Hobbying to grow flowers is a wonderful choice for many people to cultivate their body and mind. Observing the process of flowers and plants growing vigorously day by day can really make people feel happy. However, all efforts may be in vain once the plants are attacked by pests and diseases. There are many types of common plant pests, and the harm they cause to flowers cannot be ignored.

Today I will introduce to you the 10 most terrifying plant and flower pests, including scale insects, whiteflies, small black flies, spider mites, aphids, thrips, spotted leafminers, etc. These pests can cause varying degrees of damage to flowers, resulting in stunted growth or even stunted growth. Therefore, timely identification and effective response to these pests is crucial to protecting the growth and health of flowers.
1. Scale insects (the first of the "Five Small Pests"/difficult to control)
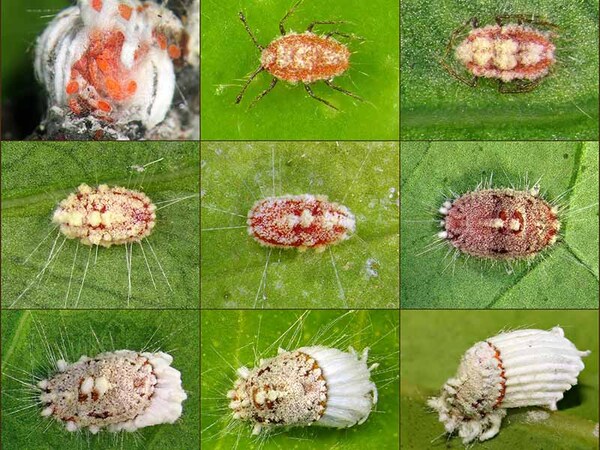

Which flower pest is the most harmful? Scale insects are undoubtedly one of the top five garden pests. There are many types of this insect, which are extremely destructive to flowers and trees. They are the number one pest among flower pests and cause a lot of trouble to gardening enthusiasts. Plants susceptible to scale insect damage include camellia, money tree, anthurium, philodendron, pothos, rhododendron, hibiscus, cherry blossom, plum, peach, crabapple, dieffenbachia, monstera and other plants, and even various types of plants. succulent plants.
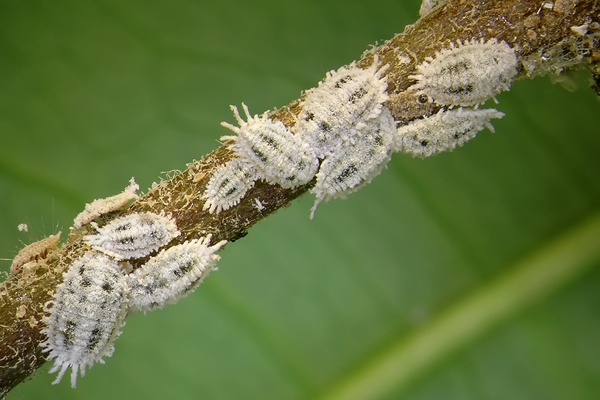

This pest mainly gathers on the tender stems and leaves of plants and uses its piercing-sucking mouthparts to suck plant juices, causing wounds to become susceptible to disease and may also cause sooty stains. The honeydew secreted by scale insects can also attract ants and other insects for symbiosis, increasing the damage caused by pests. Due to the waxy protective layer on the body surface of scale insects, traditional spraying pesticides have limited control effects, and professional insecticides are usually required for targeted control.
2. Whitefly (strong fecundity/easily contagious)
Whitefly is a common pest and disease in horticultural plants. It is widely parasitic on various types of plants. The number of hosts reaches more than 600, including various types of flowers, vegetables, special crops, pastures and woody plants. Adults and nymphs usually gather on the underside of leaves of host plants and use their piercing-sucking mouthparts to suck plant juices, causing the leaves to turn green, yellow, shrink or even die; the honeydew they secrete can contaminate the leaves, affect photosynthesis, and may also cause sooty stains. and spread various viruses.
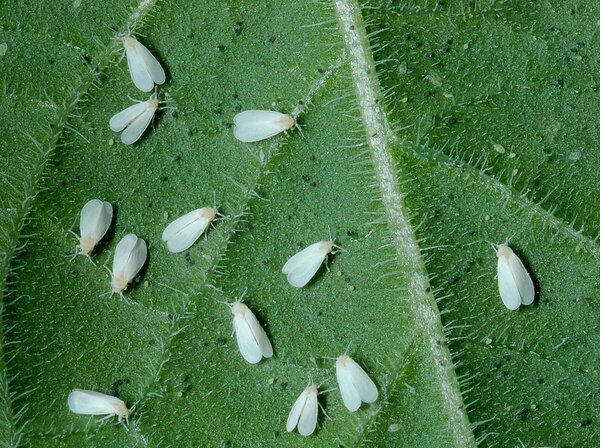

In addition to infesting plants in protected environments such as greenhouses, whitefly also causes serious damage to plants grown in the open field. This kind of pest has strong reproductive ability, fast reproduction speed, large group size, and likes to live in groups, causing more destructive harm. Once a plant is infected, it should be immediately isolated to another area, or preferably the entire plant should be sprayed to curb the spread and further damage of the pest and disease.
3. Xiao Heifei (rapid reproduction/infectious fungus)
The small black fly, also known as the sharp-eyed mushroom mosquito, has gray-black adult wings. It is a small black mosquito that is good at flying. These insects like to grow in moist soil, and their host range includes succulents, orchids, clivias and other plants. They feed on fungi and algae, and the larvae multiply rapidly in the soil, causing the fungus to spread by gnawing on the roots and harming the health of the plant.

Adult insects will not only fly indoors and cause trouble to people, but may also eat plant leaves and affect the health of flowers. Female adults can even sting humans. Because these pests escape quickly when pesticides are sprayed and reappear after the pesticide effect wears off, they are difficult to eradicate. However, keeping the potting soil moderately dry can effectively curb their growth. In severe cases, you can consider using root irrigation drugs to kill the larvae.
4. Red spider (strong fecundity/strong adaptability/wide spread method)
Red spider mites are listed as one of the top ten plant and flower pests. They belong to the mite family and are so tiny that they are almost indistinguishable to the naked eye. This pest has strong fecundity and can produce multiple generations in one year. It grows and develops quickly and has a short reproduction cycle. Both males and females can reproduce alone. It has strong adaptability and a wide range of transmission methods. There are many plants susceptible to damage, including roses, roses, peach blossoms, cherry blossoms, rhododendrons, Milanese, kumquats, jasmine, etc.

Spider mites often form clusters on the underside of plant leaves and suck plant sap, initially causing the leaves to lose their green color and eventually may lead to leaf fall and the death of new shoots. Because of its small size, it is difficult to detect, but once discovered, it often indicates that the plant has been seriously damaged. And even after elimination, it is easy to relapse, especially when the air humidity is insufficient, it is more likely to break out in a large area. Therefore, it is usually necessary to use specialized insecticides for control of spider mites.
5. Aphids (high fecundity/spread viral diseases)
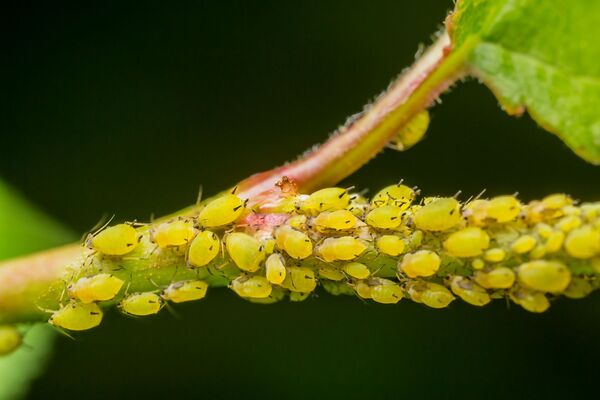

Aphids are common flower pests and like to attack peaches, roses, plum blossoms, cherry blossoms, peonies, rhododendrons, begonias, ivy, peace lilies and other plants. They can reproduce for 20 to 30 generations per year, giving birth to a new generation in just 5 days, and can even be spread to other plants by wind. Aphids often appear on young shoots, peduncles, and leaf undersides, causing the stems and leaves of plants to curl, wither, or even kill the entire plant. They excrete large amounts of honeydew, which can contaminate leaves and fruits, promote the occurrence of sooty disease, and interfere with photosynthesis of plants. In addition, aphids can transmit various viruses and cause widespread virus epidemics. Although aphids have low resistance to drugs, their spread can be effectively curbed as long as they are discovered and sprayed in time.
6. Thrips (complex feeding habits/can parthenogenetically reproduce)
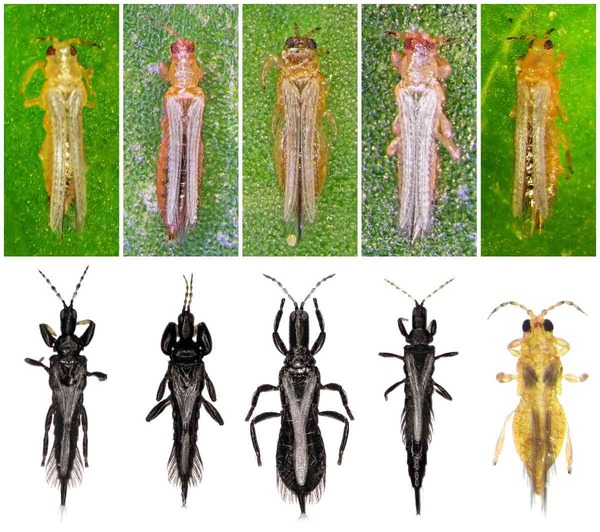

Thrips are garden plant pests widely distributed around the world. Their feeding habits are complex, including herbivory, mycophagy and predatory, with herbivorous species accounting for more than half. As one of the major economic pests, thrips often use their razor-sucking mouthparts to damage plant epidermal tissues and suck sap. They mainly harm the tender buds of plants. The affected leaves will show discoloration and food marks, initially appearing as white spots, and then gradually spreading into pieces. In severe cases, the leaves will become smaller, shriveled, or even yellow, dry and wither. . Infected flowers show discoloration of petals and food marks, and flower organs may show white spots or turn brown. Thrips particularly prefer flowers such as lilies, roses, and chrysanthemums as their host plants.
7. Leafminer (difficult to control/highly resistant to pesticides)
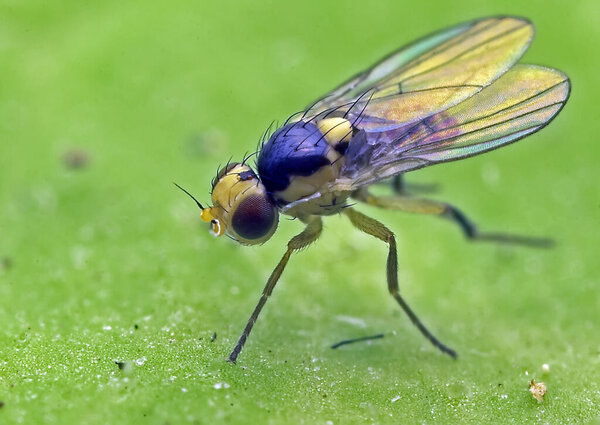

The spotted leafminer, commonly known as the ghost fly, appears frequently on the list of green plant pests and is known to attack a variety of hosts, including more than 100 species of plants. Cucurbits and leguminous crops are often prime targets because of their reputation for scribbling like scribbles inside their leaves. This pest is nicknamed "Ghost Painting Talisman". The female will choose to lay eggs in the leaf tissue of the host plant. After hatching, the larvae will begin to eat the leaf flesh under the leaf epidermis. Adult insects mostly suck sap from injured parts of plant leaves, causing plant growth retardation and leaf fall. In severe cases, they can damage flower buds and fruits, and even cause the destruction of seedlings. Since the larvae are hidden inside the leaves and difficult to deal with effectively, and they are highly resistant to drugs, the first step should be to replace or disinfect the soil.
8. Nematodes (hard to detect and can only be prevented)
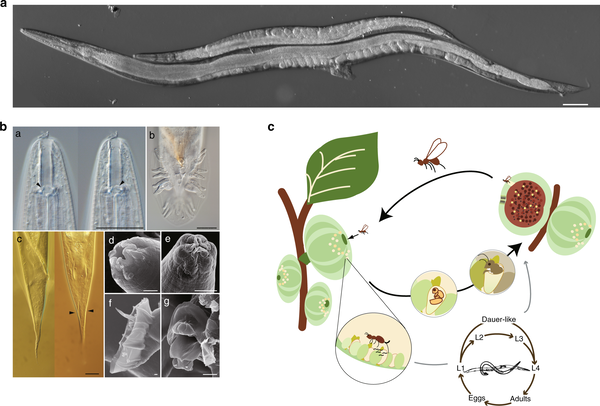
Nematodes are common green plant pests. They also attack orchids, carnations, narcissus, peonies and other flowers. They mainly damage the roots and other underground organs of the host plants, and sometimes occasionally attack aboveground parts such as stems and fruits. Mild insect infestations are often not easy to detect. The infected tissue will turn dark brown and appear water-soaked, with obvious scars on the surface. The roots will be short-cut and rotten, and the above-ground parts will show restricted growth, wilting or even die. Since there are many kinds of nematodes in the soil, and these nematodes are so young that they are almost invisible to the naked eye, prevention can only be focused on. One method is to add 20 to 30 3% furan granules per kilogram of planting soil. These granules will dissolve in the soil and be slowly released to eliminate nematodes.
9. Military caterpillars (destroy chlorophyll/hinder photosynthesis)

The armyworm is one of the famous pests in flowers, causing serious harm to azaleas in particular. It also affects hibiscus, papaya, gardenia, wisteria, rose, plum blossom, cherry blossom, smile, cherry blossom, camellia, jasmine, and four-season crabapple. , Tiegan Begonia, Silk Begonia, Wintersweet, Poplar and other types of garden plants. Adults and nymphs gather on leaves to suck sap, causing yellow and white spots to appear on the leaves, destroying chlorophyll, and severely hindering photosynthesis. A large amount of dark brown insect droppings and peeling shells are often seen on the leaves, and yellow-brown rust-like spots appear on the back of the leaves, causing the leaves to be pale or even fall off prematurely.
10. Grubs (damage the tender stems and roots of flowers)

Grubs and nematodes are both underground pests and are the larvae of scarab beetles or scarab beetles. They can be divided into three categories according to their different feeding habits: herbivorous, coprophagous and saprovorous. Herbivorous grubs are known for their wide range of feeding habits, and their damage range covers a variety of crops, cash crops and flower seedlings. These pests prefer to feed on newly sown seeds, roots, tubers and seedlings and are a global underground pest. Because they live in the soil, they often harm the tender stems, roots and tubers of some plants, causing root rot and eventually plant death. In terms of control, it is not easy to catch these pests, and it is usually necessary to use pesticides to fumigate the soil and water them for control.
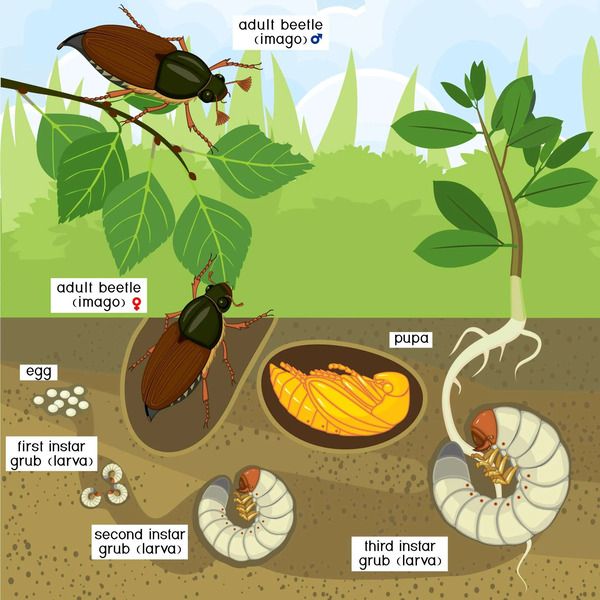
It is worth mentioning that some species of grubs have been found to have medicinal value and are beneficial to humans. They also have high edible value, with a sweet taste and rich protein content.
animal tags: pests
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.