The Ice Age, or Pleistocene Epoch, was a period that lasted from about 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago. It was characterized by repeated glaciations and freezing temperatures, which created unique and challenging environments for the animals that lived during this time. From massive megafauna like the woolly mammoth to smaller creatures like rodents and amphibians, many animals developed extraordinary adaptations to survive the cold. This article explores the diverse range of Ice Age animals, their survival strategies, and their fate as the planet warmed.
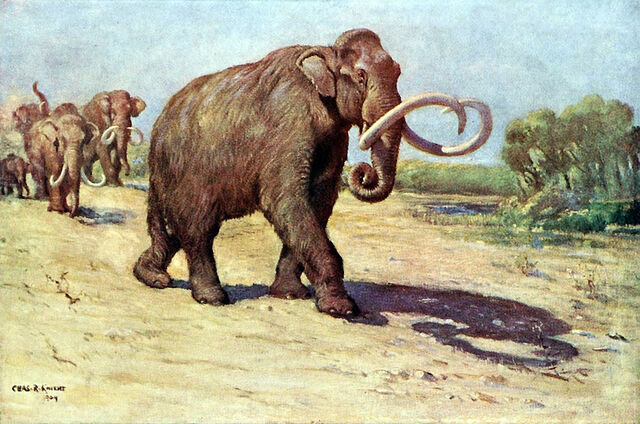
Habitat: Northern Europe, Asia, and North America
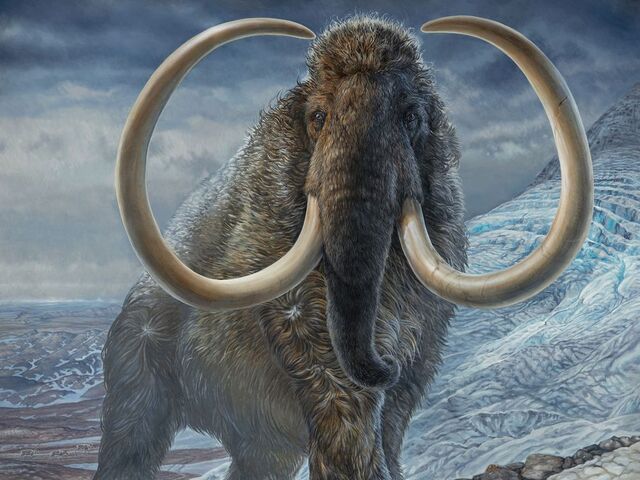
Characteristics: Standing up to 12 feet tall, woolly mammoths were covered in thick fur to insulate them from the freezing cold. Their large tusks helped them dig through snow to find food.
Survival: Woolly mammoths survived the cold by relying on a thick layer of fat and migrating across the tundra in search of food. They became extinct around 4,000 years ago due to climate change and overhunting by humans.

Habitat: North and South America
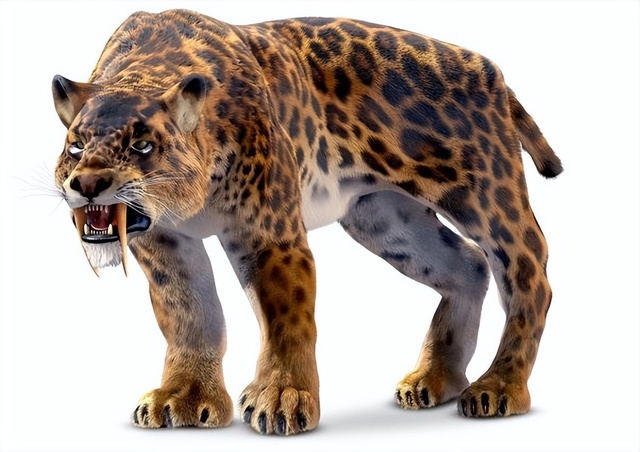
Characteristics: Known for their long, curved canine teeth, saber-toothed cats were muscular predators that hunted large prey like mammoths and bison.
Survival: These cats relied on their powerful build and strong jaws to capture prey. Despite their adaptations, they went extinct about 10,000 years ago, likely due to a combination of the extinction of large prey and changing environments.

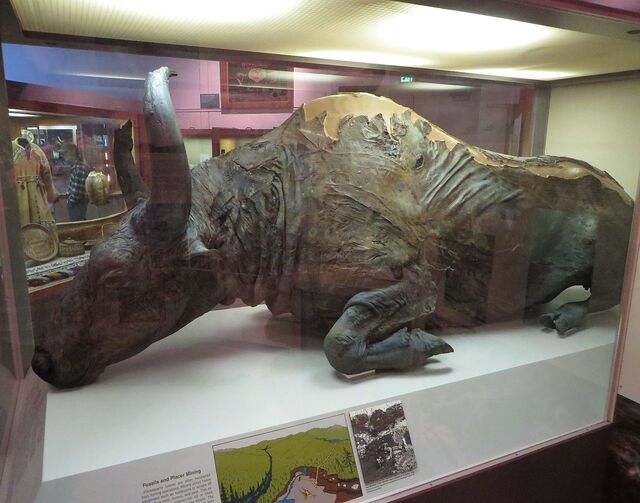
Habitat: Northern Europe and Asia
Characteristics: Similar to the woolly mammoth, the woolly rhinoceros had a thick fur coat and two large horns. It stood about 6 feet tall and weighed up to 3,000 pounds.
Survival: These rhinos lived in cold, grassy areas and used their horns to dig through snow to find food. They became extinct around 10,000 years ago, likely due to warming climates and human activity.

Habitat: South and parts of North America
Characteristics: These enormous herbivores could grow up to 20 feet long and weighed up to 4 tons. They had large claws and tough skin.
Survival: Ground sloths were slow-moving but relied on their size for protection from predators. Despite this, they went extinct around 10,000 years ago, likely due to climate change and human hunting.
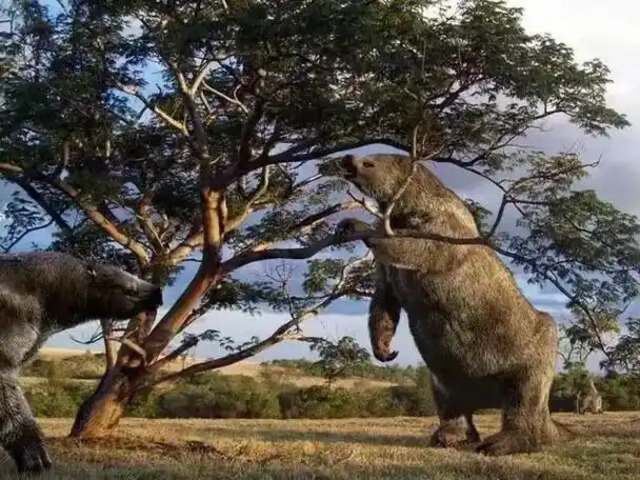

Habitat: North America
Characteristics: Similar in appearance to mammoths but slightly smaller, American mastodons had long, curved tusks and were covered in coarse hair.
Survival: Mastodons were forest dwellers that fed on leaves and shrubs. They became extinct about 10,000 years ago due to a combination of climate change and human hunting.

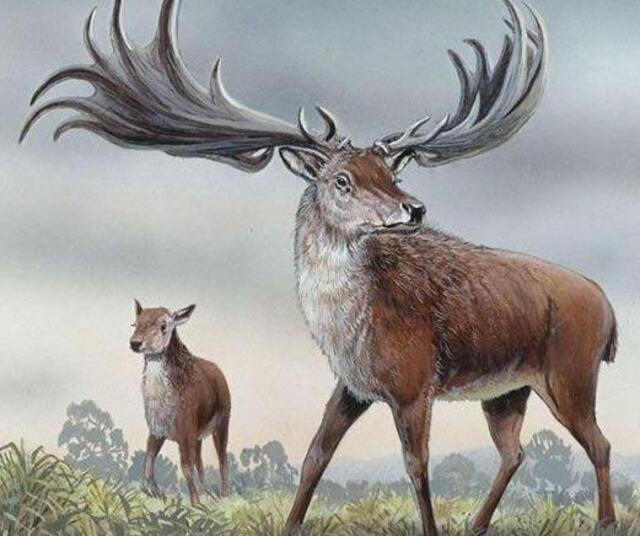
Habitat: Europe and Asia
Characteristics: This enormous deer species had antlers spanning up to 12 feet across and stood about 7 feet tall at the shoulder.
Survival: The Irish elk thrived in open grasslands, feeding on grasses and shrubs. It became extinct around 7,700 years ago due to habitat loss and competition as forests replaced grasslands.

Habitat: North and South America
Characteristics: Larger and more robust than modern wolves, dire wolves had powerful jaws designed for hunting large prey like bison and horses.
Survival: Dire wolves lived in packs and hunted large animals. They went extinct around 10,000 years ago, likely due to the disappearance of large prey and competition with smaller, more agile wolves.
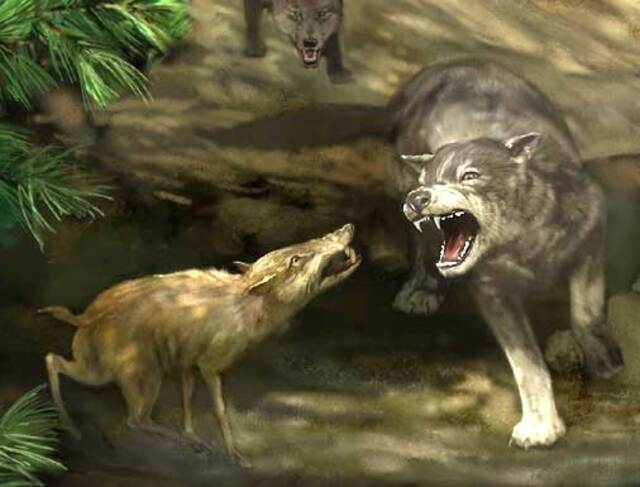

Habitat: North America, Europe, and Asia
Survival: The steppe bison roamed in large herds and survived on cold-tolerant grasses. They were well-insulated with thick fur and fat, and their herds provided protection from predators. Some bison species survived the Ice Age and evolved into modern-day bison.

Habitat: North America
Survival: This larger relative of the woolly mammoth lived in temperate climates and fed on a wide range of vegetation. It went extinct around the same time as the woolly mammoth, likely due to climate change and human hunting.
Habitat: North America
Survival: The short-faced bear, one of the largest terrestrial carnivores, hunted large prey and scavenged carrion. It went extinct around 11,000 years ago, probably due to competition and the disappearance of large prey.

Habitat: South America
Survival: These flightless birds stood up to 10 feet tall and were fast, efficient predators. They went extinct due to competition with other predators and environmental changes.

Habitat: North and South America
Survival: Large scavengers like Ice Age condors fed on megafauna carcasses. As large animals disappeared, so did these birds, although species like the California condor survived.


Habitat: Southern regions of North America, Africa, and Asia
Survival: These ancient reptiles survived the Ice Age by migrating to warmer areas and slowing their metabolism in colder environments. Their thick, armored bodies helped protect them from predators.

Habitat: Oceans worldwide
Survival: Species like the bowhead whale adapted to cold waters by developing thick layers of blubber. They survived by migrating to warmer waters and feeding on the abundant marine life in cold oceans.

Habitat: Cold coastal regions
Survival: Seals and sea lions had thick layers of blubber to protect against the cold. They thrived in the icy waters, foraging for fish and aquarium/52-marine-animals.html">marine animals. Many species from the Ice Age still exist today.


Habitat: North America and Eurasia
Survival: Rodents like marmots and groundhogs survived by burrowing underground and hibernating during the winter. They adapted to cold environments and are ancestors of modern species.

Habitat: Freshwater rivers and oceans
Survival: Fish like salmon and sturgeon adapted to cold environments by migrating through rivers and streams. These species were important food sources for humans and other Ice Age animals.

The Ice Age was a time of dramatic environmental change, and only the most adaptable species survived. While many iconic animals like the woolly mammoth and saber-toothed cat became extinct, some species, like bison, alligators, and condors, evolved and still live today. Understanding how these animals adapted to the challenges of the Ice Age helps us learn more about evolution, survival, and the impact of climate change on ecosystems.
animal tags: Rodent Seal Sea-Lion Whale Alligator Crocodile Large-Condor Raptor Irish-Elk Woolly-Mammoth
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.
you may also like

Lizards: A unique role in wildlifeLizards are a very unique and diverse wildlife in nature. As a member of the reptile family, lizards not only play a role in the ecosystem This article will take a closer look at the basic characteristics of lizards, their habitats, and their importance in the ecosy...

Jellyfish are an ancient aquatic creature found in all oceans and freshwaters around the world. They have attracted much attention for their unique appearance and simple physiological structure. The following is detailed information and living habits of jellyfish: Appeara...

Pig is a common mammal, belonging to the Suidae family (Suidae) of the order Artiodactyla, and is mainly distributed around the world. The following is a detailed introduction to pigs and their living habits: 1. Appearance characteristics:...

Crickets belong to the phylum Arthropoda, class Insecta, order Orthoptera, and family Gryllidae. Closely related to grasshoppers, crickets have hind legs adapted for jumping, though they are less agile.Here are 10 different types of crickets, along with their features and habitats:Fall Field Cricket...

What animals live in the tundra? Explore the biodiversity in the tundra ecosystemTundra is one of the most extreme ecosystems on Earth, usually located in high latitudes or high altitudes near the Arctic and Antarctic circles. The cold, dry environment, short growing season, and the presence of perm...

The egret is a common large wading bird belonging to the family Heronidae. They are commonly found in wetlands and coastal areas around the world. Here are detailed information about egrets and their living habits: Appearance features Body size: Egrets are relat...

Which animals Sleep the most? Revealing the world's most sleep-loving animalsIntroductionIn nature, sleep is essential for animals. It not only helps them recover their physical strength, but also enhances immunity and consolidates However, different animals have different sleeping habits. Some...
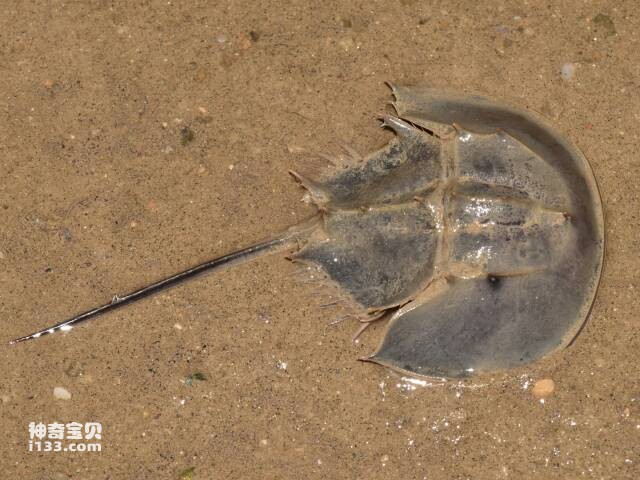

Look at this strange animal, it looks like a scoop. Do you know what kind of animal it is? Let me tell you! It is the famous horseshoe crab!The horseshoe crab is an animal that once lived in the same era as the dinosaurs. However, the huge dinosaurs did not escape the catastrophe at the end of the C...
Email: jsset668#gmail.com (change # to @) Please indicate your purpose of visit! Guangdong ICP No. 2022053326 XML| map| Chinese

