Bathypterois spp is a fascinating genus of fish commonly known as deep-sea dragonfish. These unique creatures are renowned for their remarkable adaptations to life in the dark depths of the ocean. This article will delve into the characteristics, habitat, behaviors, and reproduction of Bathypterois spp, shedding light on what makes these deep-sea dwellers so intriguing.

Bathypterois spp primarily inhabit the deep ocean, typically found at depths ranging from 200 to 2,000 meters (656 to 6,561 feet). This deep-sea environment is characterized by extreme pressure, low temperatures, and complete darkness, creating a challenging habitat for most marine life. Bathypterois spp have evolved specialized adaptations to thrive in these conditions.
Appearance: Bathypterois spp. are known for their elongated bodies and large mouths filled with sharp teeth. They often have bioluminescent organs along their bodies, which help them attract prey in the dark.
Coloration: Their coloration varies, but they are generally dark brown or black, which aids in camouflage against the dark ocean backdrop.

Bathypterois spp. are carnivorous and primarily feed on smaller fish and zooplankton. Their large mouths and sharp teeth allow them to capture and consume prey efficiently. They are known to use their bioluminescent features to lure prey closer, exploiting the darkness of their habitat to their advantage.
Swimming: Bathypterois spp. are strong swimmers and use their streamlined bodies to navigate the deep waters. They are known to perform vertical migrations, moving closer to the surface at night to feed and returning to deeper waters during the day.
Bioluminescence: One of the most fascinating aspects of Bathypterois spp. is their ability to produce light. This bioluminescence serves multiple purposes, including attracting prey, communication, and camouflage.
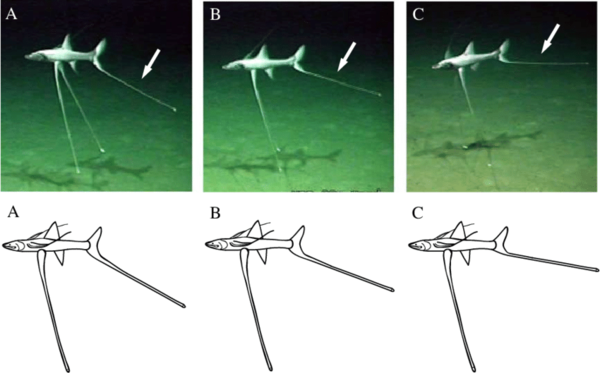
Details about the reproductive habits of Bathypterois spp. are not extensively documented, mainly due to their deep-sea habitat and the challenges of studying them in their natural environment. However, like many deep-sea fish, they are believed to have unique reproductive strategies adapted to the harsh conditions of their habitat.
Spawning: It is thought that Bathypterois spp. engage in spawning activities at various depths, with the larvae drifting in the ocean currents before settling into deeper waters as they grow.
Growth: The growth rate of Bathypterois spp. is relatively slow, which is common among deep-sea fish. This slow growth rate can be attributed to the limited food availability and the harsh environmental conditions.
While specific data on the conservation status of Bathypterois spp. is limited, deep-sea ecosystems are increasingly threatened by human activities, such as deep-sea fishing and climate change. Protecting these habitats is crucial for the survival of species like Bathypterois spp.

Bathypterois spp exemplifies the extraordinary adaptations that marine life has developed to survive in the deep sea. With their unique physical characteristics, feeding behaviors, and mysterious reproductive strategies, these deep-sea dragonfish continue to captivate scientists and ocean enthusiasts alike. As we learn more about these enigmatic creatures, it becomes increasingly important to protect their delicate habitats to ensure their survival for future generations.
animal tags: Bathypterois-spp
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.