Xu Xing's team from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences published their latest results on the evolution of sauropod dinosaurs in the British journal Nature Communications on July 24, reporting a species from the early Middle Jurassic in China. The discovery of a new genus of diplodocoids called Lingwulong shenqi (174 million years ago) challenges traditional views on the origin and spread of diplodocoids and other new sauropods.
Sauropods are a group of herbivorous dinosaurs that include the largest land animals in Earth's history. It has long been thought that neosauropods - a late-stage branch of sauropods - diverged during the breakup of Pangea, which profoundly affected their evolution. East Asia is thought to have been isolated from other continents about 164-158 million years ago. Traditionally, it is believed that some animal groups, including diplodocides, had not yet spread to East Asia before it was isolated from other continents, and their isolation led to the development of mid-late dwarfism. The East Asian region formed its unique dinosaur fauna, which is known as the East Asian isolation hypothesis. New discoveries show that diplodocoid dinosaurs were once widely distributed in Pangea, including East Asia. The fauna of East Asia in the Middle and Late Jurassic may not be as unique as we thought. Past understanding is likely due to fossil sampling. Impact (i.e., due to geological and anthropogenic factors, there are differences between the biota inferred based on collected fossils and the real biota during geological history), which highlights the importance of more field work.
Through evolutionary and biogeographic analysis of the amazing Lingwuosaurus, researchers believe that during the Middle Jurassic (about 174 million to 164 million years ago), new sauropod dinosaurs had become diversified and widely distributed, which challenges The traditional view of sauropod evolution is that new sauropods appeared and rapidly differentiated in a short period of time from the late Middle Jurassic to the early Late Jurassic, and eventually occupied a dominant position in the earth's terrestrial ecosystem. New findings suggest that major sauropod subgroups may have originated in the Early Jurassic and had a long evolutionary history before becoming dominant groups in Earth's terrestrial ecosystems.
The miraculous Lingwuosaurus fossil was first discovered in 2004 by a villager named Ma Yun in Ciyaopu, Lingwu City, Ningxia while herding sheep, and later handed it over to the local cultural management department. In 2005, Yang Guozhu and Liu Hongan from the Cultural Bureau of Lingwu City brought the fossils to the Institute of Paleovertebra of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. After identification by Xu Xing, they were confirmed to be dinosaur bone fossils. Xu Xing then organized several field excavations in the area. Under the leadership of Wang Haijun and others, A total of at least 8-10 individuals of different sizes and representing different age groups have been discovered.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Original link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05128-1
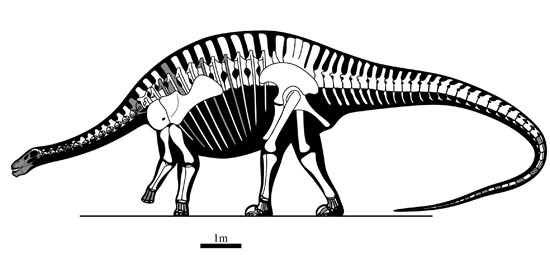
Figure 1 The outline of the magical Lingwulong skeleton, the gray part indicates the preserved skeleton (drawn by Shi Aijuan)

Figure 2 The restoration of the magical Lingwu Dragon (painted by Zhang Zongda)

Figure 3 The miraculous Lingwulong fossil excavation pit (photo provided by Xu Xing)

Figure 4 A large scapula of the magical Lingwulong preserved in situ (Photo provided by Xu Xing)
animal tags: Jurassic diplodocoids dinosaurs Lingwulong sauropods evolution
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.