Introduction
The frilled shark (Chlamydoselachus anguineus) is a unique and intriguing species that captures the imagination of marine enthusiasts and scientists alike. Known for its ancient lineage and distinct appearance, this deep-sea predator is often referred to as a "living fossil." In this article, we’ll explore the frilled shark’s habitat, physical characteristics, diet, reproduction, and conservation status.
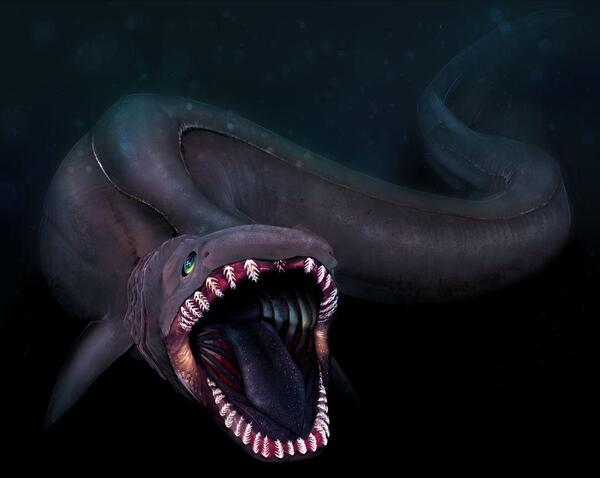

Habitat and Distribution
Frilled sharks are typically found in deep waters, often at depths of 200 to 1,500 feet (60 to 460 meters). They prefer continental slopes and deep oceanic regions, where they can easily hunt for prey. Their range extends across the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, with sightings reported near Japan, New Zealand, and the eastern coast of the United States.
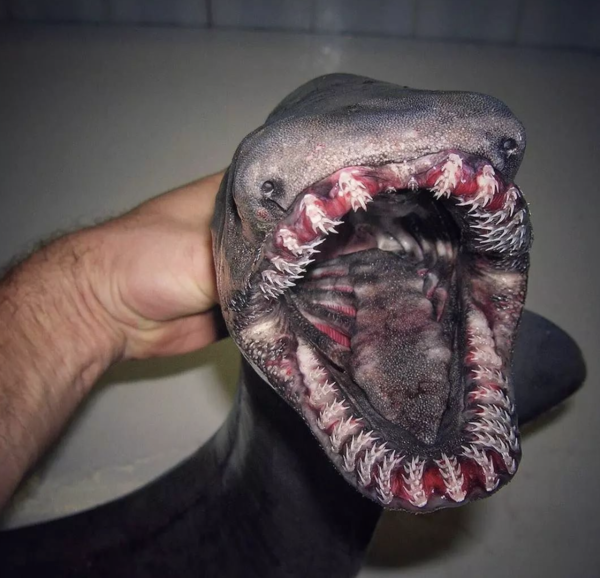
Physical Characteristics
One of the most striking features of the frilled shark is its elongated, eel-like body, which can grow up to 6.5 feet (2 meters) in length. The shark gets its name from the unique frilled appearance of its gills, which are made up of several fleshy flaps. These gills give the shark a distinctive look that sets it apart from other shark species.
Frilled sharks have a mouth filled with 300 needle-like teeth arranged in 25 rows. This specialized dental structure allows them to grasp slippery prey like squid and small fish effectively. Their dark, brownish-gray coloration helps them blend into the deep-sea environment, providing camouflage against predators and prey alike.
Diet and Hunting Behavior
As carnivorous predators, frilled sharks primarily feed on squid, fish, and other small marine creatures. They are known for their unique hunting technique: they can bend their bodies into a U-shape, allowing them to ambush prey from various angles. With their sharp teeth, they can quickly grab and consume their catch, often swallowing prey whole.

Reproduction
Frilled sharks have a fascinating reproductive process. They are ovoviviparous, meaning that the eggs develop inside the female's body, and the young are born live. After a gestation period of approximately 3.5 years, the female gives birth to about 2 to 15 pups, each measuring around 12 to 14 inches (30 to 35 cm) in length. This long gestation period is one of the longest in the animal kingdom, which can impact population recovery rates.
Conservation Status
Currently, frilled sharks are not considered endangered, but they face threats from deep-sea fishing practices, habitat destruction, and climate change. As bycatch in commercial fisheries, they are often unintentionally caught and discarded. Protecting their deep-sea habitats is crucial for their survival, and ongoing research is necessary to understand their populations better.

The frilled shark is a remarkable example of how diverse and resilient life can be in the ocean’s depths. With its unique physical traits and fascinating behaviors, it offers insight into the evolutionary history of sharks. As we continue to explore and study these mysterious creatures, it’s essential to prioritize their conservation to ensure they remain a part of our planet’s rich marine biodiversity. Whether you’re a marine enthusiast or just learning about ocean life, the frilled shark is a captivating species worth knowing more about!












