Human parasites are those that use humans as their hosts. They can usually be divided into two categories: internal parasites and external parasites, which mainly include different categories such as protozoa, nematodes, platyhelminthes, annelids and arthropods. In parasitology, protozoa are usually called protozoa, while nematodes and flatworms are collectively called helminthes. Important types of internal parasites mainly include protozoa, nematodes, flukes and tapeworms.
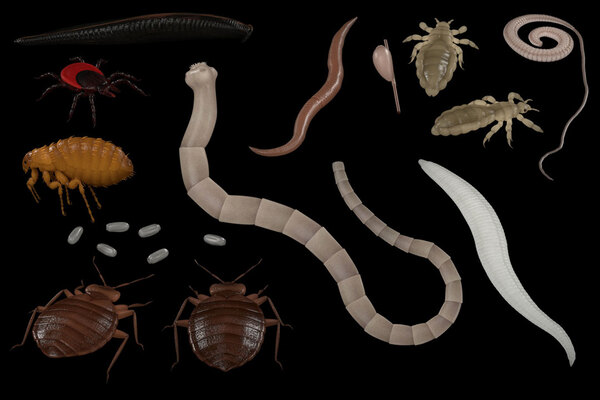

These parasites usually enter the body through ingestion. The larvae of some parasites, such as cysticercosis, may also be distributed in the lungs, subcutaneous, and even the brain and eyes. The harm caused by parasites to the human body is usually negative. They will rob the body of nutritional resources, cause inflammation, cause blood vessel obstruction and other pathological problems.
1. Hookworm
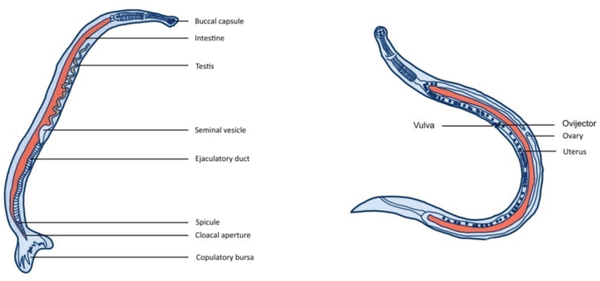 The life cycle of this parasitic nematode begins outside the human body, often through contaminated water , fruits and vegetables enter the human body. Once inside the body, hookworm larvae grow in the host's guts. They attach themselves to the walls of the host's internal organs and feed on the host's blood, sometimes causing intestinal parasitosis, a disease associated with anemia.
The life cycle of this parasitic nematode begins outside the human body, often through contaminated water , fruits and vegetables enter the human body. Once inside the body, hookworm larvae grow in the host's guts. They attach themselves to the walls of the host's internal organs and feed on the host's blood, sometimes causing intestinal parasitosis, a disease associated with anemia.
Symptoms: Weakness, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, anemia
2. Scabies
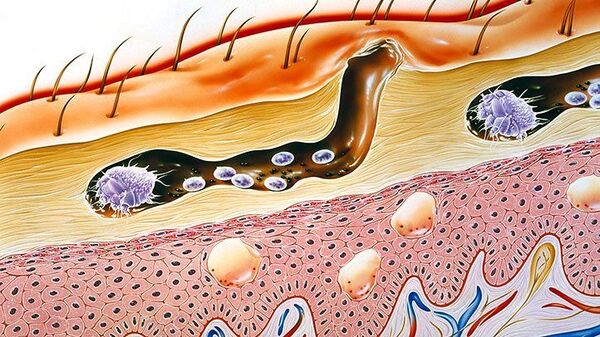 Commonly known as human scabies, this parasite is mainly spread through physical contact. Female scabies choose human skin as a site to lay their eggs, which causes skin reactions and inflammation. When female scabies lay eggs under human skin, they trigger a strong reaction in the host, including severe itching and other scabies symptoms.
Commonly known as human scabies, this parasite is mainly spread through physical contact. Female scabies choose human skin as a site to lay their eggs, which causes skin reactions and inflammation. When female scabies lay eggs under human skin, they trigger a strong reaction in the host, including severe itching and other scabies symptoms.
Symptoms:Itching, pain, pus, skin irritation
3. Ascaris
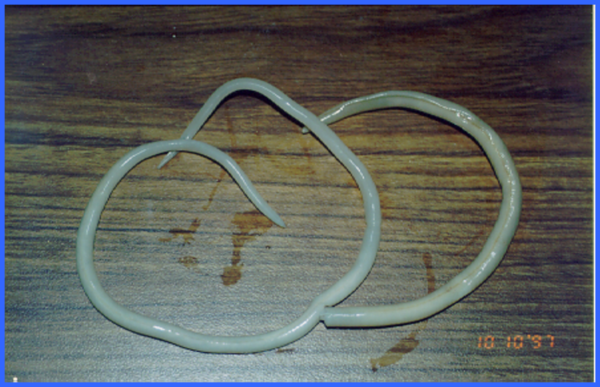
Ascaris is one of the largest parasitic nematodes in the human body and can grow to 15 to 35 years old cm long. They are spread primarily through food ingestion. Once the roundworm eggs hatch, they will quickly pass through the wall of the human body's internal organs and enter the blood circulation system. As blood flows to the lungs, the roundworms are coughed up and swallowed back into the intestines, where they can reenter the visceral area.
Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, allergies, rash, vomiting, diarrhea, neurological problems, wheezing and coughing.
4. Schistosomiasis
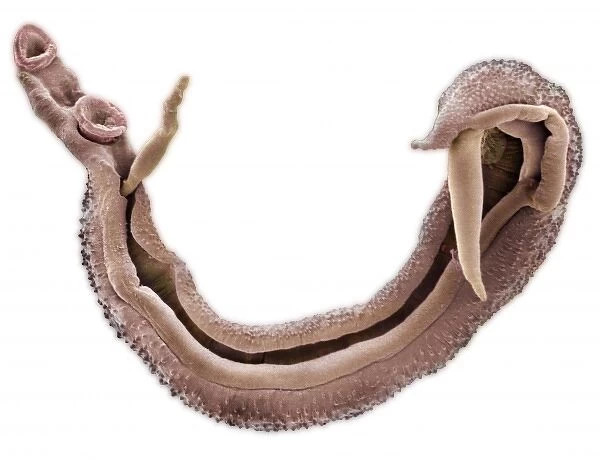 These tiny parasites invade the host's bloodstream, causing the host to become infected with schistosomiasis. They usually live in water, and when people come into contact with contaminated water, schistosomiasis can penetrate the human body through the skin. These parasites cause inflammation (swelling) and cause damage to organs, especially the liver. Adult schistosomiasis can parasitize human hosts for many years, sometimes without showing symptoms. They exit the body through the host's excrement and spend the rest of their life cycle in the host, a snail.
These tiny parasites invade the host's bloodstream, causing the host to become infected with schistosomiasis. They usually live in water, and when people come into contact with contaminated water, schistosomiasis can penetrate the human body through the skin. These parasites cause inflammation (swelling) and cause damage to organs, especially the liver. Adult schistosomiasis can parasitize human hosts for many years, sometimes without showing symptoms. They exit the body through the host's excrement and spend the rest of their life cycle in the host, a snail.
Symptoms: Fever, pain, cough, diarrhea, swelling, lethargy
5. Tapeworm
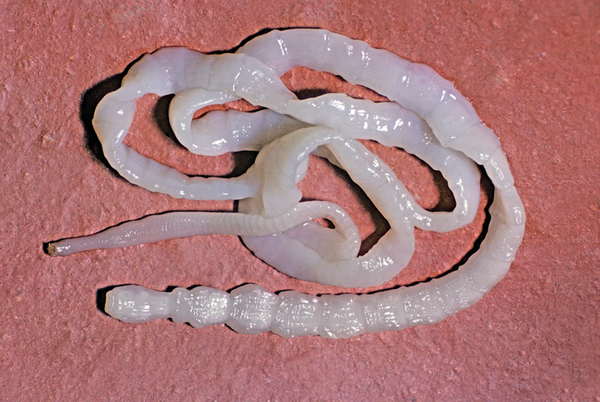

Taenia is usually spread through food contamination, using the "hook" on its head in the host's internal organs Attachment. Mature tapeworms may form in as little as 3 to 4 months, but they can remain in the human body for up to 25 years. Tapeworm eggs can be excreted in feces, survive in plants, and then be ingested by cattle or pigs, or transmitted to humans.
Symptoms:Nausea, vomiting, inflammation of internal organs, diarrhea, weight loss, dizziness, cramps, malnutrition
6. Pinworm
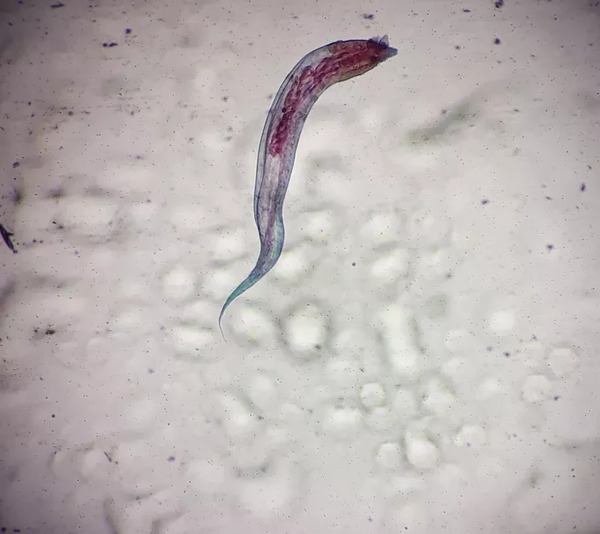
Pinworm is a common human parasite that may cause pinworm disease. The body length of adult female insects can range from 8 mm to 13 mm. The pinworm's tail is long and needle-shaped, hence its name. They mate through traumatic insemination, in which the male pierces the female with his penis and dies. Pinworms often choose to settle in the host's internal organs. Unlike other parasites, they do not enter the bloodstream and cannot survive in other parts of the human body. Pinworms lay their eggs in the external environment, usually around the anus, causing itching, and the larvae are spread through scratched hands.
Symptoms: Inflammation and itching
7. Wuchella bancrofti
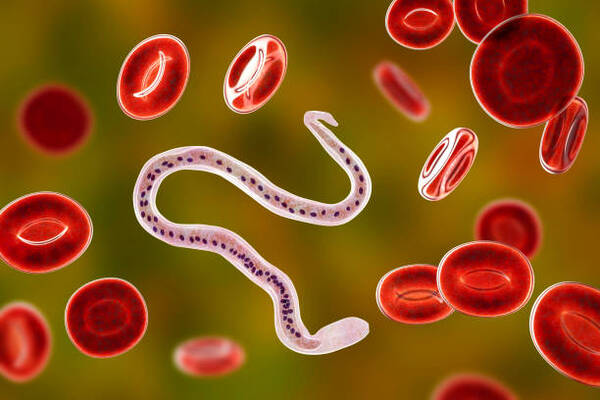
Mosquitoes carry this parasite and release it by biting humans. into human blood. The larvae of Wuchella bancrofti invade lymph glands, especially those in the legs and reproductive organs, and take a year to grow into adult worms. They may cause tropical diseases and sometimes lead to the occurrence of elephantiasis.
Symptoms: Fever, chills, skin infection, lymphadenitis, skin thickening, swelling
8. Toxoplasma gondii

This common crescent-shaped parasite may invade the human central nervous system . Humans can become infected by eating undercooked meat or coming into contact with infected pets. While most people have been infected with this parasite and show antibodies to it, few people show symptoms. Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infection with Toxoplasma gondii, and if a pregnant woman is infected, her fetus may suffer severe or even fatal effects.
Symptoms:Flu symptoms, fever, chills, weakness, headache
9. Giardia lamblia
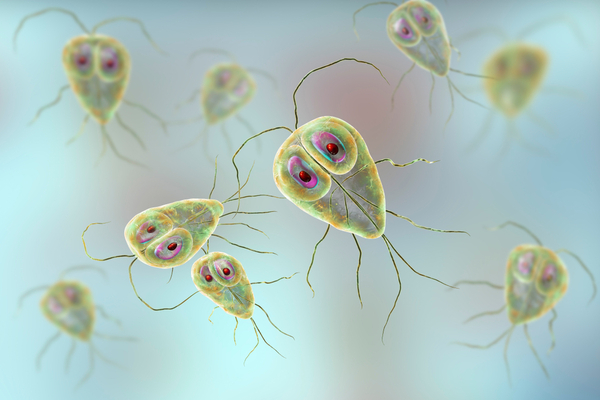
Giardia lamblia is a protozoal parasite with flagella . It lives and multiplies in the human gut and can cause giardiasis. Once this parasite colonizes human internal organs, it can cause inflammation and other damage, impairing the internal organs' ability to absorb nutrients, thereby causing symptoms such as diarrhea. This parasite is commonly found in drinking water and is a potential hazard.
Symptoms: Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, weight loss, burping that smells like rotten eggs.
10. Amoebic dysentery
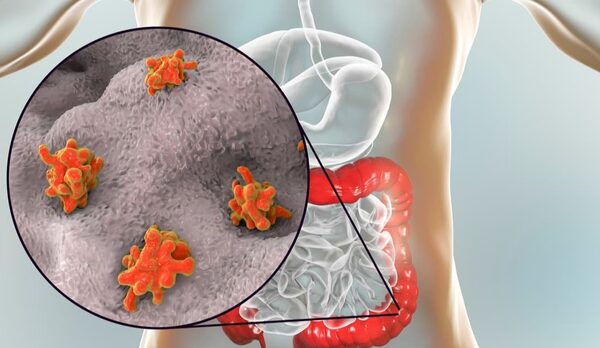
Amoebic dysentery is a disease caused by a single-celled organism. Can be transmitted by amoeba. This parasite primarily infects humans and other primates. Entamoeba dysenteriae can be found in water, moist environments and soil, potentially contaminating fruits and vegetables. The mode of transmission is mainly through feces. Unlike other protozoa such as Plasmodium, amoeba parasites have a higher fatality rate and are more likely to cause serious consequences.
Symptoms:Abdominal pain, weight loss, weakness, diarrhea, liver abscess
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.