Humanity's understanding of its own development history began with modern Homo sapiens, then early Homo sapiens, and then Homo erectus, and finally determined the status of Homo habilis and Australopithecus ape as human ancestors.
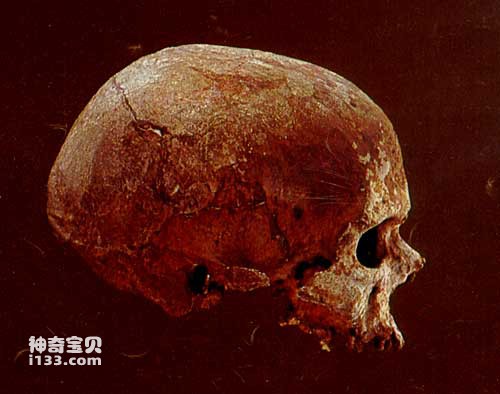
Cro-Magnon
This understanding process began in the mid-19th century. As Darwin's theory of evolution was gradually recognized and accepted, anthropologists began the arduous work of searching for human beings' own ancestors. This work, of course, started in Europe, which was considered by Westerners to be the cradle of mankind because of its technological leadership at that time. However, until the 20th century, except for some late-stage Homo sapiens (such as Cro-Magnon) who lived very recently, most of the human fossils discovered in Europe were from 200,000 to 40,000 years ago. The former Neanderthals (referred to as Neanderthals, belonging to early Homo sapiens).
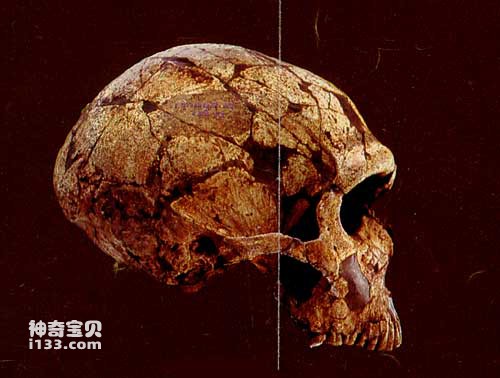
neanderthal
In 1848, some ancient human fossils were discovered in Gibraltar, in the southwest corner of Europe. The ancient humans represented by these fossils were the first to be discovered and later called Neanderthals (Neanderthals for short). However, But it didn't attract people's attention at the time. The name Neanderthal comes from the Neandertal Valley near Dusseldorf, Germany. In August 1856, fossils of an adult male's skull and some limb bones were discovered in a cave here. Named Neanderthal. After that, Nepalese fossils began to be discovered in large numbers in a vast area stretching from Spain and France in the west, to northern Iran and Uzbekistan in the east, to Palestine in the south, and to the 53rd parallel in the north. The Nigerian people lived between 200,000 and 37,000 years ago.
The brain volume of Nepalese people has reached 1300 to 1700 ml; compared with Homo erectus, the skull is smoother and rounded and the thickness of the skull is reduced; the face (from the brow ridge down to the lower dentition) protrudes forward to the same extent as Homo erectus. resemblance. The nasal bones of European Neanderthals are abnormally protruding, indicating that their noses must be very high; however, because they have large teeth and upper jaws, it is speculated that their noses cannot have a narrow nasal cavity like modern Europeans, but have a vertebral cavity. The nasal cavity is greatly enlarged anteriorly. In other words, they had a large nose that was as tall as modern Europeans and as wide as modern Africans; moreover, the nostrils may have been pointed further forward.

funeral
The Nepalese created a stone tool industry known as the Most culture, represented by small pointed tools and scrapers. The climate in Europe at that time was cold, and the Nepalese were able to use fire and were already able to make fire. The Nigerians also began to have the custom of burying their dead.
In addition to Neanderthals, some early Homo sapiens fossils with both primitive traits of Homo erectus and advanced traits of Homo sapiens have also been discovered in Europe. They include the Petralona man in Greece (the age may be 160,000 to 160,000 years ago). 240,000 years ago, but there is debate) and the Totaville man in southwestern France (also called Arago man, about 200,000 years ago). Some scholars regard them as a transitional type between Homo erectus and early Homo sapiens. In addition, the Steinheimer Man who dates back to 200,000 to 300,000 years ago was found in Germany, and the Swanscombe Man who dates back to about 250,000 years ago was found in the UK. The skull features of the two are very similar, and their shapes appear to be more similar. The Nigerians are progressive, but their era is earlier than that of the Nigerians. Therefore, some scholars call them "Progressive Neanderthals" or "Pre-Nepalese" and believe that they are the ancestors of the later late Homo sapiens; while other later Neanderthals are called "typical Neanderthals", who were born between They became extinct 33,000 years ago or were replaced by late Homo sapiens.
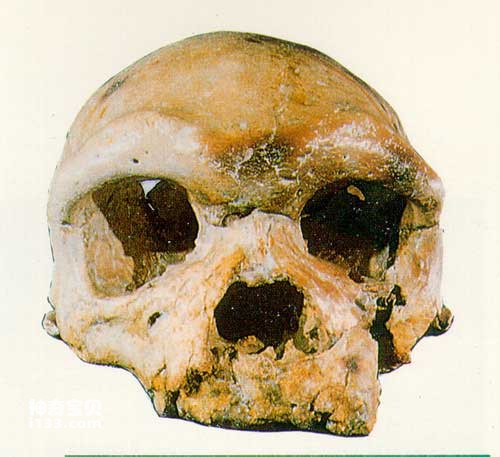
Dali people
In Africa, early Homo sapiens include the Bodo people found in Ethiopia, who are considered to be transitional types (about 200,000 to 300,000 years ago), and the Broken Hill Homo found in Zambia (about 130,000 years ago). before).

Taurus Mountain Man
Fossils of early Homo sapiens in China were all discovered after 1949. The materials mainly include Dali Man (discovered in Dali County, Shaanxi Province), Jinniushan Man (discovered in Yingkou County, Liaoning Province), and Xujiayao Man in the northern area. (found in Yanggao County, Shanxi Province), Dingcun people (found in Xiangfen County, Shanxi Province), and the Maba people (found in Qujiang County, Guangdong Province), Yinshan people (found in Chaohu City, Anhui Province), Changyang people (found in Changyang County, Hubei Province) and Tongzi people (found in Tongzi County, Guizhou Province).
Early Homo sapiens in other parts of Asia also include the Ondon Homo (also called Solo Homo) found along the Solo River in Indonesia. Their morphology shows some transitional conditions from Homo erectus to early Homo sapiens.
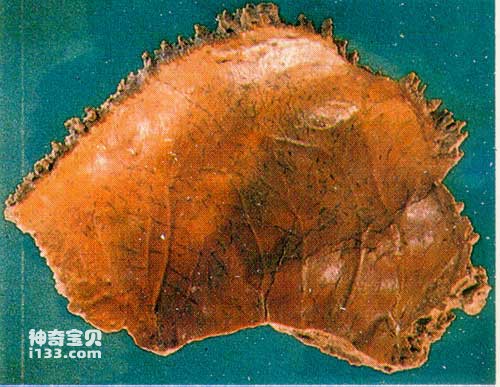
Xujiayao people
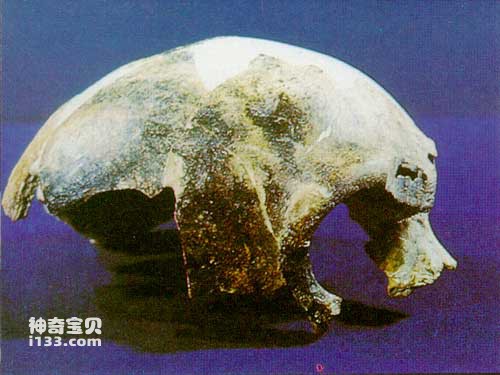
Maba people
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.