Exploring the "lowest animal species" is an interesting and complex question, because how we define "lower" or "higher" is itself a controversial scientific topic. In biology, there is no real hierarchy of "higher" or "lower" organisms. All species play a unique role in their specific ecological niches and survive and reproduce in nature in their own way. However, if we discuss the lowest animals based on indicators such as animal complexity, body structure, and nervous system, then we can focus on sponges and unicellular animals - they are the simplest life forms in the animal kingdom.
In early biological taxonomy, scientists usually divided animals into so-called "lower" and "higher" animals based on the complexity of their body structure, especially the degree of development of their nervous system and organ system. Simpler organisms, especially those lacking complex organs or nervous systems, are generally considered "lower". However, modern biology has gradually abandoned this overly linear classification method and instead viewed all organisms from an evolutionary perspective, believing that each species is the product of long-term natural selection and adaptation to the environment, and there is no such thing as high or low.
In this context, we can discuss some animal types that are relatively simple in morphology, structure and function, starting from simplicity and primitiveness.
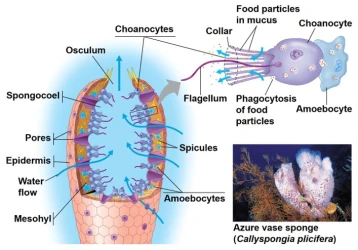
The phylum Porifera is recognized as one of the simplest multicellular organisms in the animal kingdom. Sponges are one of the oldest and most primitive multicellular animal groups, and scientists believe that they may have appeared on Earth 500 million to 700 million years ago.
Sponges have an extremely simple body structure, with no true organs, tissues, or nervous systems. They consist of a porous structure made of a gelatinous matrix, with numerous small pores (called pore cells) and a small number of cell types. Despite the lack of complex organ systems, sponges are able to effectively filter nutrients and remove waste from the water.
Sponges also have a simple lifestyle. They usually attach to the seafloor or other solid surfaces and rely on water flow to filter feed. Water flows through the pores in their bodies, and tiny food particles are captured and digested. This simple structure allows sponges to survive in complex ecological environments
Despite their simple structure, sponges have an important place in the history of animal evolution. As the earliest differentiated multicellular animals, sponges prove that the multicellular structure of animals may have evolved through the coordinated action of simple cell groups. The simplicity of sponges also provides an important clue to understand how animal complexity gradually evolved.
Another amazing feature of sponges is their ability to regenerate. Even if they are cut or broken, a sponge's cells can still reassemble and form a complete individual. This regenerative ability is very rare in the animal kingdom and highlights the unique biology of sponges.
Unicellular animals, also known as protozoa, are tiny organisms composed of a single cell. Although they do not have the complex structure of multicellular animals, they are traditionally included in discussions of the animal kingdom because they have many similarities with animals in life form.
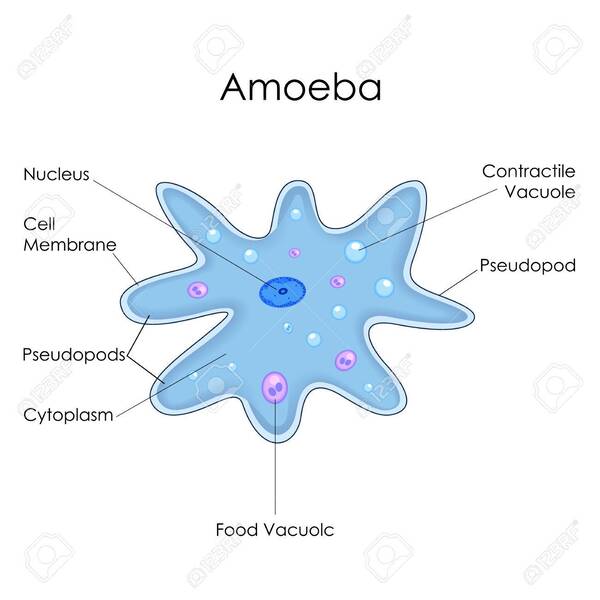
Amoeba is one of the representatives of protozoa and is often called one of the lowest animals. Amoeba's body is composed of a single cell, has no fixed shape, and can move through pseudopodia. They use pseudopodia on the cell membrane to propel themselves toward food or escape threats.
Despite their simple structure, amoebas display complex survival behaviors, such as feeding, locomotion, and responding to external stimuli. Amoebas are able to capture food particles outside the cell through endocytosis and digest them inside the cell, a mechanism that shows that even single-celled organisms have certain complex functions.
Paramecium is also a common single-celled protozoan. Paramecium is more regular in shape and has a surface covered with cilia that help it move quickly through water. Paramecium has a mouth groove that allows it to introduce tiny food particles into its body.
Compared with amoeba, Paramecium, although a single-celled organism, exhibits more complex behavior patterns and structural functions. Paramecium has a contractile vacuole for excretion and a nucleus for controlling cell activity, indicating that even single-celled organisms can
Despite their tiny size, single-celled animals play important roles in ecosystems. Protozoa are an integral part of the food chain and are consumed by many animals that rely on aquatic environments. At the same time, some single-celled organisms, such as malaria parasites, can have important health effects on humans and other animals, further demonstrating their ecological importance.
These lower animals provide us with valuable clues to understand the diversity of life and the evolutionary process. Their existence not only proves the diversity of life forms, but also reminds us that in the ecosystem, every species, no matter how complex it is, has its unique importance. The simplicity of lower animals is the result of evolution, not its disadvantage, and their ability to adapt to specific environments is the reason why they can continue in nature. Therefore, all life forms deserve our attention.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.