The Sanjiangyuan area of Qinghai is located in the southeastern part of the Qinghai Plateau. It has a special geographical location and a unique ecological environment. It has always been regarded as a hotspot for plateau biodiversity. It is home to snow leopards, rabbit cats, Tibetan foxes, blue sheep, alpine It is an important habitat for vultures and other rare animals, among which the snow leopard is the most famous. The diversity of amphibians and reptiles in the Sanjiangyuan area is very low due to reasons such as high altitude, high intensity of ultraviolet radiation, and low temperature.
From 2016 to 2017, the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with Shenyang Normal University and other units, conducted an investigation on the diversity of amphibians and reptiles in the Sanjiangyuan region of Qinghai Province. A plateau viper was discovered in the Tongtian River Basin. According to traditional Through multiple methods such as morphological comparison, skull CT three-dimensional reconstruction and molecular phylogeny, we discovered a new species of viper that has not been described before, and named it "Gloydius rubromaculatus Shi" based on its unique morphological characteristics. Li and Liu, 2017". The research was published in Amphibia-Reptilia, Issue 4, 2017, the journal of the European Society of Amphibians and Reptiles (SEH).
Vipers have cheek pits to detect infrared rays radiated from the surface of small warm-blooded animals. However, this study found in field observations that the red-spotted alpine viper feeds on moth insects (Sideridis sp.), which is It is relatively rare in the genus Asiatic vipers and in the entire suborder of snakes.
The discovery and report of a new species of red-spotted alpine viper has added an important record to the diversity of Chinese vipers and reptiles in the world. It has revised the classification system of Asian vipers to a certain extent. It also provides insights into the plateau environment of reptiles. laid a certain foundation for adaptation research.
CT three-dimensional reconstruction technology has brought great convenience to the study of bone morphology of fossils and living animals without damaging the bones. The 225micro CT currently used in the Institute of Paleovertebral Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences was developed by the Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, with a maximum resolution of 5 microns. The traditional observation and research methods of skeletal anatomy of living animals have great limitations and cause great damage to specimens. CT three-dimensional reconstruction can clearly show the internal bone structure of the specimen without damaging the specimen.
Original link http://booksandjournals.brillonline.com/content/journals/10.1163/15685381-00003134


Figure 1 New species of red-spotted alpine viper (Photo by Shi Jingshu)
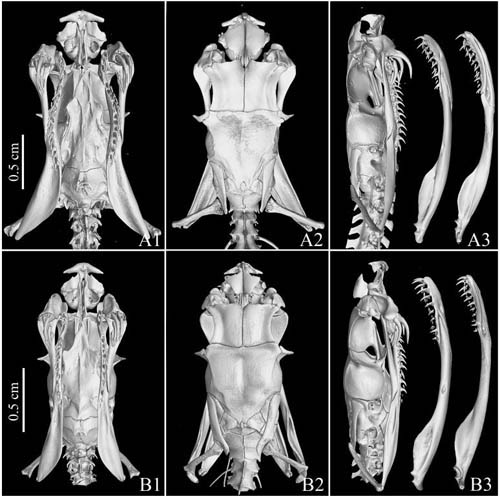
Figure 2 Three-dimensional CT reconstruction model of the skull of a new species of red-spotted alpine viper (photo courtesy of Hou Yemao)
animal tags: vipers amphibians reptiles fossils
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.