Protostomes are one of the two major clades of bilaterally symmetrical animals, the other being deuterostomes. Defined by a distinctive embryonic development process, protostomes encompass a vast array of invertebrates and dominate the animal kingdom in terms of species richness. This article provides a scientific overview of what protostomes are, their developmental traits, major groups, ecological roles, and evolutionary importance.
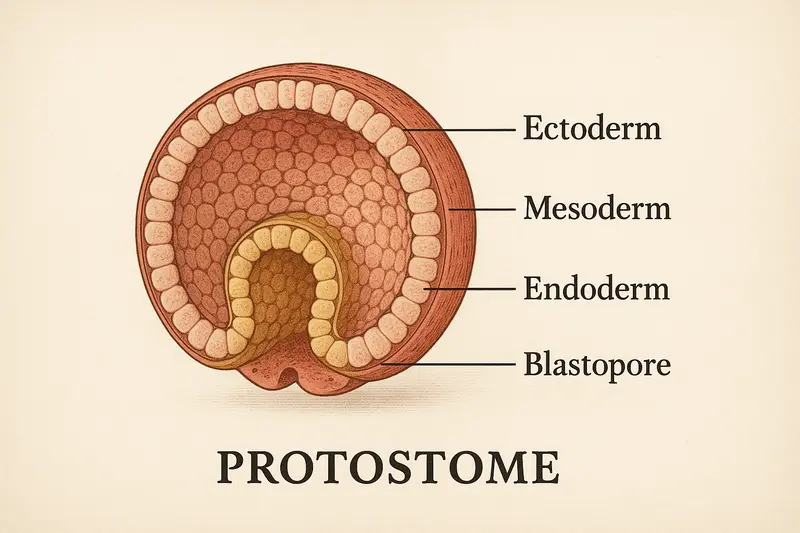
During embryonic development, the first opening (blastopore) formed during gastrulation becomes the mouth in protostomes. This is in contrast to deuterostomes, where the blastopore becomes the anus.
Protostomes: mouth develops first, spiral cleavage, determinate development
Deuterostomes: anus develops first, radial cleavage, indeterminate development
These distinctions position protostomes as a distinct evolutionary branch.
Protostomes exhibit spiral cleavage during early embryogenesis, where cells divide at oblique angles.
Each embryonic cell's fate is determined early, known as mosaic development.
The mesoderm (middle embryonic layer) forms from specific cell groups rather than from pouches of the gut.
Includes insects, arachnids, and crustaceans
Most diverse animal phylum on Earth
Characterized by exoskeletons and segmented bodies
Includes snails, octopuses, clams, and mussels
Notable for their soft bodies and often calcareous shells
Earthworms, leeches, and polychaetes
Exhibit segmentation and closed circulatory systems
Includes tapeworms and flukes
Simple, unsegmented, often parasitic
Includes pinworms, hookworms
Unsegmented, with pseudocoelomic body cavities
Earthworms aerate soil and aid in organic matter recycling
Insects assist in pollination and decomposition
Mollusks and crustaceans are essential to aquatic food chains
Filter feeders maintain water quality
Nematodes and platyhelminths include species that infect humans, animals, and plants
Protostomes thrive in almost every ecosystem, from deep-sea vents to mountaintops
They display an incredible range of body plans and survival strategies
Many protostomes show a trend toward cephalization, the development of a head and central nervous system
Fruit flies and nematodes are used extensively in genetics, developmental biology, and neuroscience
Crop pests like locusts and parasitic nematodes affect food security
Helminthic infections remain public health concerns in many regions
Shellfish, crabs, and other crustaceans are vital in global food economies
Pearls and dyes are derived from mollusks
Insights from protostome model organisms have informed Nobel-winning research
Protostomes represent a foundational branch of animal evolution. With unparalleled species diversity and ecological presence, they are central to our understanding of life’s complexity. From their embryonic development to their roles in ecosystems and research labs, protostomes continue to inform, support, and challenge scientific inquiry across disciplines.
A deeper understanding of protostomes enriches our grasp of evolutionary biology and underscores the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
animal tags: Protocolata
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.