
Luciobramamacrocephalus
Luciobramamacrocephalus,longspiky-head carp,Blowgun, pointed-headed catfish, horse-headed catfish, duck-billed catfish, trumpet fish, catfish, catfish
Features:It has a pointed head, a long beak, and a slender body. It is commonly known as a blowpipe.
The Latin name of the carp is Luciobramamacrocephalus, and the English name is longspiky-head carp. It is a large predatory fish and a species endemic to my country.The carp is a large economic fish, fierce in nature, and likes to live alone. Individuals under 30 cm are generally active in the middl...

Gobiocypris rarus Ye et Fu
Gobiocypris rarus Ye et Fu,Raregudgeon,Golden white lady, ink line fish, rare goby
Features:Endemic to China, very rare
The Latin name of the rare gobiocypris is Gobiocypris rarus Ye et Fu, and its foreign name is Raregudgeon. It belongs to the genus Gobiocypris of the Cyprinidae family. There is only one species in this genus, which is endemic to my country.Rare goby mainly feeds on small aquatic invertebrates. The...

Tanichthys albonubes
Tanichthys albonubes,White Cloud Mountain Minnow, Baiyunshan fish, Tang fish, Baiyun golden fish, golden fish, redtail fish, Guangdong crucian carp, Pan's crucian carp
Features:It is a very small freshwater fish that can tolerate cold weather.
The Latin name of the minnow is Tanichthys albonubes, and its foreign name is White Cloud Mountain Minnow. There is no subspecies.The minnow is bold, lively and gentle. Although distributed in the subtropics, it is still cold-resistant and can still live normally when the water temperature drops to...

Myxocyprinus asiaticus
Myxocyprinus asiaticus,,Rouge fish, grilled bream, yellow steak, leaf plate, red fish, purple bream, bird fish, blood steak, pink steak, etc.
Features:The Myxocyprinus rubripes is the only species of the family Myxocyprinus distributed in the Asian continent and has important academic value.
The Latin name of the mullet is Myxocyprinus asiaticus, and there is no subspecies.The ancestors of the mullet can be traced back to the Mesozoic era when dinosaurs ruled. The earliest ancestor of the mullet is called the primitive bony swim bladder fish. According to research, this fish appeared in...

Gyrinocheilus aymonieri
Gyrinocheilus aymonieri,Wall Climbing Fish, Scavenger Fish, Algae Eater Fish, Double-Porifera
Features:There is a small gill opening above the normal gill opening, hence the name.
The Latin name of the diapsid fish is Gyrinocheilus aymonieri, which is endemic to Yunnan, China.The mouth of the diapsid fish forms a suction cup, which is used to attach to the surface of stones and shovel algae on the surface of the stones. As an ornamental fish, it is kept in an aquarium. It can...

Anguilla marmorata
Anguilla marmorata,Marbled eel、Giant Mottled Eel,Big eel, perch eel, flower eel, snow eel, king eel, black ear eel, reed eel, stream eel, stream slide
Features:It is called "the dragon among fishes" and has the property of "infinite growth"
The Latin name of the flower eel is Anguilla marmorata, and its foreign names are Marbled eel and Giant Mottled Eel. There are no subspecies.In 1824, French zoologist Jean René Constant Quoy (1790-1869) and French naturalist Joseph Paul Gaimard (1796-1858) reported on the Voyage autour de monde, en...

Acipenser schrencki
Acipenser schrencki,Amur Sturgeon,Seven floating fish, Heilongjiang sturgeon, Amur sturgeon, Acipenser schrenckii, Acipenser schrenckii
Features:It is the most valuable and high-quality rare fish among the existing sturgeons in China.
The scientific name of Acipenser schrencki is Acipenser schrencki, and its foreign name is Amur Sturgeon. It has the characteristics of large size, long lifespan, high survival rate of young fish, and fast growth rate. It is both ornamental and delicious.Acipenser schrenckii is an animal-eating fish...

Acipenser ruthenus
Acipenser ruthenus,Sterlet,Acipenser
Features:The body color varies greatly, but the back is often dark gray-brown and the abdomen is yellow-white.
The Latin name of the small-bodied sturgeon is Acipenser ruthenus, and its foreign name is Sterlet. There is no subspecies.The small-bodied sturgeon is a freshwater sedentary fish that usually does not migrate long distances. The migratory species of sterlet start to migrate upstream to spawn during...

Acipenser nudiventris
Acipenser nudiventris,Barbel Sturgeon、Ship Sturgeon.sturgeon, naked sturgeon
Features:Long cylindrical body, wide, flat abdomen
The Latin name of naked sturgeon is Acipenser nudiventris, and its foreign names are Barbel Sturgeon and Ship Sturgeon. There are no subspecies.The naked sturgeon is an advective, carnivorous fish. Naked sturgeons are divided into migratory populations and sedentary populations. Sedentary population...

Acipenser baerii
Acipenser baerii,Siberian sturgeon,Acipenser siberianus
Features:There are two ecological types: semi-migratory and sedentary.
The Latin name of Siberian sturgeon is Acipenser baerii, and its foreign name is Siberian sturgeon. It has no subspecies.The appearance and biological characteristics of the Siberian sturgeon are similar to those of the small-bodied sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus). In the Ob River, the Irtysh River (a...

Huso dauricus
Huso dauricus,kaluga sturgeon,sturgeon, amur sturgeon, sturgeon, sturgeon, sturgeon
Features:One of the ancient biota preserved from the Cretaceous period, it is the largest freshwater fish and is known as the "king of freshwater fish".
The scientific name of Dauricus sturgeon is Huso dauricus, and its foreign name is Kaluga sturgeon. It has no subspecies.As one of the ancient biological groups preserved in the Cretaceous period, the Dahurian sturgeon once lived on Earth with dinosaurs. Its primitive and simple appearance has hardl...
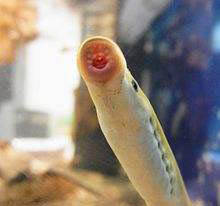
LampetrareissneriDybowski
LampetrareissneriDybowski,ReissnerLamprey,River lamprey, river lamprey, seven star lamprey, Ray's lamprey
Features:Landlocked type, pale tail fin
The Latin name of Reissner's lamprey is LampetrareissneriDybowski, and its foreign name is ReissnerLamprey. It is a relatively small freshwater species.The Lamprey's lamprey is a relatively small terrestrial species that is semi-parasitic and prefers to live in freshwater streams with slow c...

Lampetra moriiBerg
Lampetra moriiBerg,Seven-star fish, Northeast lamprey
Features:One of two freshwater lampreys
The Northeastern lamprey's Latin name is Lampetra moriiBerg, and it lives in fresh water all its life.Northeast lampreys live in fresh water all their lives, in mountain rivers with microcurrents and sandy bottoms; they burrow into sand or gravel during the day and come out to forage at night; t...

Silurus asotus
Silurus asotus,Amur catfish, mullet, catfish, catfish, mullet, croaker, croaker, yellow croaker
Features:The body is cylindrical and dark gray or grayish yellow, with a flat head, a large mouth and whiskers.
Catfish is commonly known as pond catfish, also called catfish, belonging to the genus Siluridae and the family Siluridae. It is a ferocious carnivorous fish. It has strong adaptability, lives on the bottom, swims slowly, tolerates low oxygen, and can survive below 1 mg/L. During the day, it rarely...

Parabramis pekinensis
Parabramis pekinensis,Changchun bream, grass bream, oil bream, long-bodied bream, chaotou bream, shrink-necked bream
Features:The head is very small, the mouth is small, long and rhombus-shaped, and silver-gray.
Bream can grow in still water or flowing water, and generally swims and feeds in the middle and lower layers. In China, it is distributed in the plains from Heilongjiang to the Pearl River and Hainan Province, but not in the Tumen River, Yalu River, and above the Longmen of the Yellow River. Juvenil...

Coilia nasus
Coilia nasus,Bitter fish, anchovies, hair fish, razorfish, hairy fish
Features:The body of knife fish is narrow and thin, like a sharp knife, silvery white, tender, but with many fine hair-like spurs. The meat is delicious, fat but not greasy, and slightly fragrant.
Knife fish, scientifically known as long-jawed anchovy, also known as knife anchovy and hairy anchovy, is a migratory fish. Knife fish usually live in the sea. They enter the river from the sea in February and March every year and migrate upstream for reproduction. Every spring, knife fish swim upst...

Monopterus albus
Monopterus albusApodidae, Apodidae, Genus Swiftlet, eel, yellow eel, field eel, field eel, long fish, blood fish, tilapia, scaleless prince
Features:The body is slender and snake-shaped, scaleless, and yellowish-brown in color. The body color often varies with the environment in which it lives.
Yellow eel (scientific name: Monopterus albus): also known as eel. It is a tropical and warm temperate fish, a bottom-dwelling fish with strong adaptability. It lives at the bottom of the water body, mainly in muddy waters such as rice fields, lakes, ponds, rivers and ditches, and even in swamps, fl...

Channa argus
Channa argus,Snakehead、Northern Snakehead,Black fish, mullet, black stick, snakehead fish, mullet, cuttlefish, cuttlefish,
Features:There are seven star-shaped markings on the top of the head, and the head is relatively long and pointed, like a snake.
The snakehead is a bottom-dwelling carnivorous and ferocious fish. It usually likes to live in shallow waters with dense aquatic plants along the coast. It lurks in the aquatic plants and waits for the opportunity to hunt for food. Sometimes it swims in the upper layer of the water at night. The fry...

Aristichthys nobilis
Aristichthys nobilis,bighead、bighead carp,Silver carp, bighead carp, soap carp, black carp, bighead carp, bighead carp, fathead carp, bighead carp, black carp, bighead carp, male fish, pine black
Features:
It lives in the middle and upper layers of the main streams of rivers, gentle river bays, lakes and reservoirs. Juveniles and immature individuals generally grow in lakes along the river and affiliated water bodies. When they reach sexual maturity, they go to the river to spawn. After spawning, most...

Hypophthalmichthys molitrix
Hypophthalmichthys molitrix,Silvercarp、Chinese Schemer,Silver carp, silver carp, jumping silver carp, silver carp, whale, white bream, white-footed silver carp, foreign fathead, white leaf, white fath
Features:The nostrils are high, above the front edge of the eye. The eyes are small and located below the mid-axis of the head.
Silver carp generally inhabit the upper layer of the main stream of rivers and their affiliated water bodies. They are lively and good at jumping. The newly hatched fry drift with the water; the young fish can actively swim into the river bay or lake to feed. The spawning group begins to gather in m...

Mylopharyngodon piceus
Mylopharyngodon piceus,Black carp,Black mackerel, blue carp, black carp, stream fish, black fish, black fish, snail fish, black fin
Features:The body is stout and nearly cylindrical, with a round abdomen and no abdominal ridges. The head is medium-sized and the back is wide.
The black carp is not as active as the grass carp, but it is much stronger than the grass carp. Black carp is a carnivorous fish. Its main food source is mollusks at the bottom of the water, especially snail meat, so it is also called snail green. Black carp also eats clams, mussels, shrimps, dragon...

