Dinosaurs are a type of ancient creatures that were widely distributed in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Based on their biological characteristics and evolutionary history, dinosaur groups can be divided into several families, genera and species. The following is a detailed introduction to the classification of dinosaurs:
Phylum: Vertebrates (Chordata)
Class: Reptilia
Subclass: Diapsida
Group: Dinosauria
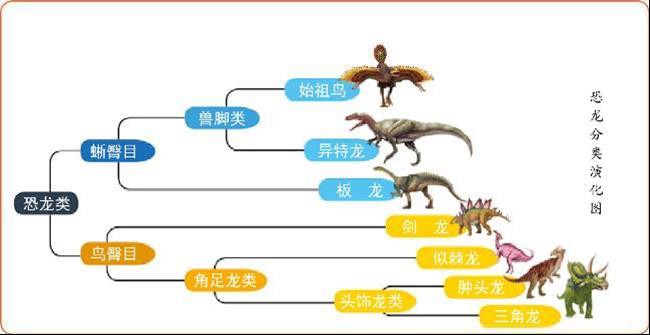
Sauurchia: distinguished from ornithischians by the characteristics of their hip bones, including sauropods and theropods.
Sauropod dinosaurs: such as Diplodocus, Stegosaurus, etc.
Theropod dinosaurs: such as Tyrannosaurus rex, Tyrannosaurus rex, etc.
Ornithischians: distinguished from archosaurs by their hip bone characteristics, including ankylosaurs and hadrosaurs.
Ankylosaurus dinosaurs: such as Tentosaurus, Triceratops, etc.
Hadrosaurus dinosaurs: such as Hadrosaurus, Brachiosaurus, etc.
Dinosaurs are further divided into different genera (Genus) and species (Species), each with its own unique scientific name and characteristics.
Tyrannosaurus Rex:
Scientific name: Tyrannosaurus rex
Classification: Archosaur theropod dinosaur
Introduction: Tyrannosaurus rex is one of the most famous theropod dinosaurs, living in the late Cretaceous period.
Triceratops:
Scientific name: Triceratops
Category: Ornithischian ankylosaurus dinosaur
Introduction: Triceratops is a huge herbivorous dinosaur with a triangular head shield and horns.
Palaeontologists and paleontological researchers continue to revise and evolve dinosaur classifications based on new fossil discoveries, research techniques, and theoretical frameworks. As a result, dinosaur classification systems continue to be updated to reflect a deeper understanding of these ancient creatures.
These classification systems not only contribute to the understanding of dinosaur biology, but also provide researchers with a framework that can be used to analyze aspects of dinosaur diversity, evolution, ecology, and more.
animal tags: Dinosaur
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.