How were oceans formed? Where does seawater come from?
At present, science cannot give a final answer to this question. This is because they are connected with another universal and equally unresolved problem of the origin of the solar system.
Current research proves that about 5 billion years ago, some large and small nebula clumps were separated from the solar nebula. They revolve around the sun and spin on their own. During the movement, they collided with each other, and some lumps combined with each other, growing from small to large, and gradually became the primitive earth. During the collision of nebula clumps, they contracted sharply under the influence of gravity, and the internal radioactive elements decomposed, causing the primitive earth to be continuously heated. When the internal temperature reached a high enough level, the materials in the earth, including iron, nickel, etc., began to melt. Under the action of gravity, the heavy ones sink and concentrate toward the center of the earth, forming the core; the light ones float up, forming the crust and mantle. At high temperatures, the moisture inside vaporizes and rushes out together with the gas, flying into the air. But due to the gravity of the earth's center, they will not run away, and will only become a circle of air and water around the earth.

The original earth without water or any life
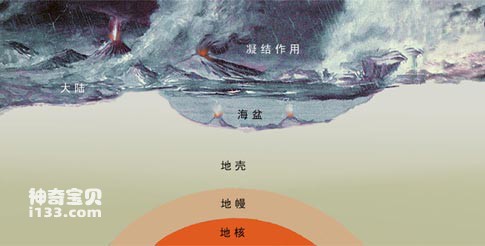
The water vapor entrained in the magma condensed, and water began to appear on the surface of the earth.
The crust on the surface of the earth is constantly impacted and squeezed by the violent movements inside the earth during the cooling and condensation process. As a result, it becomes wrinkled and uneven, and sometimes it is squeezed, causing earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, spewing out magma and hot gases. . At first, this happened frequently, then gradually became less frequent and gradually stabilized. This process of differentiation of light and heavy materials, resulting in great turbulence and reorganization, was probably completed 4.5 billion years ago.

Hot magma rushes out of the earth's crust
After the crust is cooled and shaped, the earth is like a long-dried apple, with densely wrinkled and uneven surfaces. Mountains, plains, river beds, ocean basins, all kinds of terrain are available.
For a long period of time, water vapor and atmosphere coexist in the sky; there are dense clouds. The sky is dark and the earth is dark. As the earth's crust gradually cools, the temperature of the atmosphere also slowly decreases. The water vapor uses dust and volcanic ash as condensation nuclei and turns into water droplets, accumulating more and more. Due to uneven cooling and violent air convection, thunder and lightning winds were formed, as well as heavy rain and turbid currents. The rain became heavier and heavier, and it continued to rain for a long time. The torrential floods passed through thousands of rivers and ravines and gathered into a huge body of water. This is the primitive ocean.
The first ocean
In the primitive ocean, seawater is not salty, but acidic and anoxic. The water continues to evaporate, causing repeated clouds to cause rain, and then falls back to the ground, dissolving the salt in the land and seabed rocks, and continuously collecting it in the sea water. After hundreds of millions of years of accumulation and fusion, it turned into generally uniform salt water. At the same time, because there was no oxygen and no ozone layer in the atmosphere at that time, ultraviolet rays could reach the ground directly. With the protection of sea water, life was first born in the ocean. About 3.8 billion years ago, organic matter was produced in the ocean, and first there were lower single-celled organisms. In the Paleozoic Era 600 million years ago, seaweeds began to photosynthesize in the sun, producing oxygen, which slowly accumulated to form the ozone layer. At this time, creatures began to land on land.
In short, through the gradual increase in water volume and salt content, and the vicissitudes of geological history, the primitive ocean gradually evolved into today's ocean.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.