Most conchovertebrates are small amphibians, adapted to life in shallow water and swamps. They first appeared in the Early Carboniferous Epoch and became extinct at the end of the Paleozoic Era, never flourishing. They are generally divided into three orders: Salamanders, Salamanders, and Amphipods.
Salamander
The order Salamanders are small primitive amphibians that are suitable for living underground or in swamps near water, while the order Amphipods are specialized into small, slender, snake-like amphibians without limbs.
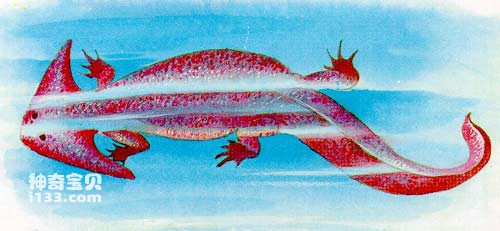
The order Newts is the most diverse family in terms of number, type, and morphology among the shell vertebrae. They began to evolve in two directions in the late Carboniferous period. One branch evolved into a slender eel-like or snake-like amphibian; the other branch developed into a flat and wide body and skull, such as the famous Permian The skull salamander is named because the bones on the sides and roof of the skull grow extremely sideways, so that the back of the skull seems to grow triangular "horns" on both sides, and the entire skull is shaped like a hat. It is called "笠头 Salamander".
The body of the newt is also flat, and the limb bones are small and weak. Obviously, this animal is likely to be a benthic amphibian and may spend most of its time at the bottom of streams or ponds.
animal tags: Salamanders amphipods
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.