The Distribution of Antedon mediterranea: Habitat and Conservation
Antedon mediterranea's Reproduction, Lifecycle, and Lifespan
The Ecological Role of Antedon mediterranea: Its Interactions with Other Marine Species
Antedon mediterranea, commonly known as the Mediterranean Feather Star, is a species of brittle star found in the Mediterranean Sea and the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Recognized for its delicate, feather-like arms and unique filtration abilities, this species plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the features, distribution, ecological role, and importance of Antedon mediterranea in marine environments, as well as its significance in scientific research and its relationship with humans.
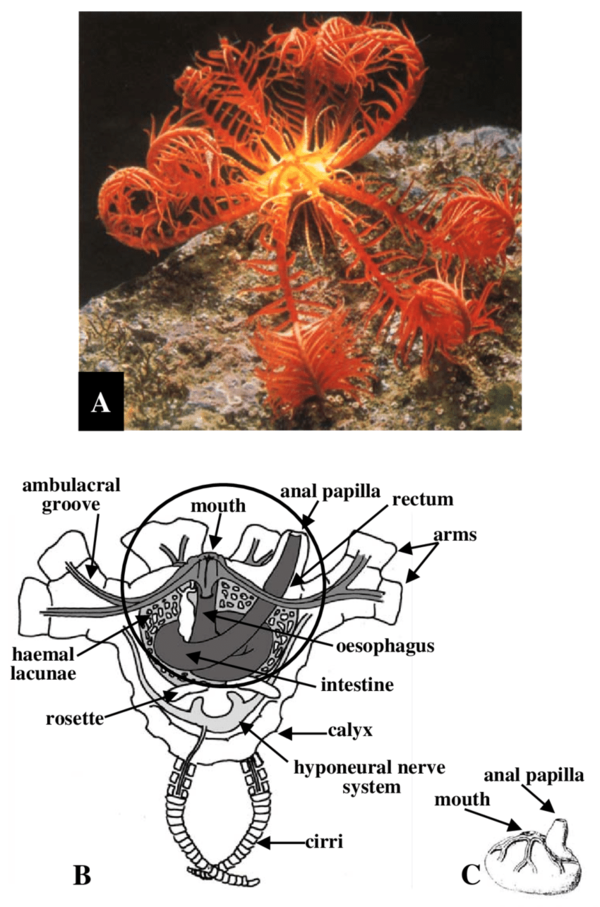
Appearance and Structure
The Mediterranean Feather Star is characterized by its long, slender, and feathery arms which radiate from a central disc. These arms are lined with numerous tube feet, allowing the organism to capture planktonic particles from the water.
Feeding Mechanism
As a suspension feeder, Antedon mediterranea uses its feather-like arms to filter plankton and other small particles from the water. The tube feet located on the arms help to capture food particles and transfer them to the central disc for digestion.
Behavioral Adaptability
The Mediterranean Feather Star has a remarkable ability to move and reorient itself in response to environmental conditions. It can slowly crawl along the sea floor using its arms and tube feet, but it primarily relies on water currents to bring food to its mouth.
Symbiotic Relationships
Antedon mediterranea often forms symbiotic relationships with other marine organisms, such as corals and sponges. These relationships can be mutualistic, with the feather star benefiting from the shelter and food provided by its hosts.
Reproductive Capabilities
Antedon mediterranea has a fascinating reproductive strategy that includes both sexual and asexual reproduction, ensuring its population can thrive even in fluctuating environmental conditions.
Antedon mediterranea is predominantly found in the Mediterranean Sea and the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. It is typically located in deep, nutrient-rich waters at depths ranging from 10 to 200 meters, although some populations have been observed in shallow coastal areas.
Substrate: These feather stars are often found on rocky or coral reefs, where they can anchor themselves securely and feed effectively. They prefer environments with stable currents and relatively calm waters.
Temperature and Salinity: The Mediterranean Feather Star is adapted to live in the relatively warm waters of the Mediterranean, with temperatures ranging from 15°C to 25°C. The species can also tolerate slight fluctuations in salinity but thrives best in stable conditions.
While Antedon mediterranea is not currently considered endangered, its populations are affected by various environmental threats. Overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution are major concerns. Conservation efforts focus on protecting coral reefs and minimizing human impacts on marine habitats. Additionally, sustainable fishing practices are being promoted to prevent the disruption of the delicate marine ecosystems that support the Mediterranean Feather Star.
Antedon mediterranea plays an important role as a filter feeder in the marine food chain. By feeding on plankton, small invertebrates, and organic particles suspended in the water, it helps to regulate the abundance of these organisms and maintain the balance of marine ecosystems.
While Antedon mediterranea itself is a consumer, it also serves as prey for a variety of predators. Larger fish, such as groupers, and other marine creatures, feed on this brittle star. As such, it is an important link in the marine food web, contributing to the nutritional cycling of marine ecosystems.
Fish: Various species of predatory fish, including groupers and wrasses, are known to consume Antedon mediterranea.
Cephalopods: Squids and octopuses are also known to prey upon feather stars, using their tentacles to capture them from the sea floor.
Antedon mediterranea, also known as the Mediterranean feather star, is a marine echinoderm species famous for its graceful, feather-like appendages that help it filter feed. Understanding its reproductive methods, lifecycle, and lifespan is essential for marine biologists, aquarists, and conservationists. These aspects of the organism are vital for both their survival in the wild and successful cultivation in aquariums. This section will delve into the fascinating processes that govern Antedon mediterranea's reproduction, lifecycle, and lifespan.
Antedon mediterranea exhibits sexual reproduction, with separate sexes in most populations. Their reproduction process is intricately tied to their environment, and they often reproduce during specific seasonal changes. Below is an in-depth look at their reproductive mechanisms.
Gonochorism means that Antedon mediterranea individuals are either male or female. The species does not exhibit hermaphroditism, meaning an individual will only possess reproductive organs of one sex.
External Fertilization: Unlike some marine organisms that engage in internal fertilization, Antedon mediterranea reproduces via external fertilization. The males and females release their gametes (eggs and sperm) into the water column, where fertilization occurs outside the body. This reproductive strategy relies on environmental factors, such as water currents, to disperse the gametes and allow for successful fertilization.
Spawning Events: Reproductive events are generally triggered by environmental cues such as water temperature, the availability of food, and light cycles. Antedon mediterranea typically spawns during the warmer months when environmental conditions are more stable and conducive to gamete release. This mass spawning can occur during specific times of the year, although the exact timing can vary based on location.
Eggs and Sperm Release: During spawning, females release eggs into the water while males release sperm. This process is synchronized within populations to increase the likelihood of fertilization.
Fertilization in the Water Column: Once the eggs and sperm are released into the water, fertilization occurs externally. Fertilization is dependent on the precise timing of gamete release and favorable water conditions. Successful fertilization produces zygotes that eventually develop into larvae.
The lifecycle of Antedon mediterranea is complex and undergoes several developmental stages, starting from fertilization through to adulthood.
Zygote Formation: After external fertilization, the zygote forms and begins its early development in the water column. These tiny, single-celled organisms begin to divide and undergo early stages of embryonic development.
Larval Stage: The fertilized egg develops into a free-swimming larvae known as a planktonic larva. The larval stage is crucial in the Antedon mediterranea lifecycle, as it allows the species to disperse and colonize new areas. During this stage, the larvae may spend several days to weeks in the plankton, where they feed on small organic particles before eventually settling onto the seafloor.
Metamorphosis: As the larvae mature, they undergo a significant transformation process known as metamorphosis. During metamorphosis, the larvae transform into juvenile Antedon mediterranea, developing their characteristic arms and central disk.
Settlement: Once metamorphosis is complete, the juvenile Antedon mediterranea settles onto a hard substrate like coral reefs, rocks, or the seafloor. This marks the beginning of the benthic (seafloor-dwelling) stage of their lifecycle. At this point, the young feather star begins its adult life, attaching to surfaces and continuing its growth.
Mature Antedon mediterranea: After settlement, Antedon mediterranea begins to grow into its adult form. Over the next few years, it develops its distinctive feather-like arms and central disk. During this time, it also begins to engage in filter-feeding, using its arms to collect organic particles from the water column. The adult stage is the longest stage of the lifecycle and can last for several years, depending on environmental conditions.
The lifespan of Antedon mediterranea is influenced by various factors, including environmental conditions, food availability, and the presence of predators. On average, the lifespan of Antedon mediterranea ranges from 5 to 10 years, but this can vary depending on the conditions in its habitat.
Water Quality: Good water quality is essential for the health and longevity of Antedon mediterranea. Poor water conditions, such as high levels of pollutants, reduced oxygen, or unstable salinity, can negatively impact their lifespan.
Predators: In the wild, Antedon mediterranea faces threats from various predators, including fish, crabs, and other marine invertebrates. While the feather star's ability to regenerate arms after damage helps it survive attacks, frequent predation can shorten its lifespan.
Habitat Quality: The presence of suitable habitats with adequate food sources also plays a critical role in lifespan. Feather stars in areas with abundant plankton and good substrate for attachment tend to live longer.
In captivity, Antedon mediterranea can live for a slightly reduced lifespan, typically between 3 to 7 years. This is primarily due to the controlled environment in aquariums, where factors like water quality, food availability, and predation risks are managed more effectively, but some challenges, such as stress, limited space, and artificial lighting, can still impact longevity.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Antedon mediterranea is its ability to regenerate lost arms. This regenerative ability plays an important role in its overall survival and lifespan.
Regeneration Process: If Antedon mediterranea loses one or more arms due to injury or predation, it can regenerate them over time. The regeneration process can take months, but the new arms are functional and capable of filter feeding once fully grown.
Impact on Lifespan: Although regeneration can help extend the lifespan of individual feather stars by allowing them to recover from damage, excessive injury or damage to critical body parts can still significantly shorten their lifespan. This makes it important for Antedon mediterranea to avoid injury and live in an environment free of predators that may cause harm.
The reproduction, lifecycle, and lifespan of Antedon mediterranea are complex and intricately linked to environmental factors and biological processes. The sexual reproduction and external fertilization followed by larval development allow Antedon mediterranea to spread across new habitats, ensuring the survival of the species. However, their delicate nature and dependence on water quality and food sources mean they are vulnerable to environmental stress.
Understanding these aspects of their biology is essential for those working in conservation, marine biology, and aquarium husbandry. The lifespan of Antedon mediterranea, typically ranging from 5 to 10 years, can be extended with proper care, protection from predators, and maintenance of a suitable environment. Their regenerative abilities offer hope for recovery in case of injury, but like all marine organisms, their future is tied to the health of our oceans.
Assessing the health of Antedon mediterranea, commonly known as the Mediterranean feather star, is crucial for both scientific study and aquarists looking to maintain healthy marine life in their tanks. Antedon mediterranea is a delicate organism that can be impacted by various environmental factors, diseases, and even stress. Understanding the signs of a healthy feather star and being able to identify any symptoms of distress or disease is key to ensuring its well-being.
In this section, we will discuss how to assess the health of Antedon mediterranea, what signs indicate poor health, and how to take action if any issues are identified.
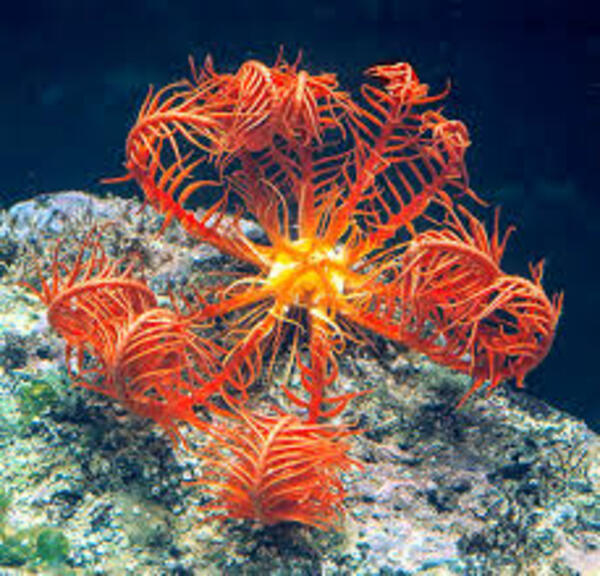

Before we dive into the ways to assess a sick or stressed Antedon mediterranea, it’s essential to understand what constitutes a healthy individual. Healthy Antedon mediterranea will display certain behaviors and physical characteristics that indicate its well-being.
Bright and Vibrant Color: A healthy Antedon mediterranea will have bright, vibrant colors. Typically, these feather stars are red, orange, or brown, with intricate patterns on their arms. Dull or faded coloration can indicate stress, poor water conditions, or malnutrition.
Fully Extended Arms: The arms of a healthy feather star will be fully extended and spread out. This is particularly important because they rely on their arms to filter feed. If the arms are retracted or appear damaged, it may be a sign of illness or poor water quality.
Arm Regeneration: While Antedon mediterranea is capable of regenerating lost or damaged arms, a healthy star will typically have all arms intact. If it’s missing arms, or if the arms appear to be growing in a strange manner, this could be a sign of injury or stress.
No Visible Damage or Lesions: Check for any wounds, cuts, or lesions along the arms or body of the feather star. These can indicate trauma, infections, or parasitic infestations. Healthy feather stars typically have smooth, unbroken arms and body segments.
Active Filter Feeding: Healthy feather stars are active filter feeders. If they are actively spreading their arms and moving gently with the currents, it’s a good sign that they are in good health. When feeding, they use their arms to filter plankton and other small particles from the water.
Normal Movement: Antedon mediterranea is generally a slow-moving organism. However, they should be able to move slowly and steadily across a substrate or cling to surfaces like rocks or corals. Unusual or jerky movements may indicate stress or a potential health issue.
If you notice any changes in the appearance, behavior, or condition of Antedon mediterranea, it could be an indication that something is wrong. Here are some common signs of poor health:
Fading Color: One of the first signs of distress in Antedon mediterranea is the loss of color. Feather stars are highly sensitive to water quality, and color fading can indicate problems such as poor water parameters, nutrient imbalances, or stress.
Shriveled or Retracted Arms: When the arms of Antedon mediterranea are not fully extended and appear shriveled or withdrawn, it could signal that the star is stressed, suffering from a lack of food, or experiencing environmental issues such as low water quality or temperature fluctuations.
Damaged Arms or Body: If you notice cuts, holes, or other visible injuries, this may be due to physical trauma, predation attempts, or bacterial infections. Damaged arms should be monitored carefully as they may not regenerate properly if the underlying cause isn’t addressed.
Discoloration of the Body: In addition to fading of the arms, discoloration of the central disc or other body parts can indicate infections or disease. If the body turns white or shows signs of decay, it could point to bacterial or fungal infections.
Loss of Activity: If Antedon mediterranea is no longer actively moving its arms or filter-feeding, it may indicate poor health. A healthy feather star continuously moves its arms to catch food particles in the water column, so a sudden reduction in activity is concerning.
Floating or Detached: Antedon mediterranea typically remains attached to hard surfaces like rocks, corals, or debris. If it begins to float aimlessly in the water column or detaches from its substrate, it may be a sign of stress, poor attachment, or even internal health issues.
Difficulty Regenerating Arms: While feather stars can regenerate lost arms, prolonged inability to do so or abnormal regeneration may indicate underlying health problems, such as insufficient food intake, poor water quality, or damage from predators.
The health of Antedon mediterranea is heavily influenced by the environment in which it resides. Below are some of the key environmental factors to monitor:
Temperature: Antedon mediterranea thrives in waters with stable temperatures, typically ranging from 18°C to 24°C (64°F to 75°F). Temperatures that are too high or too low can cause stress and health issues, affecting its ability to filter feed and regenerate.
Salinity: These feather stars are marine organisms that require stable salinity levels between 35-37 ppt (parts per thousand). Fluctuations in salinity can cause physiological stress and make them more susceptible to diseases.
Oxygen Levels: Low oxygen levels in the water can impair the ability of Antedon mediterranea to filter-feed and move. Ensure that the water is well-aerated, especially in aquariums, to maintain optimal oxygen levels.
Ammonia and Nitrite Levels: Elevated levels of ammonia or nitrites in the water can be toxic to marine organisms, including Antedon mediterranea. Test the water regularly for these chemicals, especially in an aquarium setting, and ensure they are within safe limits.
Flow Rates: Antedon mediterranea relies on water currents to help it filter food. If the water flow is too strong or too weak, it can affect their feeding behavior and overall health. Moderate currents that mimic their natural habitat are ideal.
Hard Surfaces for Attachment: Feather stars need hard substrates like rocks or corals to attach themselves. In an aquarium, providing stable surfaces is essential for their health. Lack of attachment or instability can cause stress and result in the feather star floating or detaching.
In addition to physical injury or stress, Antedon mediterranea can be susceptible to certain diseases and infections. Here are a few to look out for:
Bacterial Infections: If you notice any foul odors or rotting tissue, it could be a bacterial infection. Bacterial infections can cause rapid tissue decay and are often linked to poor water quality.
Fungal Infections: Fungal diseases can present as white, cotton-like growths on the body or arms of the feather star. This is usually indicative of compromised immune function or environmental stress.
Parasitic Infestations: Some marine parasites may infect feather stars, especially if they are stressed or exposed to contaminated water. These infestations often cause visible lesions or damage to the arms or body.
Algal Growth: Excessive algal growth on the body or arms of the Antedon mediterranea could be a sign of poor water quality, particularly excess nutrients in the water.
If you identify signs of poor health or illness, immediate action is necessary:
Isolate the Organism: If you suspect that Antedon mediterranea is ill or stressed, it may be beneficial to isolate it in a quarantine tank where you can monitor its condition more closely.
Adjust Water Parameters: Ensure that the water temperature, salinity, oxygen levels, and ammonia/nitrite levels are within the recommended ranges for the species. Make any necessary adjustments to improve water quality.
Remove Any Potential Stressors: If there are any obvious stressors, such as aggressive tank mates or poor water flow, address these issues immediately.
Provide Proper Nutrition: Ensure the feather star is able to access enough food. You may need to adjust the feeding schedule or introduce additional food sources, such as plankton or finely crushed food particles.
Consult a Marine Veterinarian: If the feather star is showing persistent signs of illness, it’s advisable to seek professional help from a marine veterinarian who can diagnose and treat any diseases or infections.
Assessing the health of Antedon mediterranea requires a careful observation of both its physical and behavioral traits. Recognizing signs of distress, maintaining optimal environmental conditions, and ensuring proper nutrition are key to keeping this beautiful marine organism in good health. Early detection of issues, whether related to water quality, injury, or disease, can prevent further complications and help ensure the long-term well-being of Antedon mediterranea.
The Antedon mediterranea, or Mediterranean feather star, is an important species within its marine ecosystem, playing key ecological roles that help maintain the health and balance of the Mediterranean and northeastern Atlantic seas. As a member of the Crinoidea class, Antedon mediterranea shares many characteristics with other feather stars, but its unique behaviors and relationships with other marine species make it a fascinating subject of study in marine ecology.
In this section, we will explore the ecological role of Antedon mediterranea, focusing on its interactions with other marine organisms, its contributions to the benthic environment, and its involvement in the larger marine food web.
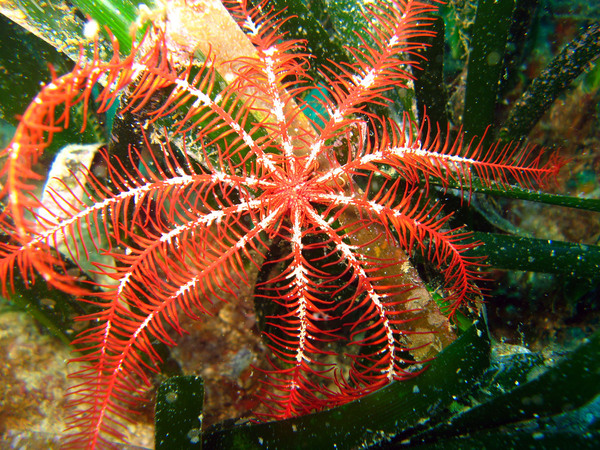

One of the primary ecological roles of Antedon mediterranea is its role as a filter feeder. These feather stars use their highly specialized, branched arms, covered in fine, hair-like structures called pinnules, to filter plankton, detritus, and microscopic organisms from the water. By doing so, they help regulate the abundance of plankton populations in their habitats. This behavior has several ecological implications:
Maintaining Water Clarity and Quality: Antedon mediterranea plays a key role in maintaining water clarity by filtering large volumes of water, removing suspended particles and plankton. This helps prevent the overgrowth of algae and contributes to the overall health of the marine environment.
Nutrient Recycling: As a filter feeder, Antedon mediterranea also contributes to the cycling of nutrients within the benthic zone. By filtering detritus, organic matter, and plankton, it helps break down these materials, contributing to nutrient cycling that supports other marine life forms.
Habitat Health: Healthy water quality is critical for the survival of many marine species, including corals, mollusks, and other invertebrates. By maintaining water quality, Antedon mediterranea helps to ensure that these organisms thrive in their habitats.
Antedon mediterranea exists in close proximity to a variety of other marine invertebrates, and its ecological role intersects with those of other species in its habitat. These interactions can be both direct and indirect, with Antedon mediterranea contributing to a balanced ecosystem.
Symbiotic Relationships with Coral and Sessile Invertebrates: In its habitat, Antedon mediterranea often attaches to corals, rocks, or other hard substrates. While these feather stars do not rely on corals for nutrition, they coexist with them in a way that benefits both species. By occupying space on coral colonies, Antedon mediterranea may provide some protection to the coral from potential herbivores or predators.
Coexistence with Sea Cucumbers, Mollusks, and Crustaceans: On the ocean floor, Antedon mediterranea interacts with a variety of other marine invertebrates, including sea cucumbers, bivalves, and crustaceans. These organisms may share the same habitat and compete for food resources, but Antedon mediterranea's filter-feeding method is non-competitive. As it filters plankton, it does not significantly impact the food supply of other species, allowing for coexistence without direct competition.
Predator-Prey Dynamics: While Antedon mediterranea is generally a peaceful organism, it is not immune to predation. Its arm regeneration abilities allow it to survive some predatory attacks, but its presence in certain areas may help deter potential predators, such as larger fish and invertebrates, by occupying space and reducing available resources.
Feather stars, including Antedon mediterranea, are a crucial component of the benthic food web. As filter feeders, they serve as both consumers and prey for other marine organisms, contributing to the cycling of energy and nutrients within the ecosystem.
Prey for Marine Predators: Though Antedon mediterranea has some protective mechanisms, it remains prey for several marine species. Larger fish, such as groupers, and marine predators like octopuses and some species of sea stars, may feed on feather stars. In turn, Antedon mediterranea contributes energy to higher trophic levels in the food chain. While these interactions may seem one-sided, they are essential in maintaining the structure of the marine food web.
Predator Avoidance: In response to potential threats, Antedon mediterranea has evolved mechanisms to avoid predation. When threatened, it can retract its arms and body to make itself less accessible to predators. This behavioral response is crucial for its survival and helps regulate predator-prey interactions in its environment.
Role in Detritus Consumption: As a detritivore, Antedon mediterranea helps consume and break down organic material from the ocean floor. This recycling of nutrients supports the growth of phytoplankton and other primary producers in the water column, indirectly sustaining the entire food web.
The Mediterranean Sea is home to a vast array of marine species, many of which rely on complex ecological interactions to maintain the stability of the ecosystem. Antedon mediterranea contributes to this biodiversity in several ways:
Supporting Small Marine Organisms: By filtering plankton and detritus, Antedon mediterranea helps support the growth of smaller marine organisms, including other plankton-feeding species that depend on these food sources for survival. This, in turn, supports larger marine organisms in the food web.
Providing Habitat for Other Species: The presence of Antedon mediterranea on coral reefs and rocky substrates creates microhabitats for other marine species. Crustaceans, mollusks, and smaller fish may use the arms of Antedon mediterranea as shelter or hiding spots, further enhancing biodiversity in the habitat.
Interdependency in Marine Ecosystems: As part of the larger ecosystem, Antedon mediterranea relies on healthy coral reefs, clear waters, and abundant plankton to thrive. In turn, it contributes to the health of the ecosystem by filtering water, providing food for other species, and serving as prey for predators. These interdependencies highlight the importance of Antedon mediterranea in maintaining the delicate balance of Mediterranean ecosystems.
The interactions between Antedon mediterranea and other species are not static; they are influenced by changes in environmental conditions. Overfishing, pollution, and climate change have all had an impact on marine ecosystems, and Antedon mediterranea is not exempt from these challenges.
Effects of Pollution: Pollution, particularly plastic waste and agricultural runoff, can negatively affect the feeding and health of Antedon mediterranea. Contaminants in the water may reduce the availability of plankton or increase the presence of harmful microorganisms, disrupting the delicate balance that the feather star relies on.
Ocean Acidification and Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification can affect the growth and health of Antedon mediterranea. These changes may alter the species' ability to filter-feed efficiently, and in extreme cases, could threaten its survival. As an integral part of the benthic food web, any disruption to Antedon mediterranea can have cascading effects on other species.
Habitat Loss and Overfishing: The degradation of coral reefs and the destruction of benthic habitats also threaten Antedon mediterranea. These ecosystems provide shelter and feeding opportunities for feather stars, and the loss of such habitats can have significant impacts on their population and ecological interactions.
Antedon mediterranea plays a vital role in the Mediterranean marine ecosystem, influencing water quality, nutrient cycling, and supporting biodiversity. As a filter feeder, it helps maintain healthy water conditions and contributes to the ecological balance of the region. Its interactions with other marine organisms, including other invertebrates and predators, highlight the interconnected nature of marine ecosystems.
However, like many marine species, Antedon mediterranea faces increasing threats from human activities, including pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction. Understanding its ecological role and the relationships it shares with other marine species is essential for implementing effective conservation strategies to protect this remarkable organism and the ecosystems it inhabits.
The Mediterranean feather star, Antedon mediterranea, has attracted significant interest from the scientific community due to its unique biological characteristics, ecological importance, and potential applications in various fields of research. Over the years, scientific studies have expanded our understanding of this species' physiology, behavior, and role in marine ecosystems. Research progress on Antedon mediterranea is ongoing, with significant contributions in marine biology, conservation, and biotechnology. This section will explore the key areas of scientific research concerning Antedon mediterranea, highlighting the latest advancements and the questions that remain unanswered.
Antedon mediterranea belongs to the class Crinoidea, a group of echinoderms commonly known as feather stars. The taxonomy of feather stars has been a subject of continuous refinement, as researchers work to better understand the relationships between different species within the Crinoidea. Early studies focused on morphological classifications, but more recent approaches have incorporated molecular techniques, particularly DNA sequencing, to create more accurate phylogenies.
Antedon mediterranea was first described in the 19th century, but its classification and relationship with other feather star species have evolved over time. Research has confirmed that Antedon mediterranea is part of the family Antedonidae, which includes other species of feather stars found throughout the Mediterranean and northeastern Atlantic. Molecular research has helped clarify evolutionary relationships within this group, providing insights into how these species have adapted to their environments over millions of years. The application of modern techniques such as mitochondrial DNA barcoding and ribosomal RNA analysis has greatly advanced our understanding of the species' evolutionary history.
Antedon mediterranea is a filter feeder, using its feathery arms to capture plankton and detritus from the water column. This feeding mechanism has been a key area of study, as it provides essential insights into how these organisms interact with their environment and contribute to the food web. Researchers have explored the structure of the arms and the specialized cilia that aid in particle capture, as well as the species' ability to filter vast quantities of water to obtain its food. Understanding the feeding ecology of Antedon mediterranea has important implications for marine ecosystem health, particularly in regions where these organisms are integral to maintaining water quality and biodiversity.
In addition to feeding, Antedon mediterranea plays an important role in the benthic ecosystem as a habitat modifier. By filtering large amounts of water, it helps regulate plankton populations and nutrient dynamics, indirectly influencing the abundance and diversity of other marine species. Studies have also examined the interaction between Antedon mediterranea and other benthic organisms, such as corals and mollusks, to assess how this species may contribute to maintaining balanced ecosystem structures.
Reproductive studies on Antedon mediterranea have shed light on the species' complex life cycle. Like other feather stars, Antedon mediterranea undergoes external fertilization, with the release of gametes into the water. Fertilization typically occurs in late spring and summer, coinciding with the warmer months of the Mediterranean. The fertilized eggs develop into larvae, which go through several stages of development before settling on the seabed as juvenile feather stars.
Researchers have closely studied the developmental stages of Antedon mediterranea to understand how environmental factors, such as temperature and salinity, influence reproduction. One important area of research is the species' ability to regenerate lost arms. Unlike many organisms, Antedon mediterranea can regenerate fully functional arms after injury, a process that has been a major topic of interest in regenerative medicine. By understanding the genetic and cellular mechanisms that allow for such regeneration, scientists hope to develop applications for human tissue regeneration.
The behavior of Antedon mediterranea is another area of active research. Feather stars exhibit a unique form of movement, often using their arms to crawl along the seabed or cling to rocks and corals. The movement is facilitated by the use of tube feet located on the underside of their arms, which allow them to "walk" or attach to surfaces.
In recent studies, scientists have investigated how Antedon mediterranea responds to different environmental stimuli, such as light, water currents, and predators. These studies have revealed that Antedon mediterranea is highly sensitive to changes in its surroundings and can adjust its position or behavior in response to environmental stressors. Some studies have also explored the species' ability to move in search of food or mates, as well as its response to the presence of potential threats, such as larger predators.
One of the most interesting findings in recent behavioral studies is the species' ability to display "feather folding" behavior when disturbed. This defensive mechanism involves rapidly retracting its arms into a compact form to protect itself from predators or unfavorable conditions. These behaviors have been studied to better understand how Antedon mediterranea interacts with its environment and ensures its survival.
As global climate change continues to affect marine ecosystems, scientists are closely monitoring the impact of environmental stressors on Antedon mediterranea populations. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and pollution are all factors that threaten the species' survival, particularly in the Mediterranean, where it is endemic. Studies have shown that Antedon mediterranea is sensitive to changes in water temperature and acidity, which can affect its growth, reproductive success, and overall health.
Research has also focused on the species' role in maintaining the health of the Mediterranean's delicate ecosystems. As a filter feeder, Antedon mediterranea helps maintain water clarity and nutrient balance, preventing the overgrowth of harmful algae. However, in the face of climate change and human-induced pollution, its ability to fulfill this role may be compromised. Understanding the thresholds of stress that Antedon mediterranea can tolerate is critical for predicting how it will fare in the future and what conservation measures may be necessary to protect it.
Although Antedon mediterranea is not currently listed as an endangered species, its sensitivity to environmental changes has raised concerns among conservationists. The degradation of coral reefs and marine habitats, along with increasing ocean acidification, poses a threat to the species' long-term survival. Researchers are working on strategies to protect the habitats of Antedon mediterranea, focusing on the creation of marine protected areas (MPAs) and the implementation of sustainable fishing practices.
Studies on Antedon mediterranea have contributed to broader conservation efforts in the Mediterranean, particularly in understanding the vulnerability of benthic ecosystems to human activities. Efforts to reduce pollution, mitigate climate change, and preserve biodiversity are key to safeguarding the future of Antedon mediterranea and other marine species that rely on similar habitats.
While Antedon mediterranea has not yet been exploited for medical use, its regenerative abilities make it an interesting subject for biotechnological research. The species' capacity to regenerate lost limbs has potential applications in human regenerative medicine, particularly in the development of treatments for injuries or conditions that cause tissue loss. Scientists are investigating the molecular processes involved in limb regeneration, with the hope of applying similar mechanisms to human tissue repair.
In addition, Antedon mediterranea's ability to filter large quantities of water may inspire new water purification technologies. The structures that facilitate this feeding behavior are of interest to engineers working on biomimetic designs for filtration systems. These technologies could potentially be used in environmental cleanup efforts or water purification processes, benefiting human industries and ecosystems alike.
The scientific research progress on Antedon mediterranea has significantly expanded our understanding of this species and its role in marine ecosystems. From taxonomy and feeding mechanisms to reproduction and behavior, the Mediterranean feather star continues to be a valuable model organism for studying marine life. As climate change and human activities threaten marine environments, continued research is essential to ensuring the survival of Antedon mediterranea and other species that rely on similar habitats. Through conservation efforts, technological innovation, and deeper ecological understanding, scientists aim to preserve the delicate balance of marine ecosystems that Antedon mediterranea helps sustain.
Antedon mediterranea, also known as the Mediterranean feather star, is a fascinating marine species that has a subtle yet significant relationship with humans. Though not directly utilized in many industries, its role in marine ecosystems, scientific research, and aquarium hobbyism has created a connection with human activities. This section explores the different ways Antedon mediterranea interacts with humans and the potential benefits it provides.
Antedon mediterranea plays an essential role in marine ecosystems, particularly in maintaining the health of coral reefs. As a filter feeder, it helps keep the water clean by consuming plankton and other small particles that float in the water. In doing so, it contributes to the overall balance of the ecosystem by preventing nutrient overloads and reducing the risk of algal blooms.
For humans, understanding the ecological importance of species like Antedon mediterranea is crucial in fostering awareness about the health of marine environments. Coral reefs, where these feather stars are typically found, are under threat due to human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change. By studying organisms like the Mediterranean feather star, scientists can monitor reef health and improve conservation efforts. Public education on these topics helps build a collective responsibility for preserving fragile ecosystems.
The study of Antedon mediterranea and other echinoderms has led to advancements in marine biology and ecological sciences. Research into the reproductive habits, feeding mechanisms, and behavior of feather stars provides valuable insights into marine life cycles and environmental interactions. For example, Antedon mediterranea’s feeding mechanism—its ability to filter particles from the water using its feathery arms—has inspired biomimetic designs in water filtration systems, leading to innovative technologies that mimic nature’s efficiency.
Moreover, Antedon mediterranea serves as a model organism in studies on marine biodiversity and environmental stress responses. Researchers use feather stars to understand the effects of ocean acidification, temperature changes, and pollution on marine life. As such, this species contributes to broader conservation strategies, shaping policies and regulations aimed at protecting marine biodiversity for future generations.
In the world of marine aquarium keeping, Antedon mediterranea is a sought-after species due to its striking appearance and its ability to add diversity to reef tanks. As an aquarium inhabitant, the Mediterranean feather star is appreciated for its grace and unique feeding behavior. However, its popularity also raises concerns about sustainability and the potential impacts of overharvesting.
The aquarium trade is a significant economic driver for the marine species market, and Antedon mediterranea is a part of this trade. While there is a growing interest in captive breeding and sustainable sourcing, the collection of wild specimens remains a concern. Over-collection can harm local populations, especially if proper harvesting practices are not followed. This highlights the importance of responsible sourcing and the implementation of sustainable practices within the aquarium trade to ensure that Antedon mediterranea populations remain healthy and abundant in the wild.
While Antedon mediterranea is not widely used in medicine, its relationship with humans in terms of biotechnological research holds potential. Echinoderms like feather stars are known for their remarkable regenerative abilities. Antedon mediterranea can regenerate lost arms, a trait that could have significant applications in the field of regenerative medicine. Studying the molecular and cellular mechanisms behind this regeneration may offer insights into human tissue repair and healing processes.
Additionally, the biochemical properties of Antedon mediterranea’s unique feeding mechanisms and defense mechanisms may provide clues for developing new marine-derived products. For example, the natural substances involved in its filter-feeding process could inspire new biofilters or environmental cleanup technologies that humans can use to combat water pollution.
The relationship between Antedon mediterranea and humans must also address the ethical considerations of conservation and sustainability. As with many marine species, overexploitation and environmental degradation threaten the long-term survival of the species. Pollution, especially from plastics, and the warming of the Mediterranean Sea due to climate change, negatively impact the habitats of these creatures.
Conservationists and marine biologists are working to mitigate these effects, often through policy advocacy and public awareness campaigns. Ensuring that Antedon mediterranea populations are protected from overfishing and habitat destruction is critical to preserving their role in the ecosystem. Moreover, marine protected areas (MPAs) are being established to safeguard these delicate environments.
While Antedon mediterranea may not have a direct cultural significance in terms of folklore or traditional uses, its aesthetic value cannot be understated. The striking appearance of the feather star, with its elegant, fan-like arms, contributes to the natural beauty of marine ecosystems and captivates marine enthusiasts and divers. In a broader sense, the appreciation of such species helps foster a connection between humans and the natural world, encouraging more people to take an active interest in ocean conservation.
As the marine aquarium hobby grows in popularity, the desire to keep unique and beautiful species like Antedon mediterranea has led to an increase in public interest in marine biodiversity. This, in turn, supports educational initiatives that highlight the importance of protecting marine life for future generations.
The relationship between Antedon mediterranea and humans is multifaceted and continues to evolve. From its ecological role in marine ecosystems to its contributions to scientific research and aquarium trade, this fascinating species connects humans to the health and preservation of the oceans. As we learn more about its biology and the challenges it faces, we can better understand how to protect it and other marine species for the future. By promoting sustainable practices, both in the wild and in aquariums, humans can ensure that the Mediterranean feather star continues to thrive in its natural habitat while contributing to broader ecological and technological advancements.
Caring for Antedon mediterranea, also known as the Mediterranean Feather Star, in an aquarium requires careful attention to its natural habitat and specific needs. These unique creatures, with their delicate feather-like arms and suspension feeding behavior, can thrive in captivity with the right environment and care. Below is a comprehensive guide on how to care for Antedon mediterranea in your aquarium.
To keep Antedon mediterranea healthy and happy, you need to replicate its natural marine environment as closely as possible. This means ensuring the water quality, temperature, and habitat conditions are ideal for the feather star.
Tank Size and Type:
Tank Size: Antedon mediterranea requires a spacious aquarium to thrive. A minimum of 100 liters (about 26 gallons) is recommended for one or two individuals, but larger tanks are preferred if you plan on keeping more than one.
Type of Tank: A saltwater tank with live rock and corals is ideal, as these creatures naturally live in marine ecosystems, often found in coral reefs. Live rock provides not only natural filtration but also offers hiding spots and surfaces for the feather star to attach itself.
Water Parameters:
Salinity: Antedon mediterranea thrives in water with a salinity level of 1.023–1.025 specific gravity. It is important to regularly monitor the salinity using a hydrometer or refractometer.
Temperature: The ideal temperature range for Mediterranean Feather Stars is between 18°C and 25°C (64°F and 77°F). Avoid drastic temperature fluctuations as they can stress the star and affect its health.
pH Levels: The water should have a stable pH of 8.1 to 8.4, similar to natural ocean conditions.
Ammonia and Nitrite: These toxins are harmful to Antedon mediterranea. Ensure that ammonia and nitrite levels are consistently at zero by maintaining a well-established filtration system and regular water changes.
Antedon mediterranea is a filter feeder, and it depends on a steady flow of water to bring in plankton and small particles that it can feed on. However, it also requires moderate to gentle water movement to simulate its natural habitat without causing stress.
Filtration: A high-quality filtration system is essential to maintain clean water, as Antedon mediterranea relies on small particles in the water for food. Use a protein skimmer to remove organic waste and maintain water clarity.
Water Flow: While they are filter feeders, Antedon mediterranea prefers moderate water movement. Strong currents may stress them and damage their delicate arms. Position your pumps and powerheads carefully to create a gentle, stable current throughout the tank.
Regular water changes (about 20% every 2-3 weeks) are important to ensure that toxins do not build up and to keep the overall water quality at optimal levels.
Antedon mediterranea does not require intense lighting, as it primarily feeds on plankton and organic particles in the water column, not through photosynthesis. However, the lighting should still mimic the natural day-night cycle for the overall health of the aquarium inhabitants.
Lighting: Moderate lighting (around 5 to 6 hours per day) is recommended. Avoid excessive lighting or bright light that could stress the feather star.
Light Cycle: Implement a 12-hour light/dark cycle to help mimic natural conditions. This cycle can be regulated using timers for consistency.
Antedon mediterranea feeds on plankton, small invertebrates, and organic particles suspended in the water. In an aquarium setting, it is important to provide these food sources.
Plankton and Micro-Particles: The best way to feed Antedon mediterranea in an aquarium is by introducing planktonic foods. You can use liquid plankton supplements or freeze-dried foods, such as rotifers, copepods, or krill. These foods should be dispersed gently into the water so that the feather star can use its tube feet to capture them.
Feeding Frequency: Feed your feather star daily or every other day, depending on its activity level and feeding response. In a well-established tank with a good flow of nutrients, they may also feed passively on particles in the water, reducing the need for additional feedings.
Avoid overfeeding, as uneaten food can decay and lead to water quality problems.
Antedon mediterranea is a relatively peaceful creature, but it is essential to select tank mates that will not harm or stress it.
Compatible Species: It does well with non-aggressive fish such as clownfish, gobies, or blennies. It also thrives in tanks with other filter feeders such as soft corals and certain types of sea sponges.
Avoid Aggressive Species: Do not house Antedon mediterranea with predatory fish (e.g., groupers, larger wrasses, and some types of triggers) that might see it as prey. Also, avoid keeping it with animals that may harm its delicate arms, such as large crabs or shrimp.
No Strong Currents: Since feather stars require gentle water flow, make sure that tank mates do not disrupt the water current too much. This will help prevent undue stress on the Antedon mediterranea.
Antedon mediterranea is fragile, and its arms are prone to damage if mishandled. When moving the feather star, it is important to handle it with care to avoid breaking or tearing its arms.
Do Not Touch the Arms: Feather stars are delicate, and their arms can break if handled roughly. It is best to move the star using the central disc, and avoid disturbing it unnecessarily.
Allow Natural Behavior: Provide enough space for the feather star to spread its arms and move freely. They are slow-moving creatures, so avoid placing them in areas where they might get trapped or disturbed by other tank inhabitants.
Antedon mediterranea can be sensitive to changes in water quality or environmental stressors. Monitoring its health is essential to ensure a thriving specimen in your aquarium.
Healthy Indicators: A healthy feather star will have fully extended, undamaged arms that are actively feeding. Its central disc should be intact and free from any injuries.
Signs of Illness: If the arms of the feather star start to curl up or retract, it could indicate stress, poor water conditions, or illness. Loss of arms or damage to the central disc can signal a more serious problem, often caused by predation, improper water parameters, or rough handling.
Water Testing: Regularly test the water for ammonia, nitrites, nitrates, and pH levels. Fluctuations in these parameters could indicate an underlying problem affecting the feather star's health.
Breeding Antedon mediterranea in captivity is rare, but not impossible. Feather stars generally reproduce via broadcast spawning, where eggs and sperm are released into the water column for fertilization.
Spawning Conditions: To encourage spawning, you would need to replicate specific environmental triggers, such as temperature changes or changes in water salinity. However, achieving successful fertilization in an aquarium setting is difficult, as it requires large numbers of feather stars in the same area.
Caring for Antedon mediterranea in an aquarium can be a rewarding experience, but it requires attention to detail and a deep understanding of the species’ natural habitat and needs. By providing the right tank conditions, food, and compatible tank mates, you can help ensure the health and longevity of your Mediterranean Feather Star. Regular maintenance and observation will keep it thriving and contribute to the overall health of your marine aquarium ecosystem.
Antedon mediterranea, or the Mediterranean Feather Star, plays an integral role in marine ecosystems by serving as a filter feeder and participating in nutrient cycling. Its delicate beauty and ecological importance make it a subject of ongoing research and conservation efforts. Understanding its behavior, habitat, and interactions with other species helps us better appreciate the complexities of marine life and the importance of protecting our oceans.
animal tags: antedon-mediterranea
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.