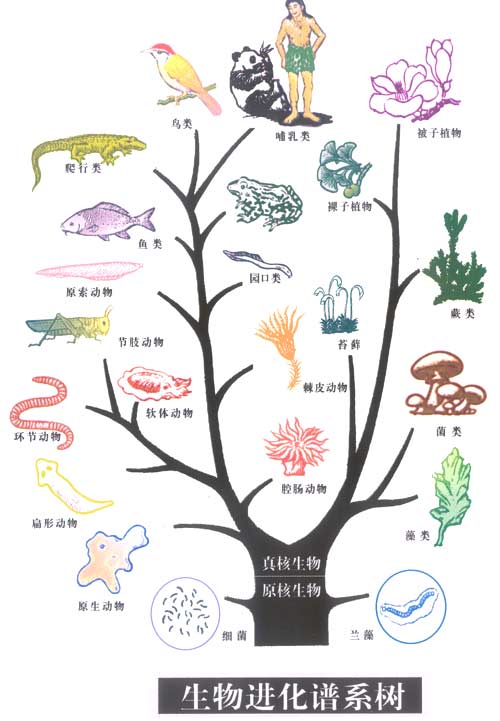
The formation of the earth has a history of 4.6 billion years. Initially, there was no life on the surface of the Earth. With the development and changes of the earth, certain substances on the earth's surface have gone through a long chemical process, and have differentiated and developed from inorganic substances to produce small pieces of protein bodies with non-cellular structures. As the earth develops to a certain stage, there are about 3.5 billion Years ago, when material chemistry evolved to a certain level, non-living substances on the earth were transformed into living substances. After a long period of time, these primitive life forms became more complex and perfect in structure, and gradually evolved into life forms in the form of primitive cells. Such organisms have evolved over a long period of time, and their internal structures have gradually become more complex, thus forming life in the form of prokaryotic cells. Such organisms have evolved over a long period of time, and their internal structures have gradually become more complex, forming life in the form of prokaryotic cells and further evolving into eukaryotic cells. The different nutritional methods of primitive single-cell organisms led to the differentiation of animals, plants, and microorganisms. The evolution of living things goes from simple to complex, from low to high. There are now 5 million to 50 million species of living things on the earth, forming a diverse biological world.
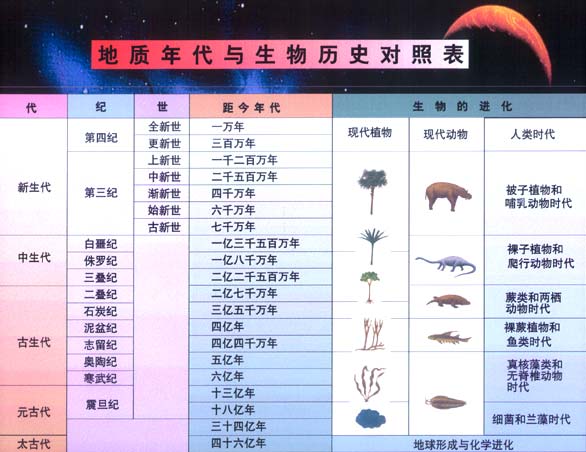
Comparison table of geological time and biological history. It has been 440 million years since the most primitive fish began to appear on the surface of the earth. These primitive fish once flourished at a certain period in the history of the earth, but in the end, they were all influenced by natural selection. Only those higher-level fishes with better adaptability to the water environment survived and are very prosperous on the earth today. The number of living fish species greatly exceeds the number of backbones of other living groups. animal.
Our country has a vast territory. With a territory of 9.6 million square kilometers, the terrain and climate vary greatly. From south to north, it spans five climate zones: tropical, subtropical, warm temperate, temperate and cold temperate, with diverse climatic conditions. The geographical environment is complex and diverse. The western plateau has Himalayan snow peaks with an altitude of more than 8 kilometers above sea level, from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to the Loess Plateau through mountains, hills and even plains. Vertical zonal differences in topography and climate affect hydrological differences and contribute to biodiversity in the biosphere. Because our country is dotted with rivers and lakes, it provides unique conditions for the habitat and reproduction of a variety of wild animals, forming different types of flora and fauna.
Marine Fishes of the Mesozoic Era Fish are the most important type of vertebrates in the water body. Among the more than 40,000 species of living vertebrates recorded in the world, fish account for 28,000 (recorded as There are more than 26,000 species, including about 8,600 species of freshwater fish. There are about 1,600 species of freshwater fish in Asia. There are about 1,000 species of pure freshwater fish living in my country’s inland waters. , about 500 of which are endemic to my countryand contain many monotypic genera and species, and a considerable number of relict species have been preserved. World fishery production exceeds the production of cattle, sheep, poultry, and eggs, and is the most important source of wild and domestic animal protein for humans.

It is estimated that in marine ecosystems, there is an average of one fish per 100,000 cubic meters of water, with an average population of 109 individuals; while in freshwater ecosystems, there is an average of one fish per 15 cubic meters, with an average population of 109 individuals per species. The average population size of species is 106 individuals; in freshwater ecosystems, compared with marine ecosystems, freshwater ecosystems are narrower and more isolated from each other. The distribution range of the fish populations inhabiting them is relatively limited, and the stability of the ecosystem Poor sex, environmental changes, sometimes even minor or local changes, may lead to the death of a certain population of fish or even the extinction of the species. It is estimated that 20% of the world's freshwater fish species (approximately 1,800 species) are in a gradually endangered or endangered state, mainly due to changes in the ecological environment (humanity's excessive water demand, water pollution, etc.), introduction and over-hunting. For example, in North America, up to 1/3 of fish species are in critical or endangered status. Among my country's freshwater fish, about 69 species are in a gradually endangered or endangered state.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.