Recently, the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that the research team discovered the first armored fish fossil with a completely preserved tail fin in a special buried biota of ancient fish from the Early Devonian in Guangxi. The fossil is an armored fish about 10 centimeters long. A small armored fish, the body and head armor are about 5 centimeters in length. The whole body is covered with tiny diamond-shaped scales, and the scales are arranged in regular, oblique rows. In addition to the typical characteristics of Duyunidae, the edge of the head carapace has small jagged spines and the number of gill sacs is more than 25. It can be clearly distinguished from other genera and species of Duyunidae, so it represents the Duyunidae. A new genus of the species - Nine-tailed Fox Turtle, its name is taken from the most legendary ancient mythical beast "Nine-tailed Fox" in "The Classic of Mountains and Seas".
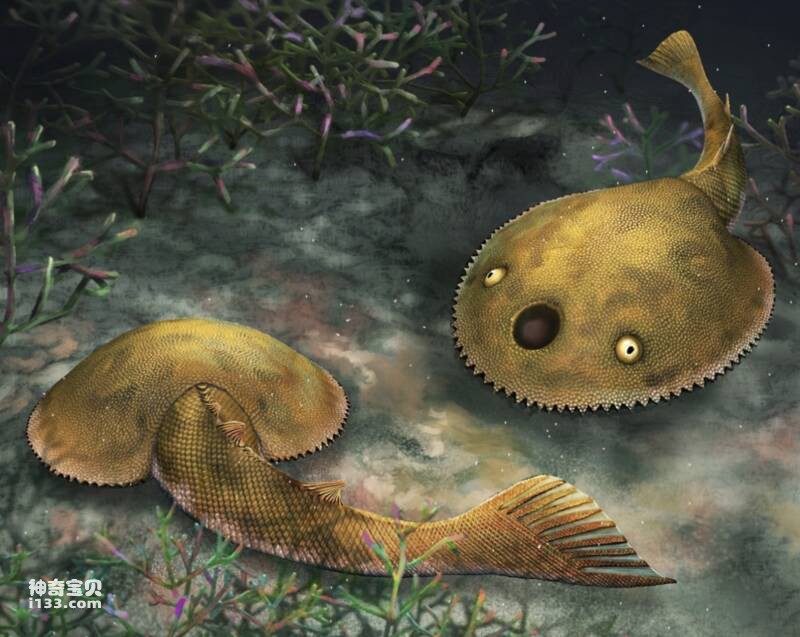

Figure 1 Ecological restoration map of the nine-tailed fox turtle
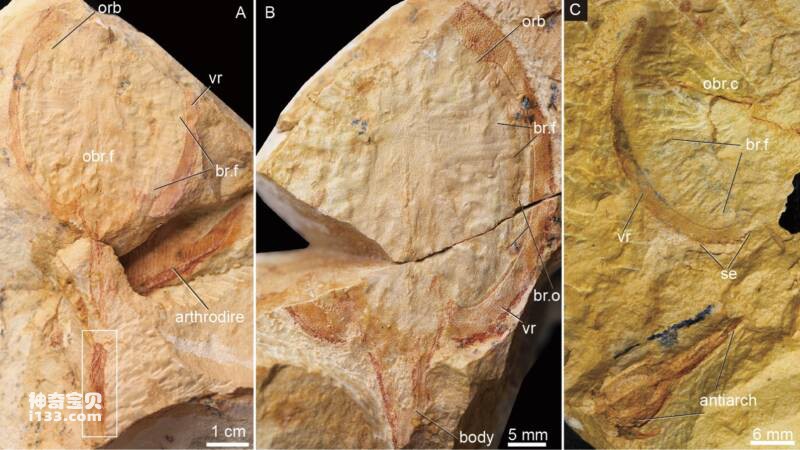
Figure 2 Photos of the nine-tailed fox turtle and its specially preserved placoderm fossil specimen

Figure 3 The description of the nine-tailed fox and the human-faced fish in the Classic of Mountains and Seas
1. The legend of the nine-tailed fox turtle and the Classic of Mountains and Seas
This time, the research team named the newly discovered new genus and species of armored fish "Nine-tailed Fox Turtle". On the one hand, it can let the world know more about traditional Chinese culture, and on the other hand, it also indicates that its tail fin has the typical lower and crooked tail. In addition, it also has nine finger-like forks, which are similar to the tail of the legendary "nine-tailed fox". The nine-tailed fox turtle belongs to the subclass Polybrachiales, order Duyunidae, in the systematic classification.
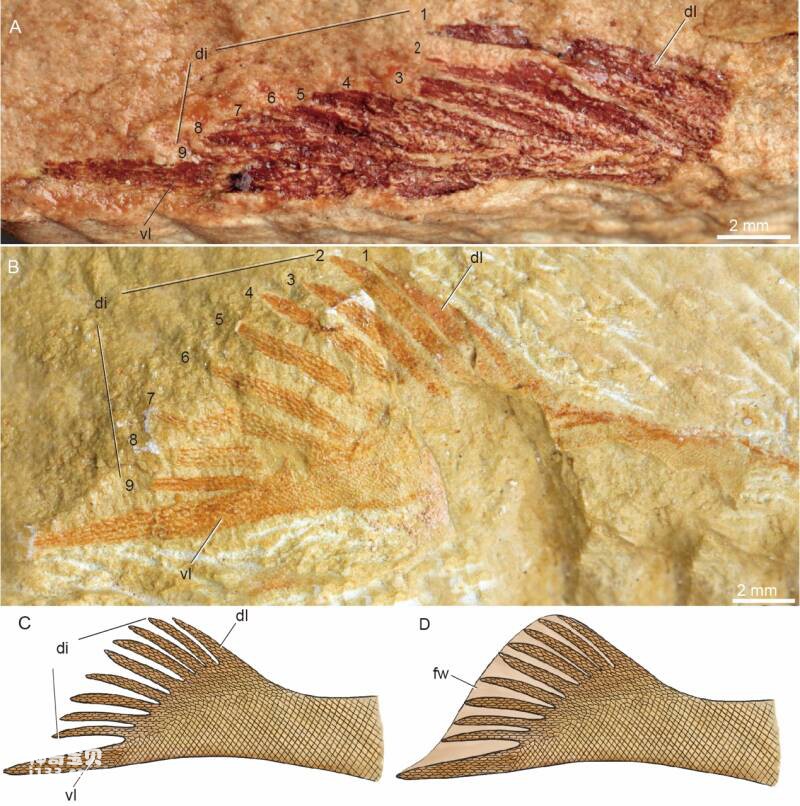
Figure 4 The uniquely preserved "nine-fingered forked" tail fin of the nine-tailed fox turtle
2. The humble swimming master
Swimming ability is crucial to the survival of fish. It is an important means for fish to escape predators, predation, migration, courtship, and avoid disaster environments. Swimming speed is an important indicator for evaluating the swimming ability of fish, which can reflect the activity index and metabolic level.
Studies have shown that in addition to the typical lower crooked tail of armored fish, the tail fin also has nine finger-like forks. It is a primitive forked tail covered with neatly arranged scaly fin rays, indicating that there are strong muscles under the fin rays. of radial muscle attachment. The nine finger-like branches of the nine-tailed fox turtle fossil discovered this time preserve two different states of relaxation and contraction, which indicates that the armored fish may be a flexible swimmer and can make good use of muscle contraction to control the tail fin and tail fin. The contact area of the water flow produces different driving forces. Its cruising swimming speed is even faster than that of some more advanced jawed fishes.
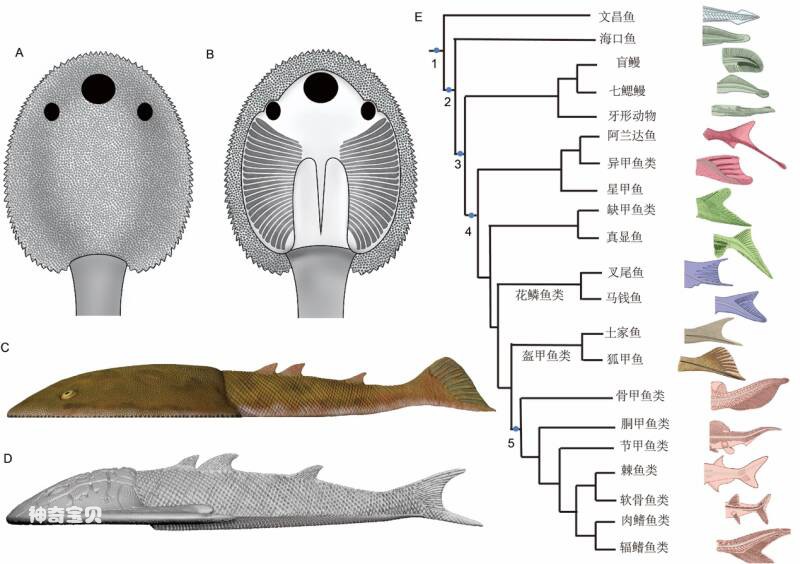
Figure 5 The restoration of the Nine-tailed Fox Turtle and the Smart Tujia Fish and the evolutionary significance of their tail fins
3. The evolutionary significance of the armored fish tail
China’s armored fish has a history of discovery of 110 years! But the research is half a century later than in the West. In 2022, the research team reported for the first time the world's first armored fish fossil with a complete body preservation discovered in the "Chongqing Special Buried Fossil Library" - the smart Tujia fish! However, the details of the caudal fin were not preserved, becoming the last missing piece of the puzzle to solve the puzzle of body anatomy behind the head of the armored fish. This time, the research team discovered the first armored fish with a uniquely preserved tail fin in Guangxi, the nine-tailed fox turtle, which just made up for the incomplete preservation of the tail fin of the smart Tujia fish in the Chongqing biota, thus gathering a solution to the problem of armored fish All puzzle pieces of post-cephalic body anatomy puzzle!
Systematic research shows that the lower crooked tail of armored fishes may represent the primitive characteristics of vertebrate animals. The lower crooked tail may have appeared as early as in Kunming fish and Haikou fish in the Cambrian period, and in the extant cyclostomes. , the early conodonts, heteroturstids, gnatfishes, and scaly fishes all maintained this original feature, but the true upwardly crooked tail only really appeared in bony turtles and gnathostomes. Therefore, armored fishes are the closest relatives to jawed fish that are currently known to retain the original characteristic of a crooked tail. The scaly rays of the caudal fin were once considered to be an advanced feature of bony fishes, but their widespread occurrence in armored fishes indicates that their origin is much earlier than originally thought, possibly before the origin of jaws. Appear!
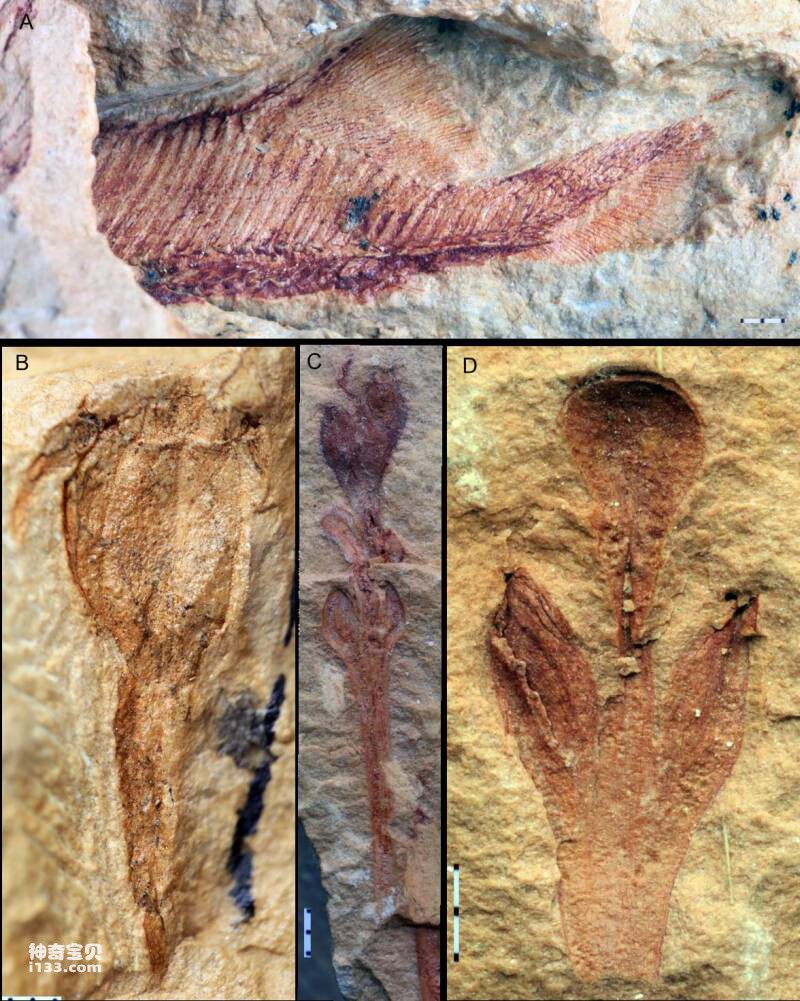
Figure 6 Ancient fish and plant fossils buried together with the nine-tailed fox turtle
4. Asia’s first unique buried biota of Devonian ancient fishes
The nine-tailed fox turtle fossil in this study comes from a very important ancient fish-specific buried biota discovered by the research team in Guangxi - the Guangxi Biota. The Guangxi biota is the first buried biota of ancient Devonian fish discovered in my country. It is roughly distributed in central and eastern Guangxi, and contains a rich variety of armored fish, placoderms, and other jawed fish. species, as well as other invertebrates such as brachiopods, as well as a rich group of early plant fossils represented by ferns and lycopods. They have high ecological diversity and unique species, and are of great significance to our study of the early co-evolution of animals and terrestrial plants. , the landing and development of plants and the great radiation and development of early vertebrates in the Early Devonian are of great significance.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.