rivers in South America, mainly feeding on small fish, occasionally preying on snakes, turtles, frogs, insects, and even small crocodiles and piranhas. Due to the low oxygen content in the water caused by the hot climate and slow-flowing waters in the Amazon region, Arapaima usually needs to surface to breathe air.

Arapaima is bulky and moves relatively slowly. Its scales are large and hard, and can be used to sharpen claw knives. Due to its large and beautiful appearance, it is often used as an ornamental fish. Its meat can be made into dried goods or pickled foods, which is a common food for people in the production area. At the same time, the teeth of Arapaima can be used as a substitute for files after being dried.
10. Great White Shark (20 million years ago)
The great white shark (scientific name: Carcharodon carcharias), also known as the man-eating shark, is a living fossil species. The earliest fossils can be traced back to the Miocene. The only existing member belongs to the genus Carcharodon. They can reach a length of 6.5 meters, weigh about 3,200 kilograms, and have a crescent-shaped tail fin. The teeth of the great white shark are large and sharp, with serrated edges and triangular shapes. Each tooth can be up to 10 cm long. As a large predatory shark, the great white shark is at the top of the food chain and is the ultimate predator in the ocean.
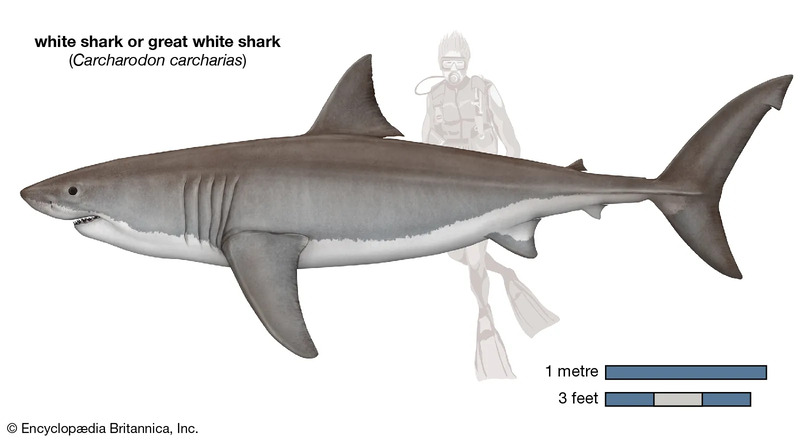
The great white shark is widely distributed and often appears in tropical and temperate waters of major oceans around the world. It usually lives in open waters, but also enters inland waters. They prefer to prey on seals and sea lions, and occasionally eat the carcasses of dolphins or whales.
The top ten surviving prehistoric fish in the world are mainly recommended based on the earliest existing time of each existing fish. They are for reference only to help you understand the top ten surviving prehistoric fish. If you have any questions, please comment and criticize at the end.
animal tags: Prehistoric-fish
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.