Are all jellyfish dangerous? The short answer is: no—not all jellyfish cause painful stings. While every jellyfish possesses specialized stinging cells called cnidocytes, many species are either too weak or too mild to affect humans. In this article, we introduce 6 harmless or minimally stinging jellyfish species that are safe to observe—and beautiful to behold!

Biologically speaking, all jellyfish have stinging cells used to catch prey or deter predators. However, not all jellyfish have venom strong enough to harm humans. Some may cause only mild irritation, while others have virtually no effect. Nevertheless, direct contact is still discouraged to avoid possible allergic reactions.
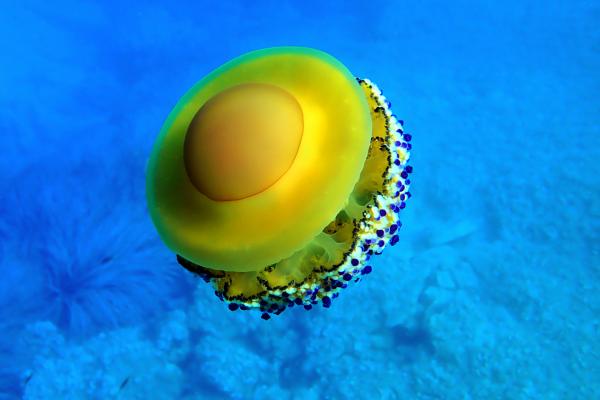

One of the best-known “non-stinging” jellyfish, mainly found in the Mediterranean Sea. Named for its yellowish-brown dome and orange central bulge, resembling a fried egg. It has no marginal tentacles but features eight oral arms with button-like appendages. Juvenile fish and crabs often shelter beneath it.
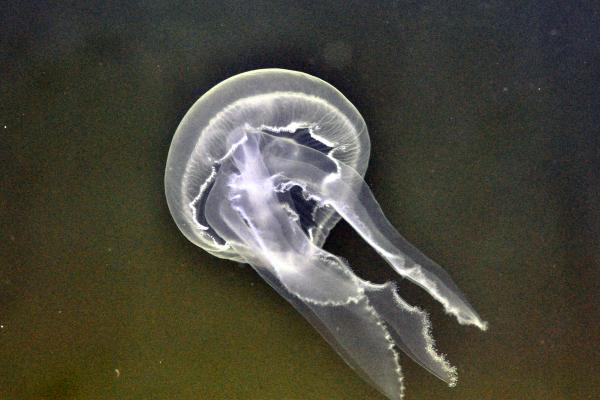
Also called the moon, saucer, or umbrella jellyfish. Widely distributed across the world’s temperate oceans. Its transparent bell displays four horseshoe-shaped gonads. Though it has many small tentacles, it causes only mild irritation if touched. Commonly kept in public aquariums.
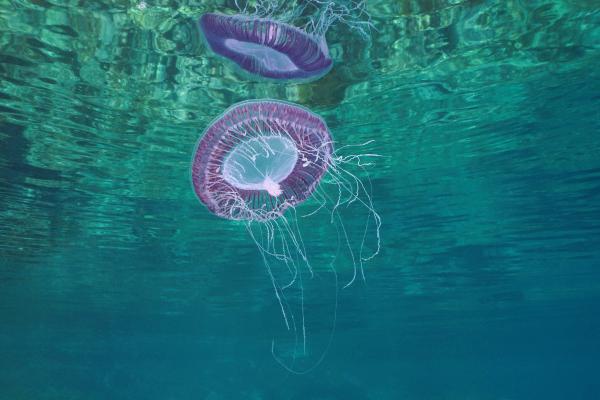

Known for its translucent appearance and bluish radial lines, reaching up to 40 cm wide. This species can bioluminesce thanks to a protein called aequorin. Found in coastal waters from temperate to tropical regions, especially in the Mediterranean during spring.
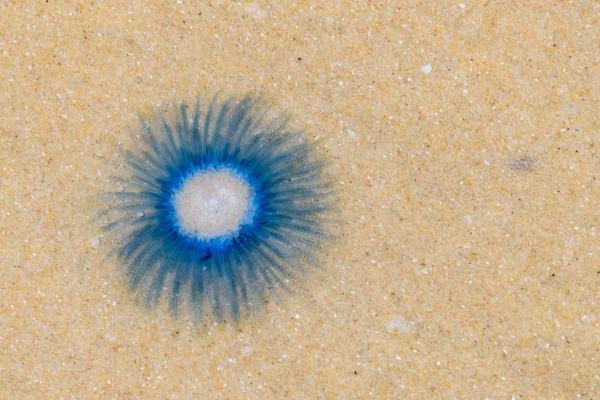

Despite its name, it’s actually a floating colony of polyps, not a true jellyfish. Features a central gas-filled float surrounded by blue, purple, or yellow hydroids that mimic tentacles. Measures up to 5 cm across. Stings are rare and usually mild.
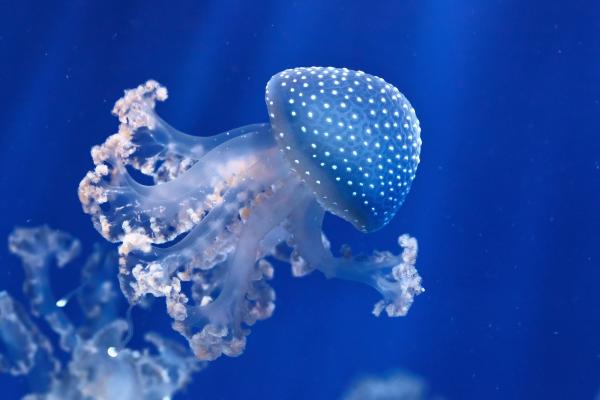

Native to the Pacific from Australia to Japan, now considered invasive in many regions. Recognizable by its translucent body covered with white spots. Can grow up to 50 cm in diameter. Low-toxicity stings, usually not harmful to humans.
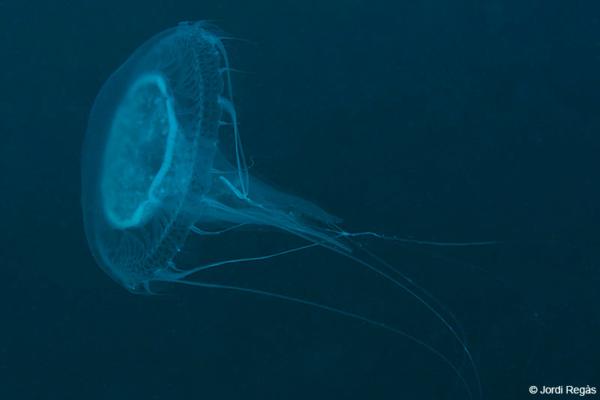

Found along Atlantic coastlines, this jellyfish has a flattened, lobed bell and short tentacles. Grows up to 15 cm. Although it contains stinging cells, its venom is non-harmful to humans. Easily confused with Aurelia, but differs in gonad shape.
Safety Tip: Even jellyfish that are considered harmless should not be touched with bare hands. Always observe marine life responsibly.
animal tags: Harmless Jellyfish
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.