
The Great long-robed echidna (Zaglossus bartoni) is a species of proto-echidna found in New Guinea, with four subspecies. They curl their bodies to defend themselves when attacked. The hard black hair on the back is covered with thorns like "steel nails", no tail, slow action, although the...

Attenborough's scientific name is Zaglossus attenboroughi, after David Attenborough. Like to dig holes, harm crops, harmful to agriculture, so it is a pest. But that's just from a human point of view, from a biological chain point of view, where moles play an important role. The hair is brow...

The Australian echidna Tachyglossus aculeatus is adapted to an ant-eating lifestyle and lives in rocky, sandy and scrub areas, living in crevasses and self-dug burrows. Come out at dusk and night. Powerful claws for digging. Usually on the ground activities, encounter danger, can quickly dig into th...
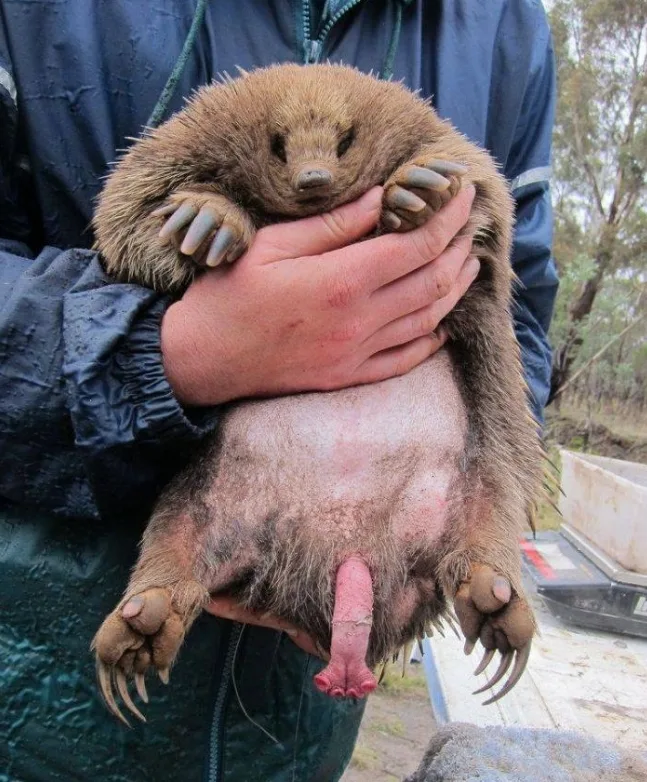

In nature, animals often have amazing diversity and complexity in their reproductive systems. Some animals have unique reproductive organs that not only play a key role in the reproduction process, but also reflect the species' unique adaptations in evolution. Here are ten animals with unique re...
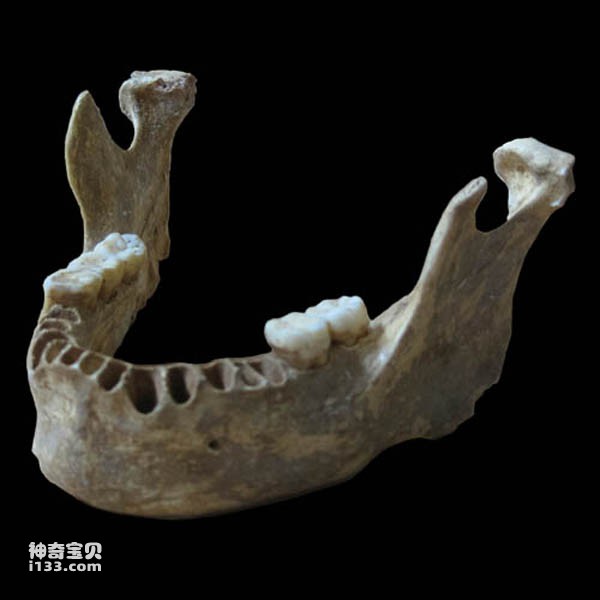
Oase1, a modern human mandible discovered in a cave in Romania in 2002, has a corrected carbon 14 direct dating date of about 37,000-42,000 years ago. It is the earliest early modern mandible in Europe with direct dating. people. Fu Qiaomei, one of the main researchers of the article, pointed...