Soil is the main place for underground pests to live, reproduce and survive. They cause damage to the underground parts of plants, seeds, seedlings and even the main stems near the soil surface in the soil. Common underground pests include grubs, mole crickets, cutworms, wireworms, root maggots, crickets, wheat root stink bugs, etc., which bring considerable damage to the growth and development of crops.

These underground pests are active in the soil, feeding on roots, underground stems, and plant tissues of underground parts, and may cause plant growth stagnation, reduced yields, and even serious death. These pests are of various types and cause serious damage, requiring farmers to take effective prevention and control measures in a timely manner to protect the normal growth and yield of crops. Understanding and preventing these underground pests is crucial for agricultural production.
1. Grubs (worldwide/many underground pests/wide distribution)

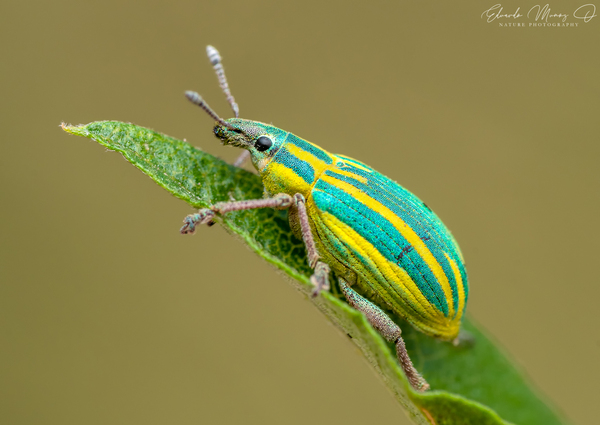
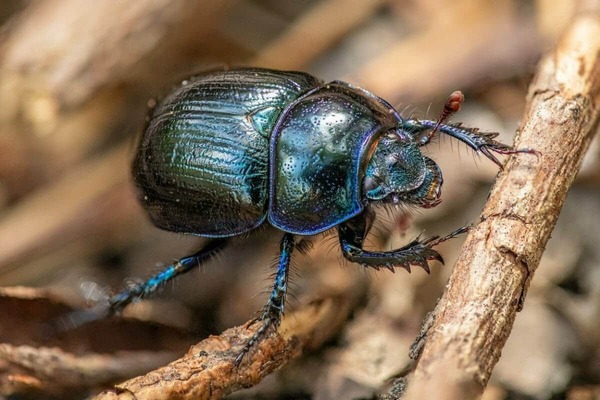
Among underground pests, grubs are the larvae of scarab beetles and are listed as one of the top ten underground pests. These pests are a global problem and are one of the most diverse, widely distributed, most diverse and most harmful groups of underground pests. Their larvae have a huge appetite. A slight infection may lead to missing seedlings or broken ridges, while a severe infection may lead to plant failure. Grubs mainly harm field crops such as millet, sorghum, various wheats, beans, peanuts, beets, cotton, and seeds, seedlings and rhizomes of various vegetables and fruit trees. They will gnaw on seeds or bite off the rhizomes of seedlings. In mild cases, they will cause missing seedlings and broken ridges, which will not only lead to reduced production, but also make it easier to further infect with pathogens.
Among these grubs, the North China black gill beetle, the dark gill beetle and the copper green beetle are the dominant species of underground pests that suffer the most serious damage in my country.
2. Mole crickets (complex diet/damage)

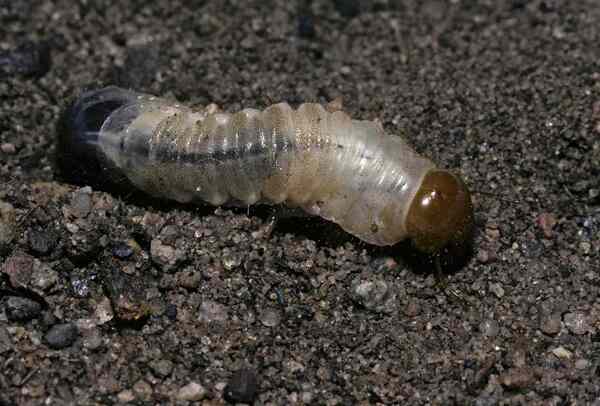
Among underground pests, mole crickets are one of the most troublesome. They are polyphagous pests, widely distributed in China, and are the most active type of underground pests. Both adults and larvae cause serious damage to crops. They like to gnaw on seeds and seedlings of various crops, especially those that have just sprouted, which leads to serious seedling shortages and broken ridges. What is particularly worrying is that mole crickets often move on the surface of the soil, move quickly, and dig tunnels, causing seeds to be hollowed out and seedlings to die of water loss due to root hanging. As people say, "I am not afraid of mole crickets biting, but I am afraid of mole crickets running away", which reveals the serious threat they pose to crops. Especially on grains and wheat crops, once mole crickets are active on a large scale, the losses will be very serious.
3. Cutworms (many species/wide distribution/large number/serious damage)

Among the types of underground pests, the common cutworms in my country undoubtedly occupy a place. These pests are of various species, widely distributed in my country, and in large numbers, causing serious damage. Cutworms are polyphagous insects that harm a wide range of plants, including cotton, various vegetables, tobacco, Chinese medicinal materials, fruit trees, etc., involving a wide range of plants, covering about 100 species. They are one of the main pests of nursery seedlings. Juvenile cutworms mainly move on the aboveground part of plants, feeding on the tender leaves, cotyledons and stems of crops day and night, and may also cause agricultural products to rot. After the third instar, the larvae begin to rest during the day and move at night. Adult larvae may bite off the near-surface part of the seedlings, resulting in missing seedlings, broken ridges, and even the need for re-sowing.
4. Wireworms (larvae harm seedlings and young shoots/cause pathogens to invade)
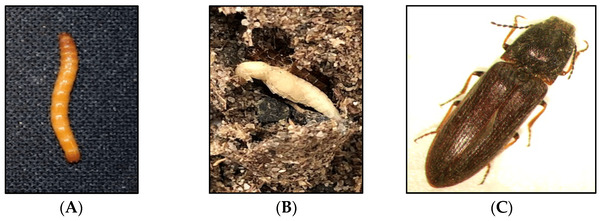
Wireworms, named because of their resemblance to golden needles, are a common pest in the soil. They are the larvae of click beetles, which are widely distributed around the world and pose a serious threat to a variety of crops such as wheat and corn. They are important representatives of underground pests. The adult insects are active for a short time and do not cause much damage when they are active on the surface. The main harm comes from the larvae. The larvae of wireworms mainly feed on the underground parts of plants, including cereals, potatoes, beans, beets, cotton, and seedlings of various vegetables and trees. They will bite seeds, seedlings, roots, including fibrous roots, taproots, and tillering nodes, and can even bore into the rhizomes of grass plants, causing the grass plants to wither and die, the lawn to be sparse, and even form irregular patches of dead grass.
5. Root maggots (omnivorous/causing missing seedlings and broken ridges)

Mole crickets, white grubs, wireworms, cutworms and root maggots are the most important types of common underground pests in my country. Root maggots are a type of omnivorous underground pests, which are the larvae of insects such as seed flies and onion flies. They mainly harm crops such as cotton, corn, various potatoes, beans, melons, cruciferous vegetables, spinach, onions and garlic. Among them, onions and garlic are particularly seriously harmed.
After hatching, the larvae of root maggots will drill into the rhizomes and eat, causing the leaves of the aboveground parts of the plants to turn yellow and wilt, or eat from the bottom to the top inside the rhizomes, eventually leading to the death of the entire plant. Due to the activity of root maggots, soft rot often occurs, which brings great trouble to crop growth.
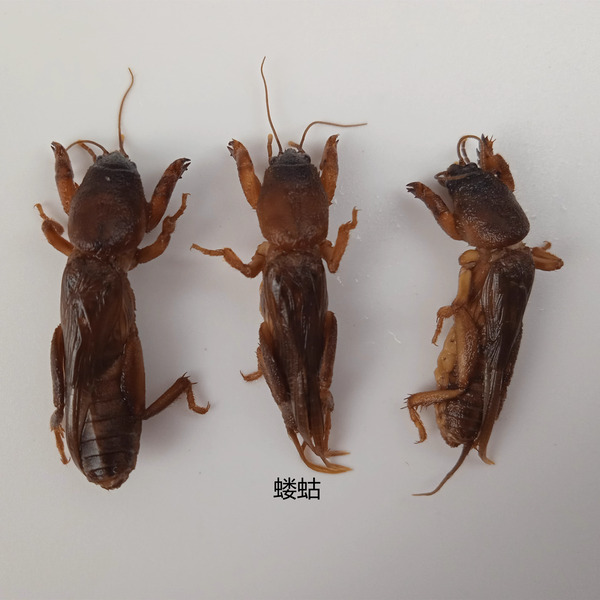
6. Crickets (omnivorous/important agricultural pests)
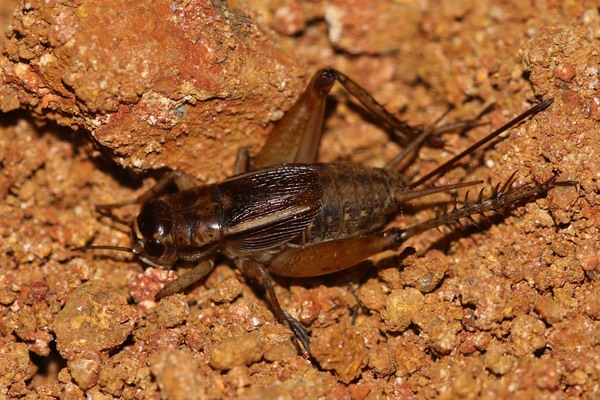

As a pest in my country's crop fields, crickets may surprise many people. Especially in Northeast China, North China, the lower reaches of the Yangtze River and South China, crickets are widely distributed in these areas. Crickets are omnivorous pests with a wide range of diets. They mainly harm beans, melons, various vegetables, potatoes and grass crops. They will damage the roots, stems, leaves, fruits and seeds of plants, especially the seedlings. In addition, crickets will also bite the bark of some plants, and will also cause damage to crops such as corn, jute, tobacco, cotton, soybeans and cassava, often causing seedling shortages, thus affecting the overall harvest.
7. Wheat root stink bug (causing missing seedlings and broken ridges)

The underground pest wheat root stink bug, also known as the root soil stink bug, is mainly distributed in North China, Northeast China, Northwest China and Taiwan. It has caused serious damage to corn, wheat, millet, sorghum, beans, tobacco and weeds of the grass family. Adults and larvae mainly absorb nutrients from the host roots through their mouthparts.
When they invade wheat, they will cause the plant to wither and die half a month in advance, resulting in small ears and few grains, which significantly affects the yield. The damage to sorghum and corn is manifested as green seedlings, short plants, or even withering and no ears in the seedling stage, reducing the yield by 20% to 30%, and sometimes even causing a total crop failure in some areas.
8. Root-knot nematodes (fast reproduction/strong vitality)
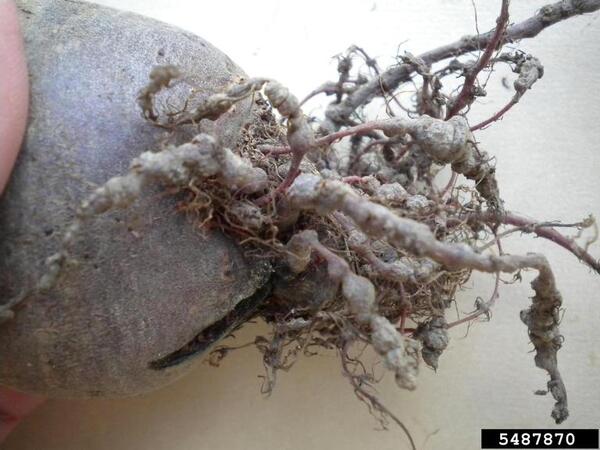

Root-knot nematodes on beetroot
Root-knot nematodes are a type of nematode that specifically parasitizes plants. They have a wide range and may harm at least 39 families and more than 130 crops. These nematodes are tiny and difficult to observe with the naked eye. They are mainly distributed in the surface layer of soil within 0-20 cm, especially in the 3-9 cm soil layer. The larvae and eggs of root-knot nematodes usually exist in the soil with nodules, and may also overwinter directly in the soil. Even in the absence of host plants, they can survive for up to 3 years.
Once parasitizing a variety of different crops, root-knot nematodes can reproduce rapidly. Coupled with its short life history and other characteristics, root-knot nematodes pose a great threat to crop production. They cause damage to the roots of crops, seriously affecting the growth and yield of crops.
9. Pseudo-ground beetles (causing missing seedlings and broken ridges)

Pseudo-ground beetles, also known as pseudo-walking beetles and pseudo-ground beetles, whose larvae are often called sand lurkers, are mainly distributed in Northeast China, North China and Northwest China, and are a type of underground pest. Adults mainly harm wheat, cotton, flax, and various bean crops; while larvae mainly target newly sown seeds and seedlings that are about to germinate. They are also capable of eating the roots and stems of seedlings, resulting in missing seedlings or lodging.
In terms of preventing and controlling pseudo-ground beetles, agricultural producers can take a variety of effective measures. For example, combining tillage and land preparation, manual killing, poison bait trapping, pesticide seed mixing, or ground spraying of powder can achieve good results.
10. Root mealybugs (strong starvation resistance/strong reproductive capacity)
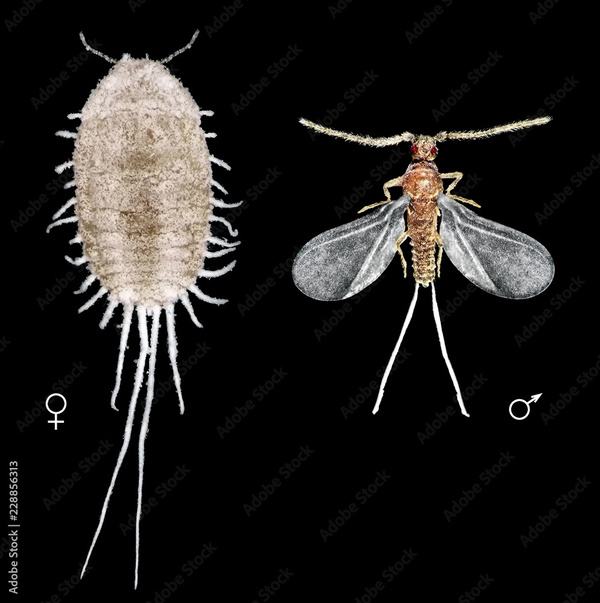

Root mealybugs in the soil are one of the pests that pose an important threat to wheat crops. They are of many species and widely distributed. They not only harm many trees, but also are distributed in Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Yunnan and other provinces in China. These pests live in the soil and like to live in the soil. Their adults and larvae gather at the roots to cause harm to plants. Root mealybugs prefer a suitable temperature between 15 and 25 degrees Celsius. Female adults have strong starvation resistance and can survive for 6 to 19 days even without food. In contrast, male mealybugs are relatively rare, while female mealybugs are capable of parthenogenesis. Root mealybugs can produce 4 to 5 generations in a year, and there is overlap between generations.
animal tags: Pests
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.