Although Down syndrome is strictly a human-specific genetic disorder because it involves trisomy 21 (an extra chromosome 21), other animals have different chromosome structures and therefore do not suffer from Down syndrome exactly the same as humans. However, many animals may experience similar chromosomal abnormalities, resulting in symptoms such as developmental delays, behavioral abnormalities, and changes in facial and body features that are somewhat similar to Down syndrome in humans.
Although there are no specific references to animals diagnosed with Down syndrome in the scientific literature, we do know that some animals have similar chromosomal abnormalities. Here are some of those animals and the genetic abnormalities they are associated with:
Chimpanzees are the closest species to humans, and their genetic structure is very similar to that of humans. Studies have found that chimpanzees have trisomy 21 and show symptoms similar to Down syndrome, such as intellectual disability and behavioral delays.
Scientists have used gene editing technology to make laboratory mice carry genetic abnormalities similar to those of human Down syndrome to study the pathogenesis and potential treatments of this disease.
Cats may experience developmental problems, such as delayed growth and a weakened immune system, due to genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities. Although these conditions are different from Down syndrome, their effects are similar.
Although there is no direct counterpart to Down syndrome in humans, dogs can also experience chromosomal abnormalities that lead to cognitive and physical developmental problems.
Chromosomal abnormalities in horses can cause developmental defects similar to the cognitive and behavioral effects of Down syndrome.
Cattle can also have chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations that cause them to have developmental delays or abnormal behavior.
Guinea pigs are one of the model animals for studying human chromosomal abnormalities. Researchers will observe the symptoms caused by guinea pig gene mutations in experiments.
Rabbits also show chromosomal abnormalities in some genetic experiments, especially in breeding experiments.
Some fish have also shown chromosomal abnormalities in genetic studies, affecting their development and behavior.
Although birds have different chromosome structures from mammals, they may also have gene mutations that affect cognitive abilities.
Hamsters have been found to have chromosomal abnormalities in experiments, which can lead to behavioral changes or developmental delays.
Salamanders may show symptoms similar to chromosomal abnormalities in genetic experiments, which are often used to study developmental biology.
dolphins.html">Dolphins are highly intelligent animals, and studies have shown that they may also show abnormal behavior due to genetic abnormalities.
Although there are few genetic studies on Elephants-Are-Endangered.html">elephants, genetic abnormalities can affect their behavior and development, similar to some symptoms of Down syndrome in humans.
Bullfrogs are used as models in some genetic studies, and their chromosomal abnormalities may cause developmental delays.
Chromosomal abnormalities in sheep may also affect their physical and cognitive development.
Although snakes have relatively little genetic research, some gene mutations may affect their normal development.
Some primates (such as monkeys) may have genetic abnormalities similar to Down syndrome, resulting in intellectual and behavioral disorders.
As intelligent animals, studies have shown that chromosomal abnormalities in sea lions may also affect cognitive abilities and behavioral patterns.
Although animals do not suffer from typical Down syndrome like humans, they may have similar genetic abnormalities, leading to symptoms such as cognitive and physical developmental delays. Scientists study chromosomal abnormalities in animals to further understand the formation mechanism of Down syndrome and explore treatments.
animal tags: Bird Chimpanzees Mice Cat Hamster Sheep
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.






you may also like

Badgers belong to the family Mustelidae, order Carnivora, and are medium-sized, adaptable mammals. Below are 10 notable species found around the world:1. European Badger (Meles meles)Native to Europe, Western and Central Asia, found in forests, grasslands, and even urban parks. Reaches elevations up...

Introduction to Rhynochetus jubatusRhynochetus jubatus, commonly known as the Kagu, is a fascinating bird native to New Caledonia, an island group in the southwest Pacific. This unique species is known for its striking appearance, distinctive behaviors, and conservation status. In this article, we’...

Roosters crow and hens lay eggs are laws in nature. However, these laws can also change under the influence of certain factors. There is a saying in rural areas that if a hen imitates a rooster when it crows, it should be killed. Why is this? What is the meaning of a hen's crow?...

The order Squamata is the most diverse of all groups of reptiles, with approximately 7400 extant species. Squamates include lizards, snakes, and worm-like lizards. Squamous animals have two characteristics. The first is that they shed their skin regularly. Some scaly animals, such a...
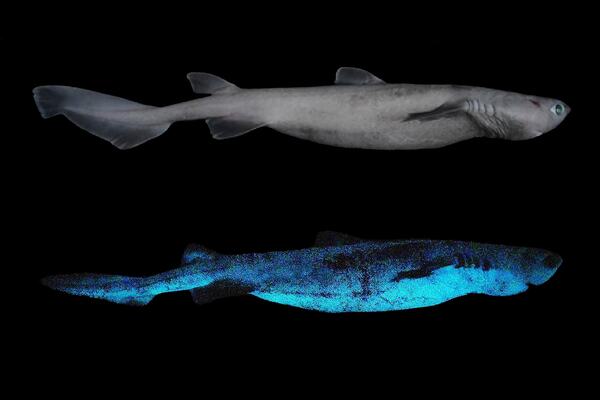
The deep oceans of our planet remain one of the last frontiers of exploration, and within the dark depths, scientists continue to discover remarkable creatures that are unlike anything found on land. Among these enigmatic beings is the kitefin shark, which has recently been recognized as the world’...

When you think of horses, what comes to mind? Graceful Arabian horses galloping across the desert, or perhaps powerful Clydesdales pulling heavy loads? Horses are among the most diverse and fascinating animals on the planet, with various breeds designed for different purposes, from racing to farming...

Rats are small mammals in the order Rodentia that are exceptionally widespread and diverse around the world. People often use the word "rat" to refer to a variety of different rodents, especially those species that live in close symbiosis with humans, such as the house mouse (Mus musculus) an...

Everyone loves pandas very much. As China's national treasure, pandas are also responsible for the friendship and diplomacy between China and other countries in the world. Citizens of many countries around the world are fans of our national treasures, and our country has rented pandas to nationa...
Email: jsset668#gmail.com (change # to @) Please indicate your purpose of visit! Guangdong ICP No. 2022053326 XML| map| Chinese

