According to the latest report in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology: Xu Guanghui’s research team from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered a new articulated fish 240 million years ago in Luoping, Yunnan, my country, named Youyouyu. Hairtail fish, and it is classified into the family Lashanidae of the order Gongyu. The graceful ribbonfish represents one of the earliest fossil records of articulated fishes in the world. Its discovery provides new fossil evidence for understanding the early evolution of holobony fish and the origin of articulated fishes.
According to reports, the hinge-toothed fishes include the order Archichthys, the order Hemivertebra, and the order Lepidopterus. The gar, which lives in the freshwater environment of Central and North America and Cuba, is a living representative of the order Lepidoptera, an articulated fish. It is called a living fossil and provides important information for the study of new finned fishes. Neofin fishes are the largest evolutionary branch of ray-finned fishes and are distributed in almost all water environments on the earth. Except for polyfins and sturgeons, all other living ray-finned fishes are neofinned fishes. Focusing on the research topic of the origin and early radiation of neofinned fishes, Xu Guanghui's research team has carried out field work at the junction of Yunnan and Guizhou in recent years and obtained a batch of well-preserved fossil specimens of neofinned fishes. Based on four beautifully preserved fish fossils collected from the Aniian marine strata of the Middle Triassic in Luoping, Yunnan, Xu Guanghui's team named a new genus of articulated fish: Elegant Otterfish. The name of the genus Yudai comes from Yudai Lake at the foot of Bailu Mountain in Luoping. "Lashan Jade Belt" is one of the famous scenic spots recorded by Xu Xiake, a great traveler and geographer in the Ming Dynasty, during his visit to Luoping.
Elegant hairtail fish is another important discovery of new finned fishes in the Luoping biota of the Middle Triassic. The Middle Triassic Luoping Biota of Yunnan is one of the Triassic marine fossil libraries with the highest biodiversity in the world, and is of high scientific value in studying the recovery of marine ecosystems after the mass extinction at the end of the Permian. The fishes found in the Luoping biota represent the world's earliest fossil record of hinge-toothed fishes, including the previously discovered Archichthys grande and Lashanus suuteri. In the past, S. sourii was placed in the genus St. George's fish from the late Middle Triassic in Europe, but new research shows that it is more closely related to the graceful hairtail and other arch fishes. Chronostratigraphic research shows that the St. George's fish in Europe is four million years later than the Archichthyidae fish in the Luoping biota of my country. The results of cladistic systematics show that the St. George's fish is more advanced than the Arch fish. Characteristics of hinge-toothed fish. In recent years, the successive discoveries of multiple species of Archichthys in the Triassic strata of the Yunnan-Guizhou region indicate that the early divergence of the angular-toothed fishes was much faster than we previously thought.
This research received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Science and Technology Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Key Frontier Science Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Excavation and Repair of Paleontological Fossils.

Figure 1 The true specimen of the graceful hairtail fish (Photo courtesy of Xu Guanghui)

Figure 2 Another complete specimen of the graceful hairtail fish (Photo provided by Xu Guanghui)
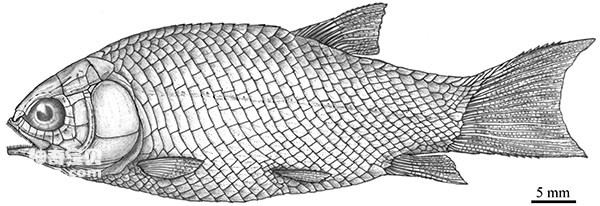
Figure 3 Restoration of the graceful jade hairtail fish (photo courtesy of Xu Guanghui)
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.