At the beginning of the 20th century, the German scientist Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift based on the outlines of the continents on the earth as well as stratigraphic and paleontological data. He believed that during the long period from the end of the Carboniferous to the Triassic, At least the continental blocks of Africa, South America, Australia, Antarctica, and the Indian subcontinent, now mainly located in the southern hemisphere, were once a single entity. He called this massive continent Gondwana. Beginning in the Jurassic, the ancient continent Gondwana disintegrated and gradually drifted, eventually reaching its current location.
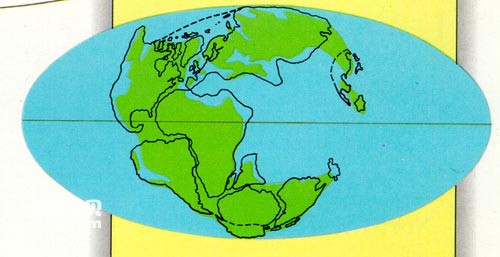
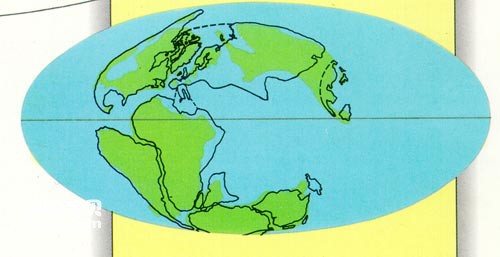
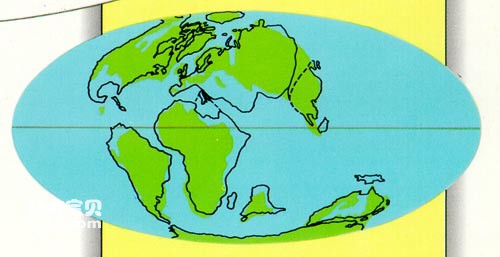
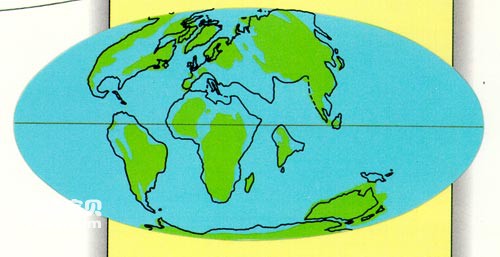
continental drift
In the 1960s, due to the progress of marine geology and seabed geophysical research, the concepts of seafloor spreading and crustal subsidence emerged. Finally, French scientist Lepichon, American scientist Morgan and British scientist Mackenzie jointly proposed it in the late 1960s. The theory of plate tectonics. The development of this theory has not only made continental drift almost an indisputable fact, but also proposed a series of explanations for the driving force of plate tectonic movements that caused its drift. Many difficult problems in earth science have been "solved", and at the same time, various disciplines continue to confirm and supplement it, including paleontology.
water dragon
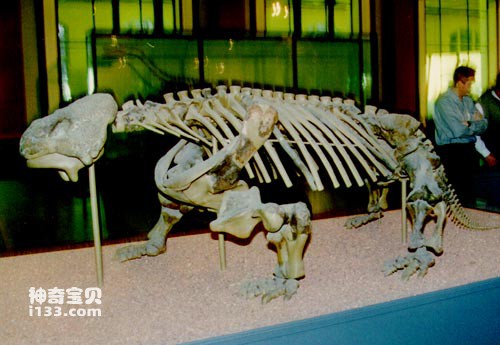
Among the dicynodonts, Lystrosaurus is the most famous paleontological fossil that serves as one of the evidences for the theory of continental drift. Lystrosaurus is a mammal-like reptile (meaning a reptile similar to a mammal) about 1 meter in length. Its fossils have been found in Antarctica, South Africa, India and China.
The discovery of the same paleontological fossils on different continents once greatly aroused the enthusiasm of scientists who supported the continental drift theory at the time. Since the 1950s, new fossil evidence has been discovered one after another, and relevant reports have followed one after another.
Zhonglong
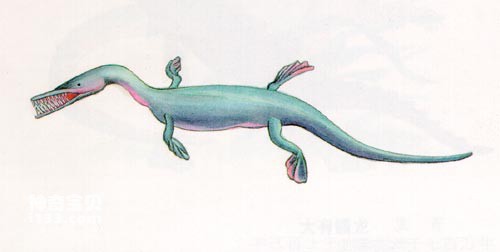
An aquatic reptile called Mesosaurus was found in South Africa and eastern South America. At that time, scientists believed that this small reptile lived in freshwater waters and could not swim across the vast ocean to migrate between South Africa and South America. Or spread, so it is considered to be strong evidence of continental drift.
Scientists believe that the Triassic period from 230 million to 195 million years ago was an important period of continental drift, so they have put a lot of effort into tracking the paleontological fossils of this period. From the 1950s to the 1970s, in addition to the discovery of early Triassic hydrosaurus fossils in Antarctica, South Africa, India, and China's Xinjiang, other fossils were also discovered in Arizona, USA, in North America. Many similarities have been found between the Crestorsuchus and Protosuchus in the late Triassic of the state and the False Crestedsuchus and Semiprosuchus in Argentina in South America. In addition, scientists have also discovered fossils of a type of reptile from the late Triassic period, the spadelepid, in the United States, Scotland, Germany, India and Argentina.
Oriental Leptodont
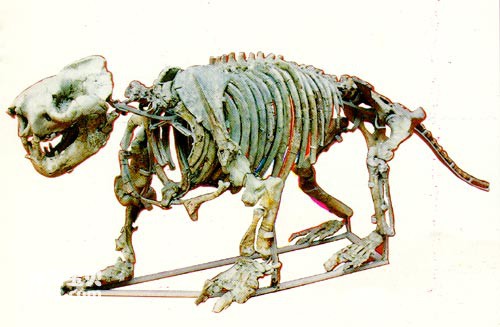
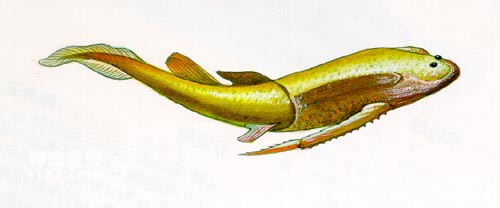
The evidence found in our country is not just about water dragons. The discovery of Lepidodontus orientalis in the Nanxiong Basin in Guangdong Province has greatly shaken the past paleontologists' belief that "just as marsupials are the symbol of modern Australia, Leptodontus is the symbol of the ancient South American continent." This A conclusion. Based on this, some scientists believe that the Nanxiong Basin in Guangdong, my country, was once part of the South American continent, and later drifted thousands of miles to the south of my country and was spliced with the ancient continent here. Other evidence also includes the discovery of a primitive fish in the early Devonian strata of the Hengduan Mountains in Antarctica, the slug-scale fish. It not only often appears in the strata of the same period in South my country, but is also found in the far north. Jingyuan area, Gansu Province.
groove scale fish
Among fossil plants, the primitive gymnosperm Glossopterus is a "world-famous" molecule that supports continental drift. The plant was once widespread in Australia, southern South America, the Malvinas Islands, Antarctica, south-central Africa, and India, areas that are now widely separated from each other. As a gymnosperm, the seeds of Glossopterus cannot be quickly dispersed by wind or sea currents; during the Permian period (280 million to 230 million years ago) when it lived, birds still It has not evolved, so it is impossible to be a carrier of the seeds of this type of plant across the ocean for long-distance dispersal.
In terms of invertebrates, some scientists found after analysis that among the early Cretaceous freshwater ostracods that survived in the coastal basin of Brazil, 20 species were exactly the same as 20 species of the same period in the coastal basin of Gabon, Africa. In the Permian strata of the Ohio Mountains in Antarctica, fossils of the famous "Bossian leaf limbs" and a large-winged insect that were once distributed in Australia, South America and Africa were also discovered. In the Cambrian strata of the Hengduan Mountains in Antarctica, 11 genera of trilobites identical to those in my country were also discovered. These discoveries have become evidence of continental drift.
Of course, the continental drift theory and the plate theory are not perfect. Some scientists in the field of paleontology have used other evidence to express doubts or even refute them. This is the normal process of scientific development.
animal tags: mesosaurus
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.