In nature, "natural selection, survival of the fittest", different environmental conditions shape the unique appearance and habits of animals. Today I will share with you the ten most distinctive animals in the world. They are blue whale, platypus, Komodo dragon, clam (clam), morphros rat, Pompeii worm, radiodurans, Water bears, archaea, and humans. Let’s take a look at their unique features!

1. Blue whale
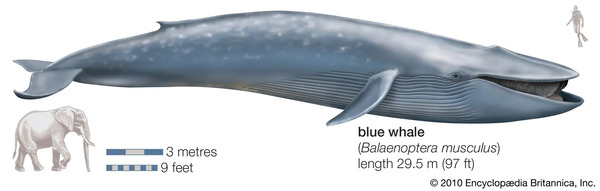
The blue whale is a marine mammal. It is not only the largest whale on earth, but also the largest known living animal. The blue whale can be up to 33 meters long and weighs 181 tons. Its head is so huge that it can accommodate 50 adults on its tongue, and its heart is about the size of a small car. The weight of a newborn blue whale calf is even greater than that of an adult elephant, which shows its huge body.

The blue whale shows amazing strength. It generates about 1500 to 1700 horsepower. It can be said to be an unparalleled giant and strong person in the animal world.
2. Platypus

The platypus is considered to be one of the most primitive mammals on earth, and it is also a strange-looking creature: a fat body, a flat tail, a duck-like bill, and unique small eyes that seem to convey a gentle and harmless atmosphere. Because the platypus mainly lives on isolated islands in the southern hemisphere, far away from the continents of the northern hemisphere, it faces relatively few natural enemies, and because it has not undergone too much evolution, it retains some genes of ancient animals.
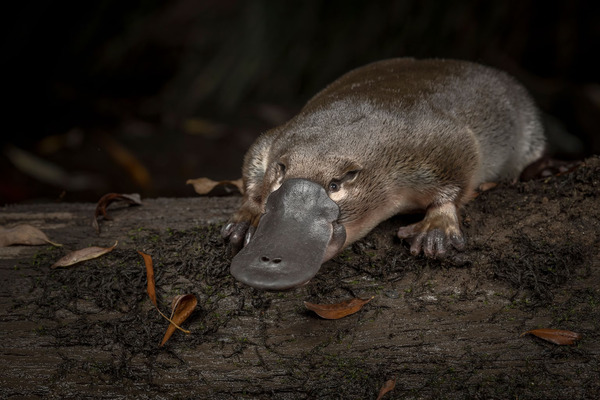

As a mammal, the platypus displays characteristics similar to those of amphibians or reptiles: it lays eggs, can live in water, and its claws are shaped like duck paws. Overall, there are many characteristics worth studying in the platypus.
3. Komodo dragon
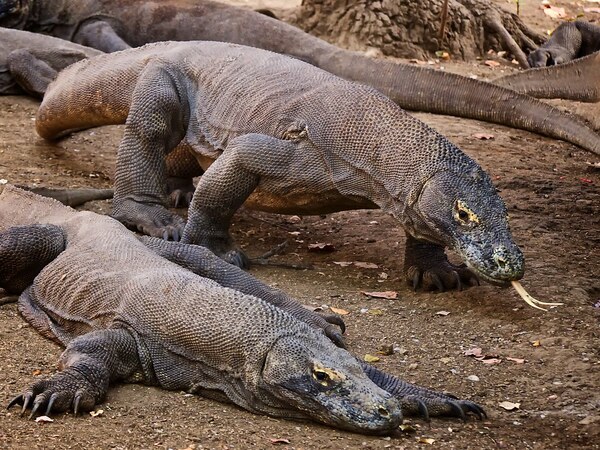

The Komodo dragon, also known as the Komodo dragon, can be up to 3 meters long and weigh up to 70 kilograms , is the largest known living species of lizard and is considered one of the living fossils of the dinosaur age. The Komodo dragon has 60 constantly changing serrated teeth that can be up to 2.5 centimeters long, and its hunting strategy relies on its deadly venom and bacteria-rich saliva. These qualities make it extremely lethal when hunting.
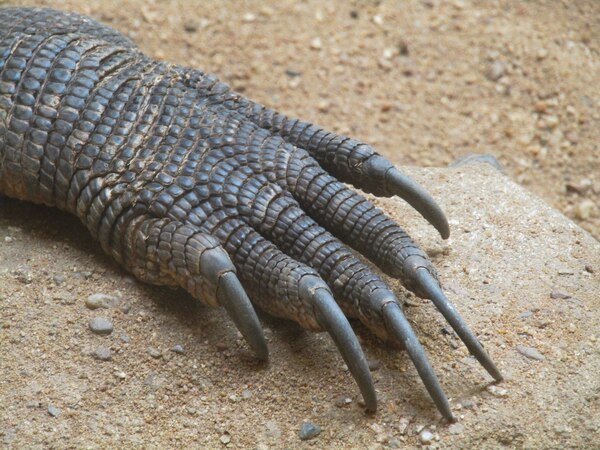

In addition, after locking the target, the Komodo dragon will chase it unswervingly until it is successfully captured, which may be one of the reasons why it can survive to this day.
4. Ming (clams)
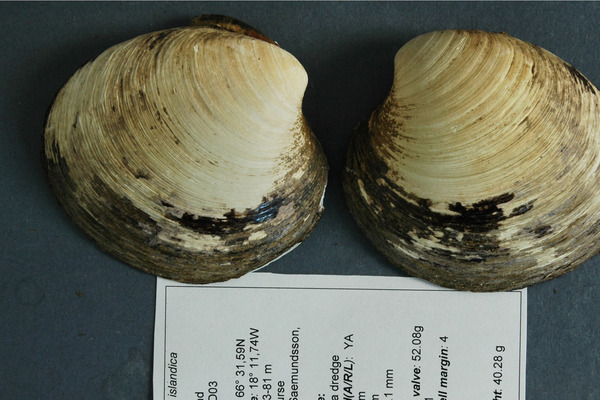

Known as the Ming clam, the clam is a deep-sea round clam named for its origins in China's Ming Dynasty and is considered one of the longest-lived animals on Earth. According to records, people once captured a round clam with a lifespan of 507 years. Unfortunately, this old mollusk died during the research process of scientists.
The average lifespan of these bright clams is difficult to pinpoint because scientists are still trying to understand the lifespan of these creatures. If not for an accidental discovery, their age may have lurked in the dark depths of the deep sea for much longer.
5. Murphy's Rat

Murphy's rat, commonly known as "MRL rat (Murphy the Great)", is a small house mouse with remarkable tissue regeneration ability that was discovered in 1999. It is one of the mouse species with the strongest regenerative potential. It is often used in scientific experiments due to genetic mutations caused by residual drugs in the body. The rats recovered quickly from injury without leaving scars, and had the ability to regenerate toes, tails, and even vital internal organs, including their hearts. Scientists hope to explore possible ways to regenerate human organs by studying MRL mice.
6. Pompeii Worm

Unless you are a lucky enough marine biologist, you have no chance of seeing a Pompeii worm. This strange-looking creature lives around the crater of a deep-sea trench, and its living environment is extremely harsh. Incredibly, these tiny bugs have to endure tremendous seawater pressure, enough to crush a human to death in seconds.
In addition, Pompeii worms can withstand extreme temperatures of up to 81 degrees Celsius. These worms, which are 6 to 8 centimeters in length, are considered to be one of the most high-temperature and temperature-resistant animals known on Earth.
7. Radiodurans
Tiny bacteria are little known, but they are the focus of research among scientists. Radiococcus radiodurans is a micrococcus that is highly resistant to radiation and shows resistance to a variety of DNA damaging agents, so it has attracted much attention from the scientific community. Experts have discovered several striking properties of Deinococcus radiodurans, including resistance to high temperatures and corrosion. The most striking thing is its amazing ability to resist radiation. Even under radiation conditions that are enough to kill other organisms, Radiodurans can continue to survive.
Scientists are currently studying the DNA of this microorganism, hoping to apply it to the field of medicine or develop computer transmission media.
8. Water bear

Water bears, also known as tardigrades, are nicknamed "little beauties". This tiny creature is one of the most vital creatures known on earth, with extremely strong endurance and tenacious vitality. Tardigrades can survive without food or water for up to 30 years, and after entering a cryptobiotic state, they can withstand extreme high and low temperatures, radiation, and even survive in the vacuum of space. Therefore, we can find traces of them whether in the deep sea or outer space.
Tardigrades can even survive dehydration, making them one of the oldest living creatures on Earth for more than 5 million years.
9. Archaea
Named Archaea in the 1950s, these tiny cell-shaped organisms are rare bacteria that can survive extremes of temperature, pH and salinity. Archaea are a group of microorganisms that are independent of other species and have a long history. They can even be found deep in the earth's crust. Despite their tiny size, archaea are an integral part of Earth's biological clock, making up the microbial component of one-fifth of the animals on Earth, and it is speculated that they may be one of the ancestors of life on Earth.
Some people even boldly speculate that the origin of archaea did not come from the earth, but may have been brought to the earth by aliens.
10. Human beings

Ultimately, we must face ourselves. According to research, thousands of animal species have become extinct at our hands over the millions of years humans have been on Earth. We have the ability to change our environment and even control the course of natural evolution to some extent. In order to meet the needs of the growing population, we do not hesitate to destroy forests to open up wasteland and hunt animals on a large scale. With the rapid development of science and technology, some emerging diseases have even been artificially created. We have changed the world, but if we offend nature, it will fight to the death with humans.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.