In nature, although human eyes have evolved to an almost perfect level, there are many animals with equally amazing visual abilities. They may be able to see further, or have a wider field of vision. The ability of animals to see depends largely on their living environment and hunting habits. Some animals need to see distant prey clearly, while others need to quickly capture changes in their surroundings. Here are ten animals with super vision: falcons, owls, crab-eating macaques, chameleons, tigers, bats, flies, horses, geckos, and tube-eye fish. Let’s take a look.
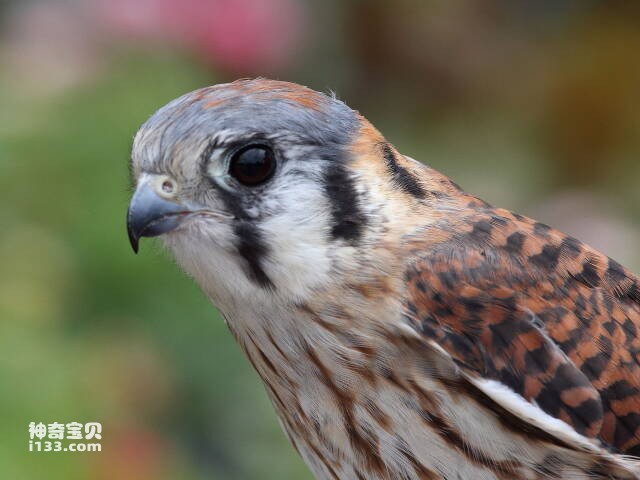

1. Falcon
The falcon is one of the animals with very powerful eyesight. They have a unique eye structure, with a central fovea and a lateral fovea on the retina of each eye, which can receive images of objects in the front field of view and images of objects directly in front, so they have a very wide field of view. In addition, the falcon's cornea and lens both have a very high refractive index, allowing light to better focus on the retina.
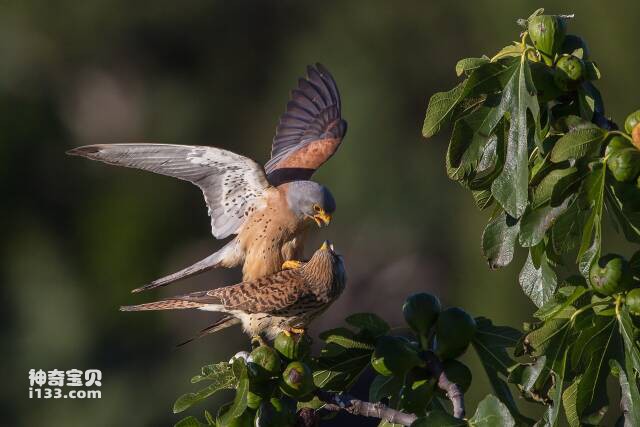

Their eyes also have a large number of cone cells, which can detect color and light intensity, and the falcon's cone cells are more sensitive than those of other birds. These characteristics allow the falcon to identify prey from a distance and attack the target quickly and accurately. In fact, the falcon's eyesight is considered to be one of the best among birds, allowing it to easily capture targets such as small mammals, birds, and insects while in flight. While soaring at an altitude of more than 1,000 meters, the falcon can still see its prey on the ground and target it for its next attack.
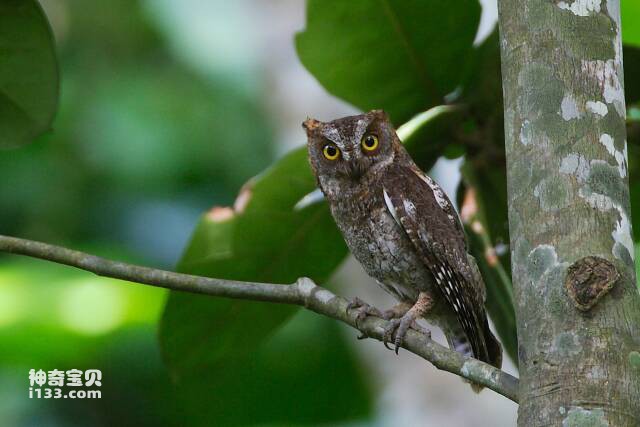

2. Owl
Owls are birds that hunt at night. They have very sharp eyesight and can see weak light in the dark. Owls' eyes are located directly in front of their face, which gives them excellent depth perception during hunting. The pupil of an owl is large, allowing light to enter the eye more easily, and the rod cells in the retina are very abundant, but do not contain cone cells, so the eye appears cylindrical and has good sensitivity to low light, especially suitable for Nocturnal.
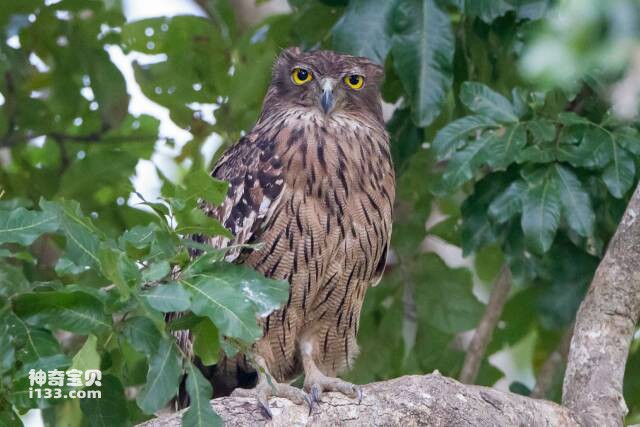

In addition, the owl's lens and cornea have a very high refractive index, which allows light to focus on the retina, and the owl's eyes also have a lot of visual fibers, making their eyes more sensitive. Owls have one of the best eyesight among birds. They are able to see prey in extremely low lighting conditions and attack their targets quickly and accurately. Studies have found that owls' vision can be more than 100 times that of humans, which is one of the important factors that make them night hunters.
3. Crab-eating macaque
Crab-eating macaques are agile animals that live in tropical coastal areas and have excellent eyesight. The eyes of crab-eating macaques are located on the sides of their heads, allowing them to expand their field of vision to both sides. This special eye structure allows crab-eating macaques to better monitor their surroundings to detect food and potential threats.
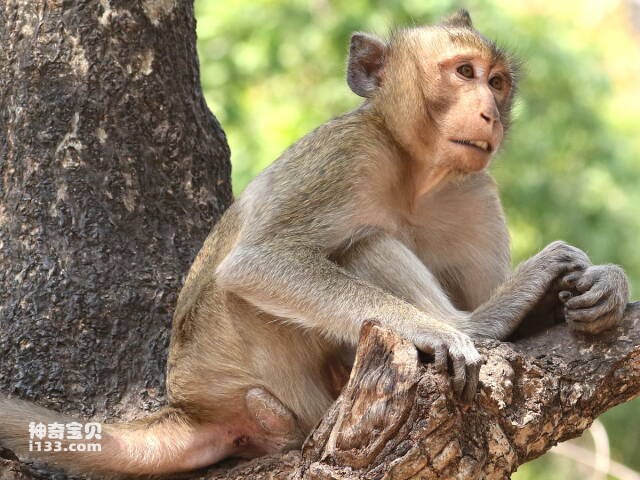

In addition, the eyes of crab-eating macaques also have very sensitive corneas and lenses, which can better focus light on the retina. The retina of the crab-eating macaque contains a large number of cones and rods, which can perceive color and light intensity, and is more adaptable to the environment under low-light conditions. The eyesight of crab-eating macaques is well adapted to their living environment in tropical coastal areas. They can quickly and accurately find and capture small marine life, such as crabs and small fish.
4. Chameleon
Chameleons are very interesting animals. Their eyes have a very unique structure and function. Chameleons' eyes can independently focus on different targets, allowing them to scan their surroundings and quickly adapt to different hunting and courtship strategies. In addition, chameleon eyes are highly sensitive and can perceive a wider range of the spectrum, including ultraviolet and infrared light. This special visual ability allows chameleons to better identify vegetation, detect predators and interact socially.
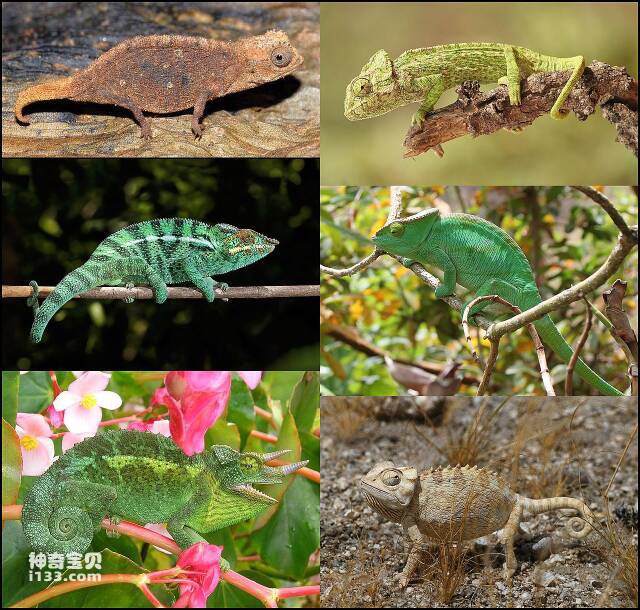

The chameleon's retina contains a large number of cones and rods, which can sense color and light intensity. The chameleon's cornea and lens also have a very high refractive index, which can focus light on the retina. Chameleons' vision is well adapted to their arboreal environment, helping them to quickly and accurately spot prey or avoid predators. Chameleons' unique visual abilities also make them one of the important subjects of study by biologists.
5. Tiger
As a predator, tigers have very good eyesight. Tiger eyes are larger than human eyes and contain more rods and cones, which allow them to perceive a wider spectrum of light and fainter light. Tigers also have very large pupils, which allows them to see and track prey in dimly lit environments. In addition, the tiger's lens and cornea also have a high refractive index, which focuses light on the retina, thereby improving their visual resolution.
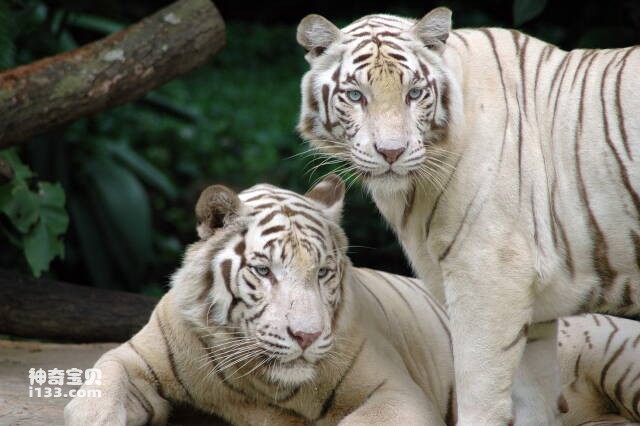

Tigers' eyes can be focused forward, which gives them excellent depth perception and allows them to better locate and track prey. Tigers' eyes are also placed directly in front of their heads, allowing them to better gaze ahead, pinpoint prey and attack. Tigers' vision is well adapted to their hunting behavior in grasslands, forests and other environments, allowing them to quickly and accurately detect prey and pursue it. Tigers' visual ability is also one of the important factors in their dominance of the food chain.
6. Bat
Bats are the only mammals that can truly fly freely. Similar to birds, bats have keen vision. However, many people have long believed that bats have poor eyesight or that they are even blind. However, contrary to this belief, a growing number of scientists point out that bats' vision is very good and has not deteriorated. In fact, different species of bats have unique levels of vision.
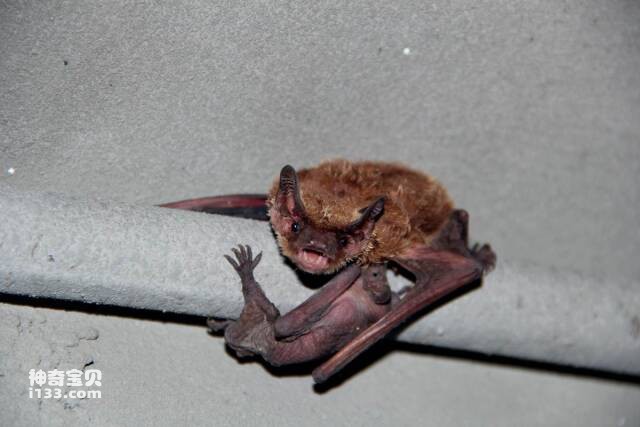

Although bats use ultrasound for positioning and navigation, their eyes are structurally intact and their opsins change in response to light, indicating that vision is still very important to them. Some species of bats can even see shorter wavelengths of ultraviolet light that humans cannot detect. Therefore, although bats mainly rely on ultrasound to locate and hunt prey, their vision has not been ignored. In real life, bats use their powerful vision and ultrasonic technology to adapt to a variety of different environments.
7. Flies
The eyes of flies have a unique structure, which is a hemispherical eye composed of many hexagonal ommatidia. Each ommatidium has very high temporal resolution and can segment moving objects into consecutive individual shots. Each ommatidium has a cornea and lens, and each can image independently. Therefore, as many small eyes as there are in the fly's eyes can form as many pictures at the same time, and then these images are combined in the fly's brain to form a clear image of a moving object. Even fast-moving objects cannot escape the eyes of flies.
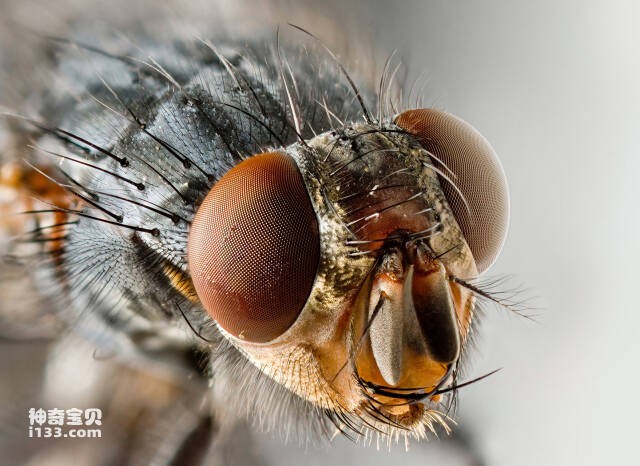

The fly's eye response + resolution is extremely high, it can see ultraviolet rays that the human eye cannot detect, and can refocus at an amazing speed. In comparison, it usually takes 0.05 seconds for the human eye to see the outline of an object clearly, while it only takes 0.01 seconds for a fly's eyes. The eyes of flies have unique structures and functions that allow them to sense moving objects and quickly and accurately locate prey and danger. The fly's visual system is one of the key factors for its success and survival in the ecosystem.
8. Horse
The eyesight of horses is amazing. They have a larger visual acceptance range and a wider field of vision that humans cannot achieve. Each of the horse's eyes has a visual range of 65 degrees. It can clearly see objects at a certain distance in front of it, and it can fully see objects behind it without turning or looking back. This expansion of visual range makes it easier for horses to detect potential prey or threats in their natural environment and to better adapt to their living environment.

However, because the horse uses binocular vision, it is difficult for it to directly detect objects located directly between the two eyes. Therefore, the horse always has a 3-degree visual blind spot, which is a limitation of the horse's vision. Horses' vision is well adapted to the demands of survival on the savannah, and despite the presence of blind spots, they still have a significant visual advantage. The range and sensitivity of a horse's vision is one of the key factors in its success and survival in the prairie ecosystem.
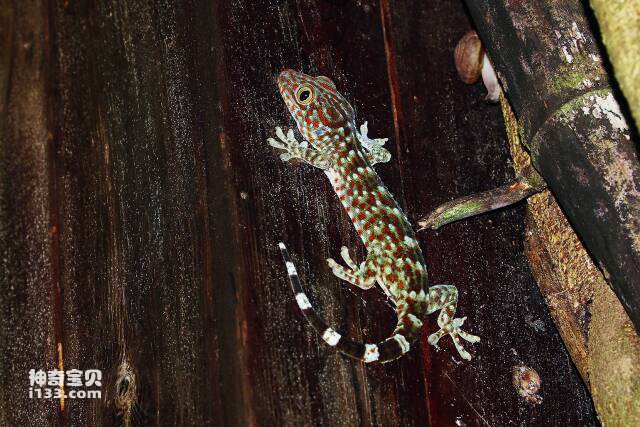

9. Gecko
Geckos are a type of reptile whose visual system helps them move quickly between trees, rocks and buildings and hunt for prey. geckoThe eyes are relatively small but have high visual sensitivity. The gecko's pupils are very large and can be freely adjusted to adapt to changes in light intensity. The gecko's retina contains many rod-shaped cells and cone-shaped cells, which can sense information such as light intensity, color, and movement direction in the surrounding environment. Humans cannot see colors under dim moonlight, but geckos can still distinguish colors under this light, and their ability to distinguish colors is 350 times stronger than humans.
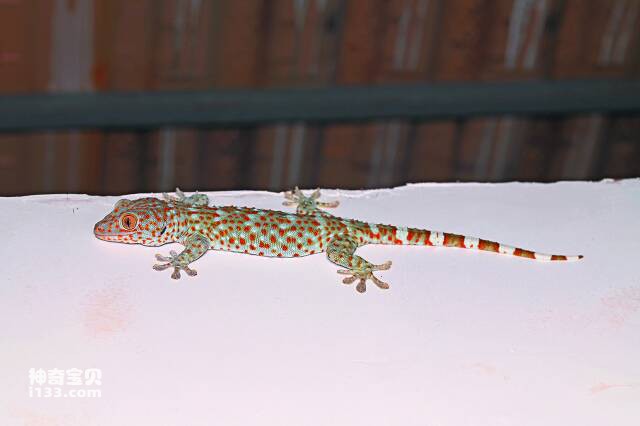

In addition, geckos’ eyes can also distinguish three-dimensional images like humans, allowing them to better locate and capture prey. The gecko's eyes can move independently, allowing each eye to see a different scene, allowing the gecko to better perceive its surroundings and prey. A gecko's vision is one of the important factors for its survival and movement. Geckos adapt to a variety of environments through their highly sensitive visual system and use their flexible eye movements to locate and hunt prey quickly and accurately.
10. Tubeeye fish
The tube-eye fish is a type of deep-sea creature that lives in an extremely high-pressure environment in the deep sea. Due to the special nature of their environment, the vision of tubefish differs from that of other fish. The eyes of the tube-eye fish are very large, taking up about one-third of the length of the head. Their eyes are long tube-shaped, composed of a transparent cornea and lens. The tube-eye fish's pupils can dilate and contract to adapt to light intensities at different depths. Because the light in the deep sea environment is very weak, the eyes of tube-eye fish have adapted to this low-light environment. Their retina contains a large number of rod-shaped cells, which are very sensitive to changes in light intensity and help tube-eye fish sense their surrounding environment.
But they are much less sensitive than visual information such as color, shape, and motion. In addition to the rod-shaped cells in the retina, the eyes of tube-eye fish also have a unique structure - a reflector. The reflector focuses light onto the retina, enhancing the fish's vision and helping it sense faint light in its surroundings. The tube-eye fish's vision is adapted to the dim light characteristics of the deep-sea environment. Although they are much less sensitive to visual information such as color, shape, and movement, their rod-shaped cells and reflectors help tubefish sense their surroundings and respond quickly and accurately.
The top ten super visual animals are mainly determined by searching relevant online platforms to find relevant animals, based on whether they have excellent vision, unique abilities, and comprehensive consideration of their popularity and influence. If you have any questions, please leave comments/criticisms at the end.
animal tags: Falcon owl chameleon tiger bat fly horse gecko
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.