Most jellyfish in the world are poisonous, but they differ in the intensity of their toxicity. Regarding the most venomous jellyfish in the world, there are several species listed as the most dangerous. The following is a list of the ten most venomous jellyfish in the world, including Australian box jellyfish, Irukandji jellyfish, jellyfish, man-of-war jellyfish, jellyfish, jellyfish, arctic jellyfish, jellyfish, sand jellyfish Jellyfish and sea nettle jellyfish. These jellyfish may look beautiful and charming, but they are actually potentially deadly dangers.

Therefore, care must be taken with these jellyfish to avoid contact to avoid unpredictable harm. Let’s learn about these potentially dangerous jellyfish and increase our understanding of these beautiful and deadly creatures. I hope this summary can help everyone learn more about these dangerous jellyfish species.
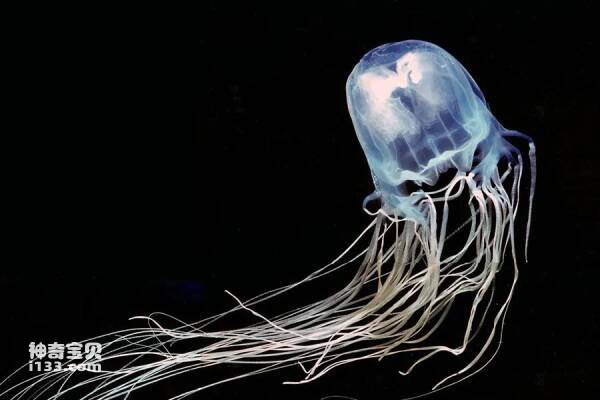

1. Australian Box Jellyfish
The Australian box jellyfish, also nicknamed the "sea wasp" or the "transparent killer of the ocean," is a jellyfish that inhabits Australia, northern New Guinea, the Philippines, and Vietnam. This jellyfish is responsible for countless injuries or deaths to humans around the world, and is considered one of the deadliest species of jellyfish. Although it is only about 40 centimeters long, it is unique in that it has 4 eye gathering parts and a total of 24 eyes; its tentacles are equipped with thousands of stinging cells that store venom.
Once this jellyfish is accidentally provoked, it will frantically inject large amounts of neurotoxins into the target, causing damage to the heart muscle and nervous system, as well as damage to other tissues. This toxin is enough to kill a person in just 30 seconds.
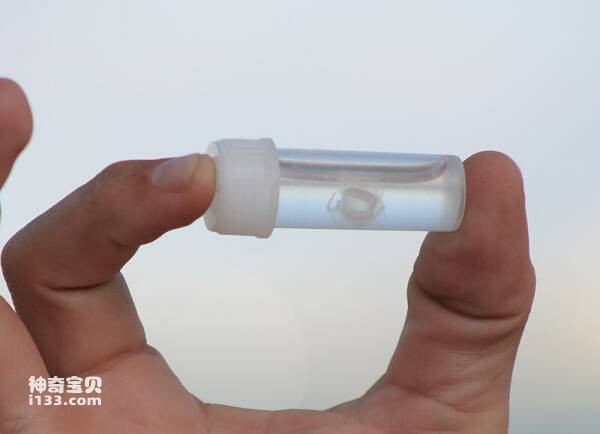
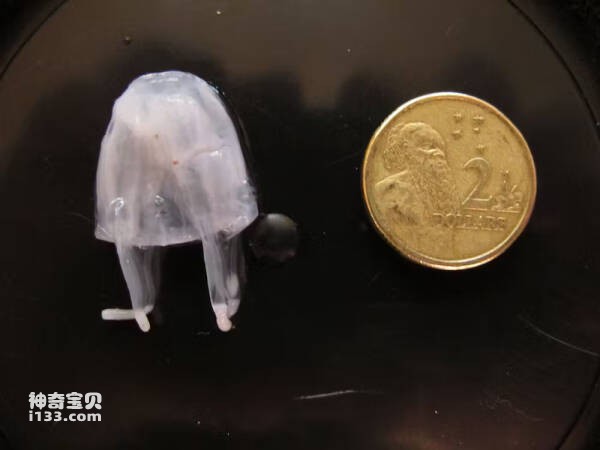


2. Irukandji Jellyfish
The Irukandji jellyfish is considered one of the most venomous jellyfish in the world. Although it is petite, only a few centimeters in size, it contains venom hundreds of times more deadly than a cobra. The sting of a single Irukandji jellyfish can be fatal. When humans are stung by an Irukandji jellyfish, they will only feel a slight sting at first, but as the toxin spreads in the body, a red rash will appear on the patient's skin, and severe pain will spread throughout the body. Thereafter, patients may suffer from pulmonary and renal dysfunction, which may even be fatal if the condition worsens.
What's even more dangerous is that this kind of jellyfish is so small that it is almost invisible to the naked eye in the water. They can even penetrate the mesh and get into the protective net of the swimming area.
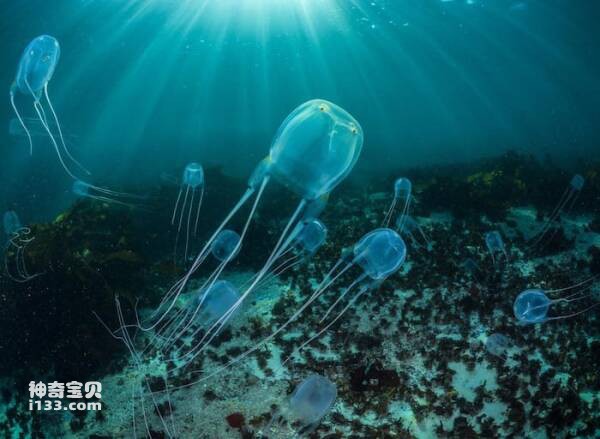

3. Hand-trapping jellyfish
This box jellyfish can be thought of as the wasp of jellyfish, a smaller version of it. Although this jellyfish is tiny, its power is considerable. It mainly inhabits the western waters of the Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. It is nicknamed "venomous snake" by the locals in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Every year, humans encounter this jellyfish unexpectedly. The sting of the quadriceps spines carried by the trailing hand jellyfish is severe and, in some cases, can be fatal. This sting can trigger cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, acute pulmonary edema, and possibly death.

4. Man-of-war jellyfish
Man-of-war jellyfish can predict storms. It has a floating bladder with long tentacles hanging from it. There are special glands inside the sac that release carbon dioxide, causing it to expand. Jellyfish means "bubble" in Greek. It is with the help of this "bubble" that it can rise and fall, allowing the jellyfish to float to places with food or away from enemies. The killer weapon of the man-of-war jellyfish is its tentacles. The tiny tentacles of the man-of-war jellyfish can reach 9 meters in length, so it is already too late for many swimmers to avoid the man-of-war jellyfish when they see it. The toxins secreted by the man-of-war jellyfish are neurotoxins. As time goes by, in addition to suffering severe pain, the injured will also experience a sudden drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, gradual loss of consciousness, systemic shock, and finally death due to pulmonary circulation failure.
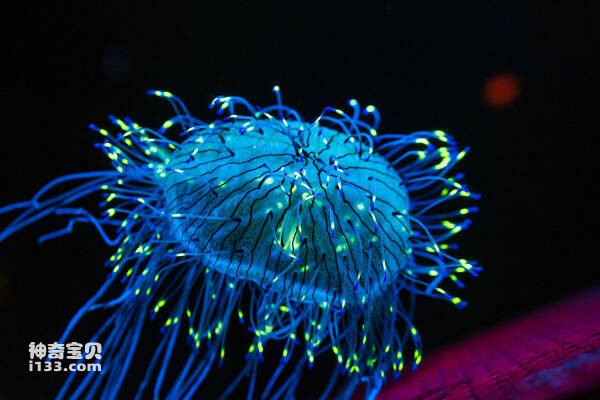

5. Flower jellyfish
Olindias formosa (also known as Olindias formosa) is a group of beautiful underwater creatures. Although they look very similar to jellyfish, they are hydrozoans and live in fresh water. Some are classified into the order Limnomedusae, which belongs to the phylum Cnidaria and the class Hydrozoa. As the name suggests, they are a group of jellyfish living in fresh water. , but it’s actually a hydra. Unlike real jellyfish in the ocean. The flower-hatjellyfishoccurs in the northwest Pacific region near central and southern Japan and on Jeju Island in South Korea. Adult worms live only a few months, usually emerging from December to July, peaking in April or May.
Hana jellyfish is one of the few species with strong toxicity Hydroid jellyfishOne, being stung will cause intense pain. Although there are no reports of being stung to death by this jellyfish, there are cases of shock caused by being stung, so it is best to see this beautiful jellyfish in the wild. It's best not to touch it.
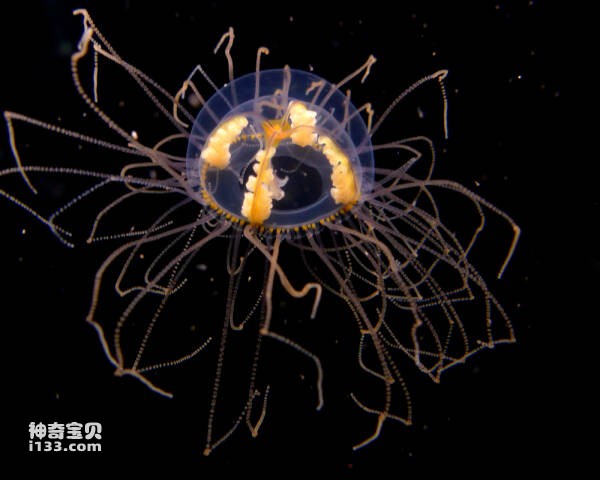

6. Hook-hand jellyfish
The jellyfish is a small marine jellyfish that often uses its tentacles to anchor on seagrass in the natural environment, waiting for opportunities to catch prey. This jellyfish has a venomous sting and often gathers in swarms in warm waters, posing a threat to swimmers. Once humans are stung by a jellyfish, they will feel burning pain on the skin, and symptoms of blisters and local edema will soon appear. Approximately 10 to 30 minutes after being stung, the patient will feel weak, begin to experience numbness, pain in the joints of the limbs, difficulty breathing and may even pause, and may also lead to abnormal liver function. Acute symptoms will last 4 to 5 days, causing long-term physical distress and pain to the victim.
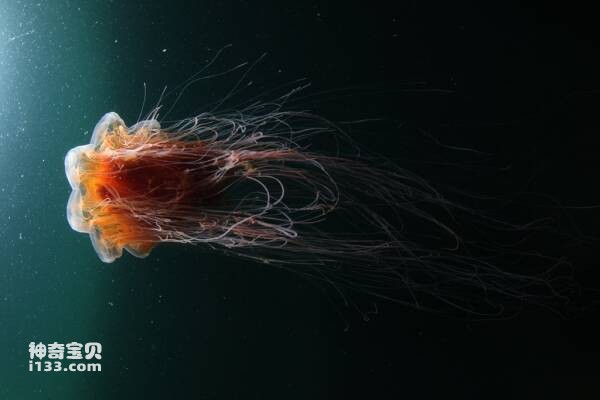

7. Arctic jellyfish
Despite their beautiful and gentle appearance, rosy jellyfish are actually quite ferocious sea creatures. The slender tentacles under its umbrella are both its digestive organs and its deadly weapons. These tentacles are covered with stinging cells, which are like poisonous threads and can spray venom. Once the prey is stung, it will quickly become paralyzed and die.
Arctic glow jellyfish are mainly distributed in rare waters of the Arctic, where humans rarely set foot. After contact with Arctic jellyfish, if not treated promptly within a few hours, life will be in danger. For this special jellyfish, once it is touched, life is difficult to save if it is not treated promptly within a few hours.

8. Hair-shaped jellyfish
Lion's Mane Jellyfish, also known as Hair Jellyfish, is one of the largest and most venomous jellyfish in the world. This jellyfish is mainly found in cooler waters. Once the lion's mane jellyfish stings the skin, its toxins will quickly invade the human body, causing paralysis and even life-threatening. In its natural environment, lion's mane jellyfish usually appear reddish-brown or light yellow in color.
The lion's mane jellyfish has a variety of characteristics in its morphological structure, including the characteristics of the marginal valve, the number of tentacles, the number of circular muscles and radial muscle bundles, etc. These characteristics vary greatly, often causing many scholars to mistake it for multiple different species. variant.
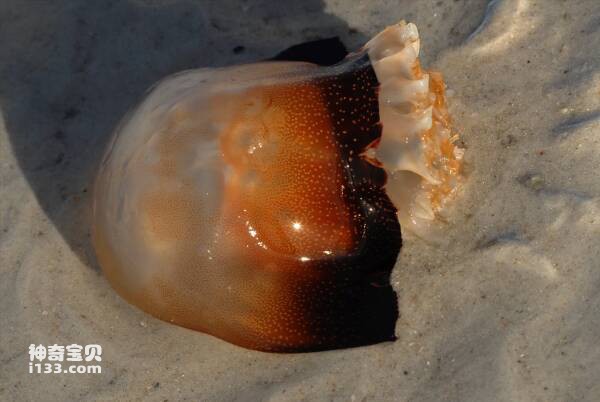

9. Sand jellyfish
Jellyfish is a type of jellyfish, among which sand jellyfish is one type of jellyfish and is widely distributed in my country's coastal waters. The umbrella diameter of adult sand jellyfish is between 25 and 60 centimeters, and the largest individual can be close to 1 meter. The surface of the outer umbrella is smooth, and the glue layer in the middle is thick and hard.
Not only does the sand jellyfish have high economic value, its umbrella part can be used for raw food, or it can be processed into sting skin, and the mouth and wrist parts can be made into sting heads. However, it must be noted that the stinging cells of this jellyfish are highly toxic. Once the human body is stung, the skin may appear red, swollen, painful, itchy and other symptoms. In severe cases, it may lead to shock or even death.
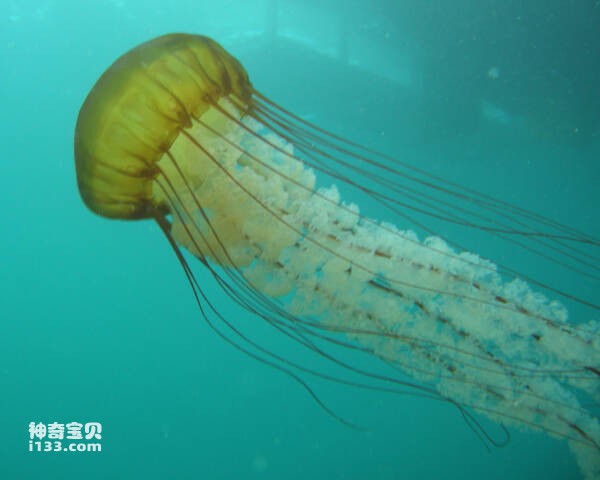

10. Sea nettle jellyfish
Sea nettle jellyfish are commonly found in the Chesapeake Bay area off the east coast of the United States. They feed on plankton and crabs, and they also prey on similar jellyfish. This jellyfish is poisonous and releases venom through the stinging cells on its body to paralyze passing small fish and other creatures to capture food. When humans are accidentally stung by sea nettle jellyfish, they may feel severe pain, but fortunately, they rarely pose a fatal threat to humans.
Although sea nettle jellyfish are highly toxic, they mainly target other animals during their predation process and pose relatively low harm to humans..
The list of the top ten most poisonous jellyfish in the world is mainly based on the comprehensive compilation of major related websites. The list takes into account factors such as the intensity of the jellyfish's toxicity, the degree of damage to humans, and the number of known fatalities to rank these dangerous jellyfish. However, it should be noted that this list is for reference only, and the specific rankings may vary slightly due to different research and data sources.
If you have any questions or criticisms about this ranking list, please leave your comments at the end of the article. For these potentially dangerous jellyfish species, relevant data may be updated and revised as further research and understanding are gained. Therefore, we need to continue to pay attention to relevant information and ensure that we have an accurate understanding of these dangerous jellyfish. Thank you for your attention and discussion on this topic.
animal tags: jellyfish
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.