Beetles (Order: Coleoptera) are among the most diverse and successful insect groups on Earth, inhabiting nearly every ecological niche, from dense forests to arid deserts. With over 400,000 species described and many more yet to be discovered, beetles play vital roles in ecosystems, including pollination, decomposition, and pest control. This article explores 15 unique beetle species, detailing their morphological features, ecological behaviors, distribution, and biological significance.
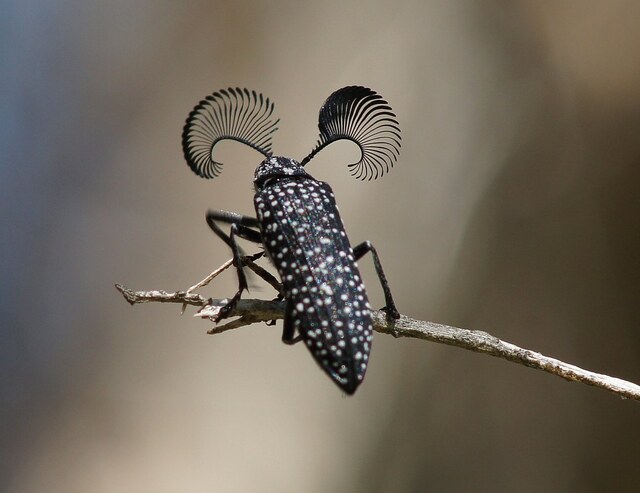

The feather-horned beetle is a rare species first described in 2013 and found primarily in Western Australia. It is recognized for its elaborate, fan-shaped antennae, which are particularly prominent in males and consist of over 20 segments. These specialized antennae help detect pheromones released by females.
Adult beetles measure 10–25 mm in length, with black femurs and distinct ridges on their heads. Their behavior and reproductive habits remain largely unknown, but their reliance on chemical signals suggests a sophisticated mating strategy. Conservationists emphasize the importance of forest preservation to protect these rare beetles.
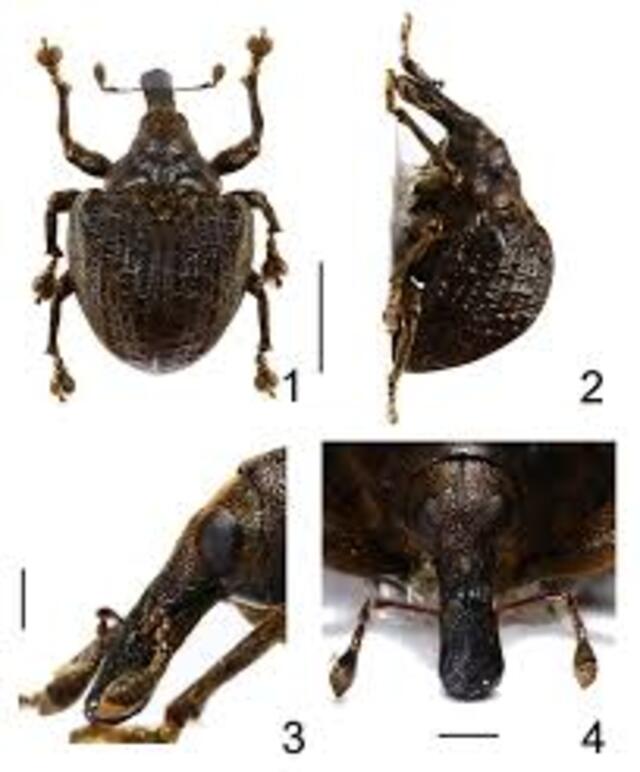

Named after Alfred Russel Wallace, this fig-associated weevil is an integral part of fig tree ecosystems in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Adults measure 10–20 mm and have robust mandibles suited for chewing plant tissues.
Closely linked to fig tree pollination, O. wallacei helps regulate fig populations while relying on them for food. However, habitat destruction and deforestation threaten this mutualistic relationship. Conservation efforts focus on protecting fig tree-rich habitats to sustain both the beetle and its host plants.
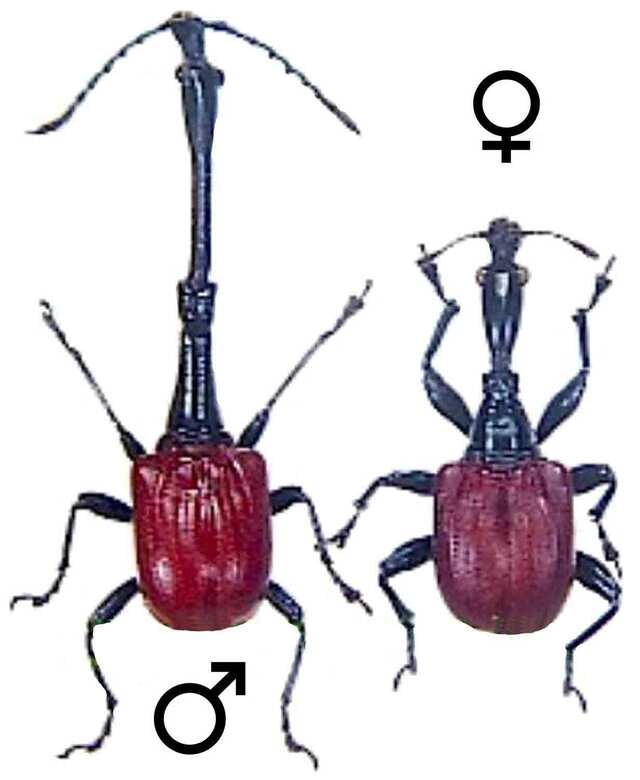
Endemic to Madagascar, the giraffe weevil is named for its extraordinarily long neck, which can be 2–3 times the length of its body in males. The elongated neck is an adaptation for male competition and nest construction, as males use it to roll leaves into protective structures where females lay their eggs.
These beetles are dependent on Madagascar’s rainforests, which are under severe threat due to deforestation. Conservationists are actively promoting habitat preservation to ensure the survival of this remarkable species.
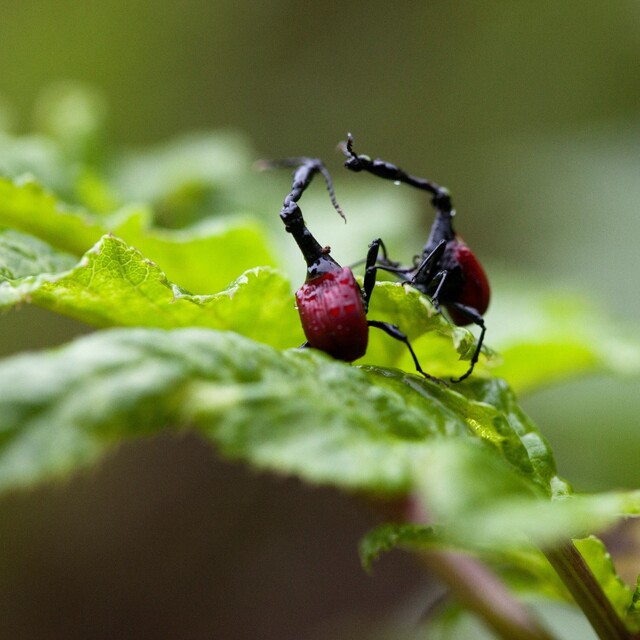
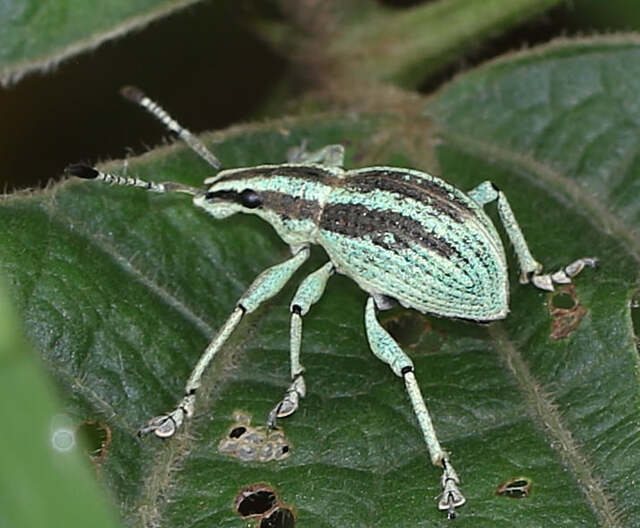


A large weevil species native to Southeast Asian rainforests, E. takahashii is recognized for its distinctively raised back and robust exoskeleton. Adults measure 15–30 mm and use their camouflaged, oval-shaped bodies to blend in with bark and leaves.
The larvae develop inside tree roots, feeding on plant tissue, which sometimes makes them pest species in agricultural settings. Due to habitat loss, populations have seen declines, highlighting the need for forest conservation.
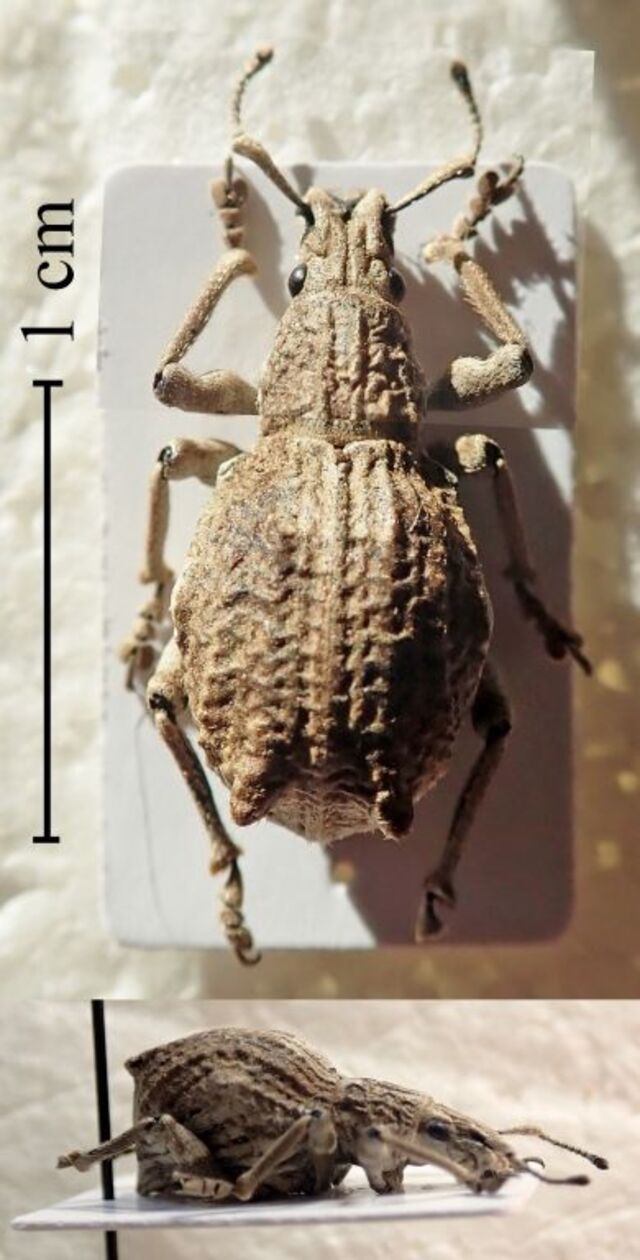


Similar to the giraffe weevil, this long-necked beetle from Southeast Asia has an extended neck used for territorial battles and mating. It measures 10–18 mm, with a dark, glossy exoskeleton and folded leaf nests where females deposit eggs.
Due to forest degradation, this species’ habitat is shrinking, making conservation efforts critical for its survival.
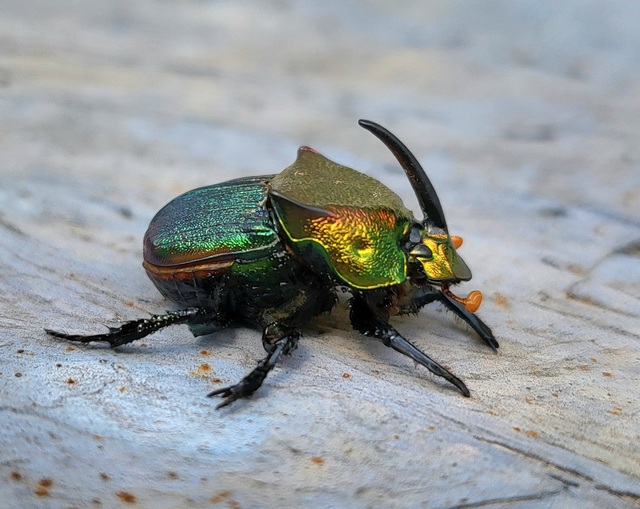

A brilliantly iridescent dung beetle from North America, P. vindex plays a crucial role in nutrient recycling by breaking down animal feces. These beetles have strong legs for burrowing and help improve soil quality.
Males possess a horned head used in competition, and the species prefers herbivore dung over carnivore waste. Conservationists stress their importance in maintaining healthy ecosystems.
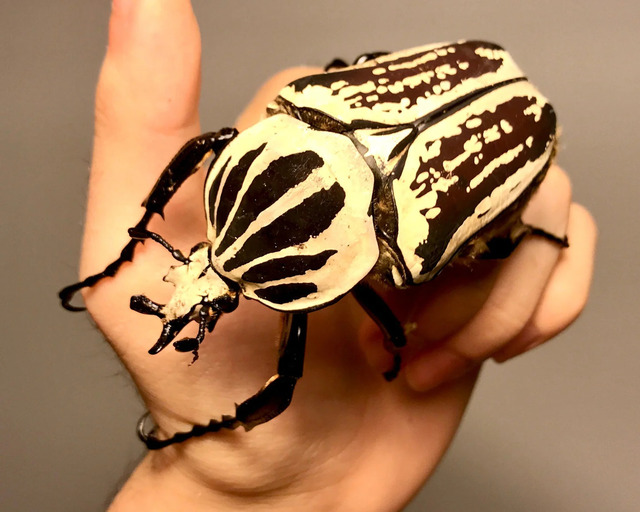

One of the largest beetles in the world, Goliathus orientalis can reach 100 mm in length. Found in Central and East Africa, these beetles feed on fruit and tree sap, while their massive larvae consume decaying wood.
Due to habitat destruction, their populations are at risk, prompting captive breeding programs to ensure their survival.

Named for their turtle-like shape, tortoise beetles have transparent or metallic-colored elytra that allow them to blend into their environment. Found globally, they primarily feed on plant leaves.
Some species use fecal shields as a defense mechanism, making them unique subjects in insect adaptation studies.
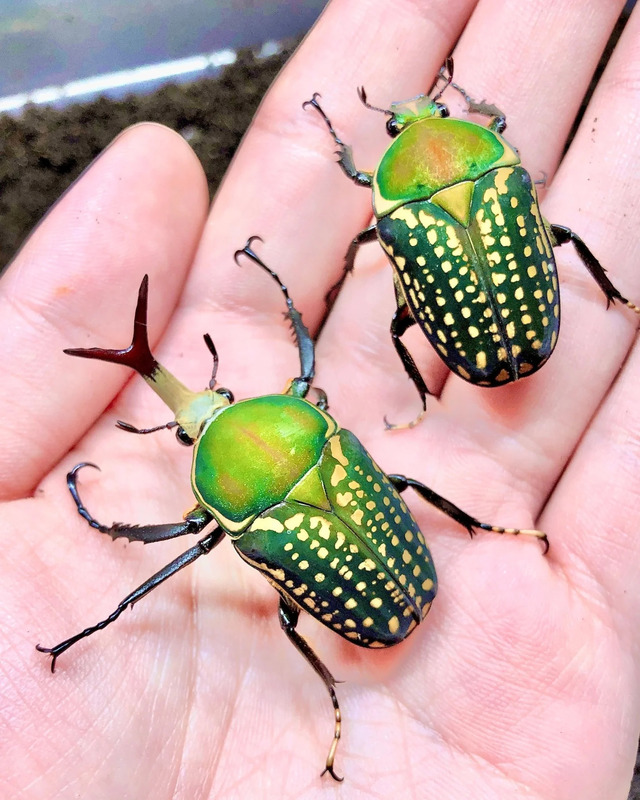

A small but powerful rhinoceros beetle from Africa, M. harrisi has a green exoskeleton and white patterning. Males feature short, thick horns for mating combat.
This species is popular among insect collectors, though over-collection and habitat loss threaten wild populations.
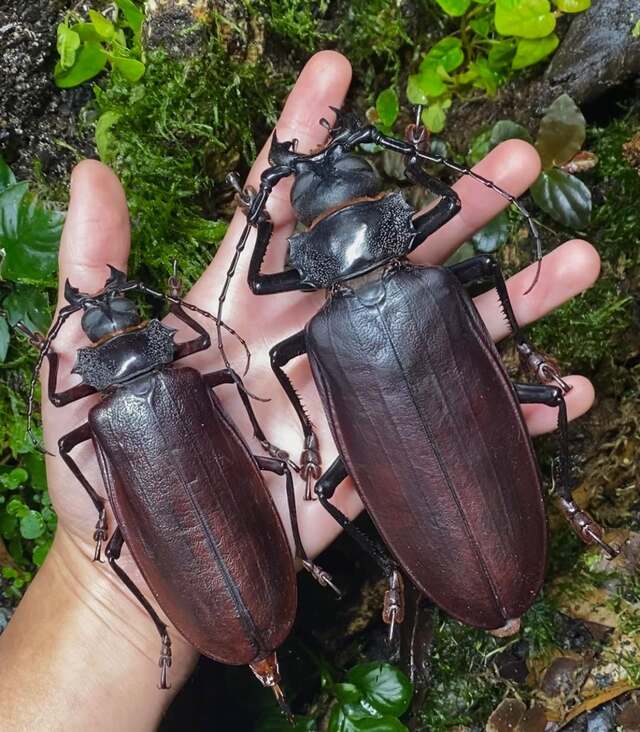

One of the largest beetles in the world, Titanus giganteus can reach up to 17 cm (6.7 inches) in length. Found in the Amazon rainforest, this beetle possesses a strong exoskeleton and powerful mandibles capable of breaking pencils.
Despite their enormous size, adult Titan beetles do not feed, relying entirely on the energy stored from their larval stage, during which they are believed to be wood-boring predators. Due to deforestation, their natural habitat is under threat, making their conservation a growing concern.
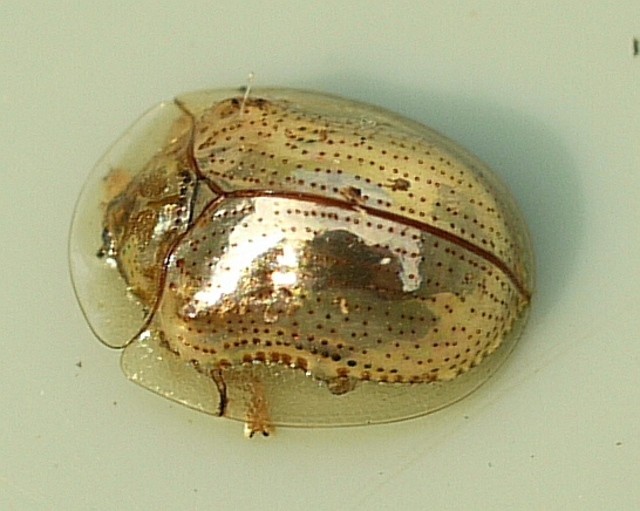

This small but visually stunning beetle is known for its golden, reflective shell, which can change color when disturbed. Found in North and Central America, these beetles primarily feed on morning glory and sweet potato leaves.
Their ability to alter their metallic sheen is due to fluid movement under their cuticle, a unique adaptation that serves as a defense mechanism against predators.
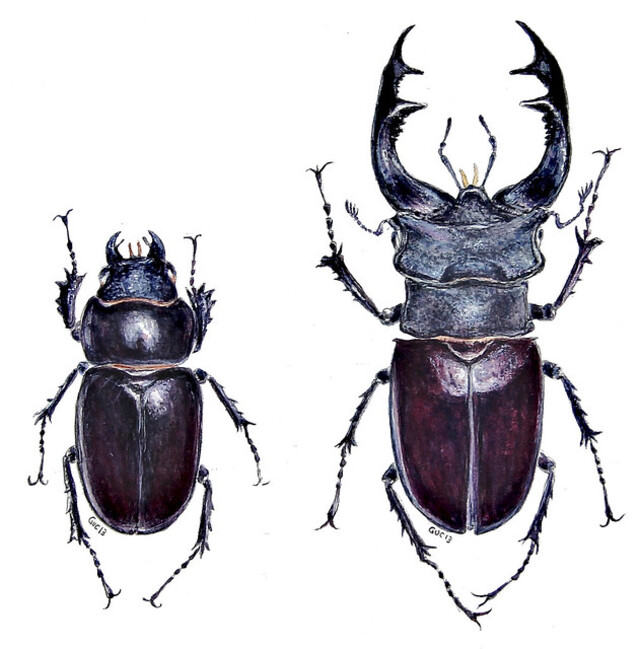
One of Europe’s largest beetles, the stag beetle is famous for its oversized mandibles, resembling deer antlers. These mandibles are used by males in combat for mates.
Despite their intimidating appearance, stag beetles are harmless to humans and play an essential role in breaking down decaying wood. Their numbers are declining due to urbanization and habitat destruction, prompting conservation efforts in several European countries.
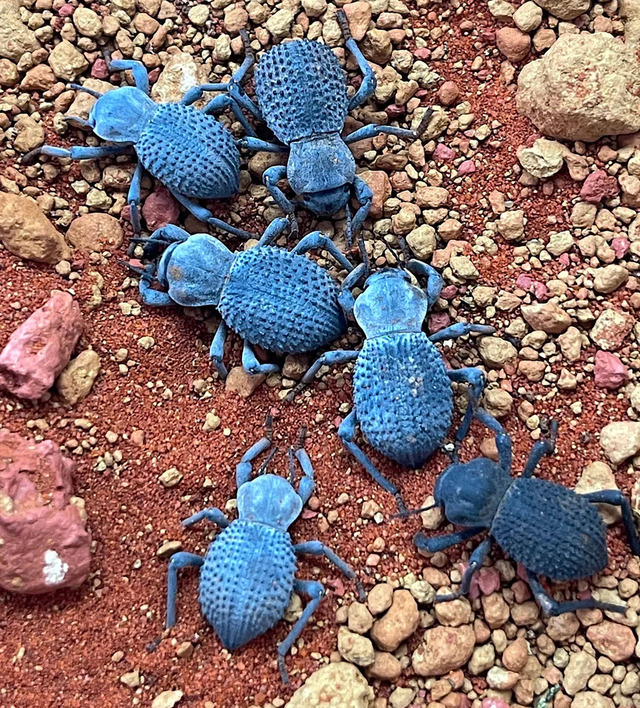

This desert-dwelling beetle from North America is well-known for its unique defensive behavior: it plays dead when threatened. Its dusty blue exoskeleton helps prevent water loss and provides excellent camouflage in arid environments.
Due to its resilience to extreme heat and long lifespan, Asbolus verrucosus has become popular in the pet trade.
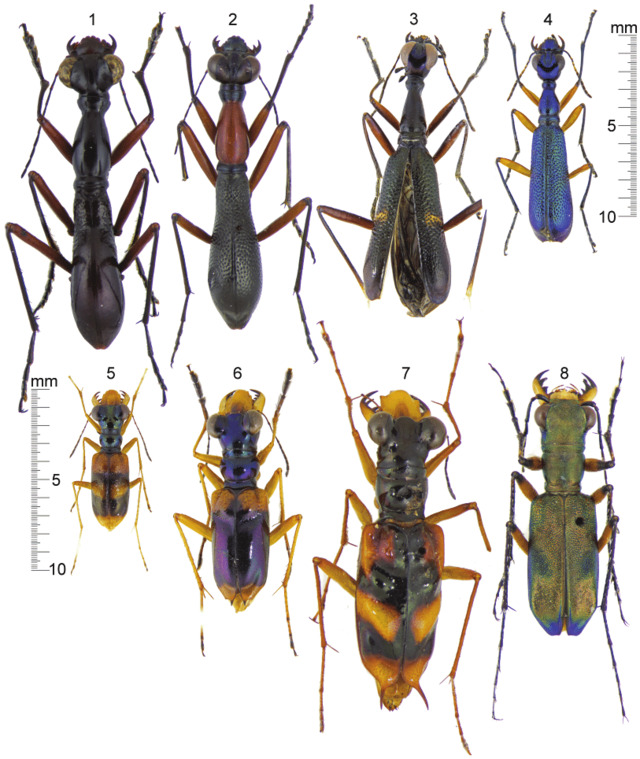
A unique arboreal beetle from tropical rainforests, this species mimics spiny plants and thorns to deter predators. Unlike many flower beetles, T. variabilis is partially predatory, feeding on small insects and plant material.
Its natural habitat is threatened by deforestation, making conservation efforts necessary for its survival.
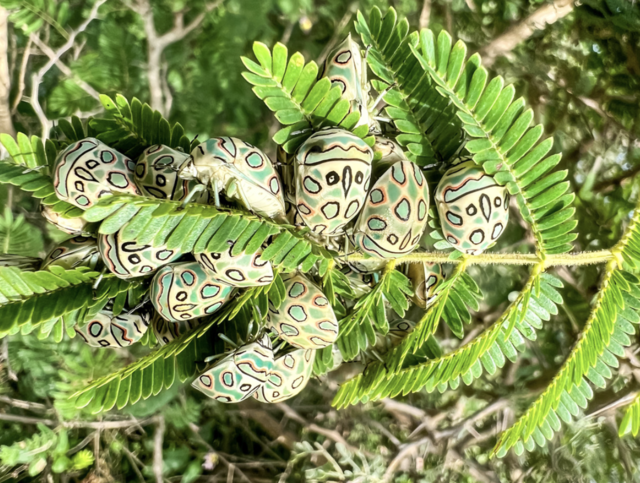

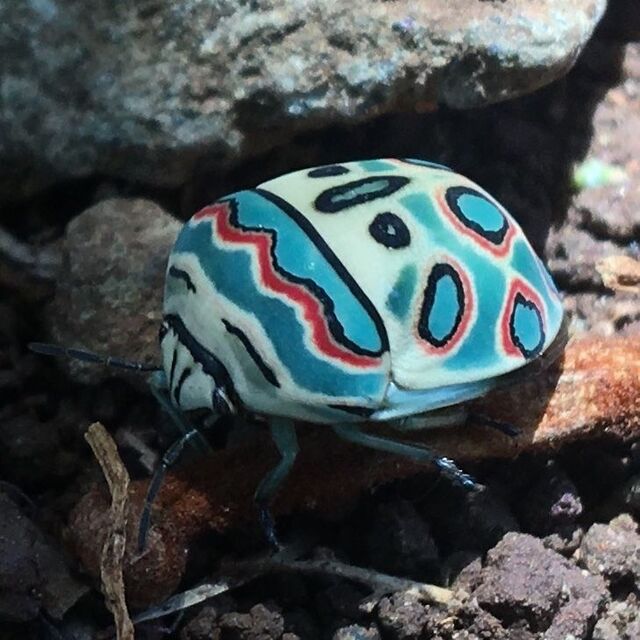
Named for its striking, abstract patterns, the Picasso bug is one of Africa’s most colorful beetles. Its bright markings serve as aposematic warning signals, deterring potential predators.
Despite their vibrant appearance, Picasso bugs are small (6–8 mm) and primarily feed on plant sap. Their natural habitats are at risk due to agricultural expansion.

Beetles are an essential component of ecosystems, playing critical roles in pollination, decomposition, and biological control. However, many species face threats from deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, and human activities.
Protecting natural habitats through reforestation and conservation efforts
Raising awareness about the ecological significance of beetles
Reducing pesticide use, which negatively impacts beetle populations
Supporting captive breeding programs for endangered beetle species
With continued research and environmental consciousness, we can ensure that these incredible beetle species continue to thrive and contribute to global biodiversity.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.
you may also like

Applying for a pet vaccination certificate usually requires the following steps: 1. Consult a veterinarian: First, consult a local veterinarian or pet clinic to understand the specific requirements and procedures for applying for a pet vaccination certificate. Different r...

When deciding between a Syrian hamster and a Siberian hamster, there are several factors to consider: size, color, lifespan, and how many hamsters you can keep together in one cage. The Syrian hamster, also known as the teddy bear hamster or golden hamster, and the Siberian hamster, often referred t...
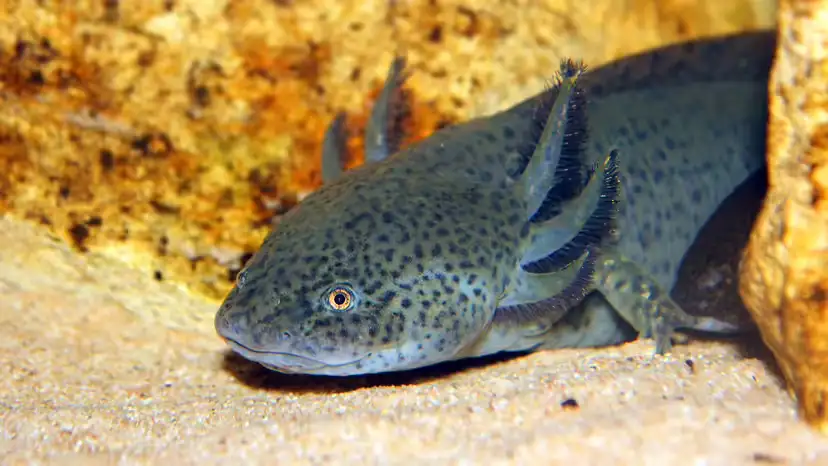

OverviewThe axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) is one of the most extraordinary amphibians on Earth—celebrated for its regenerative abilities, unusual biology, and increasingly fragile conservation status.Understanding how long axolotls live, and why their lifespan differs dramatically between the wild...
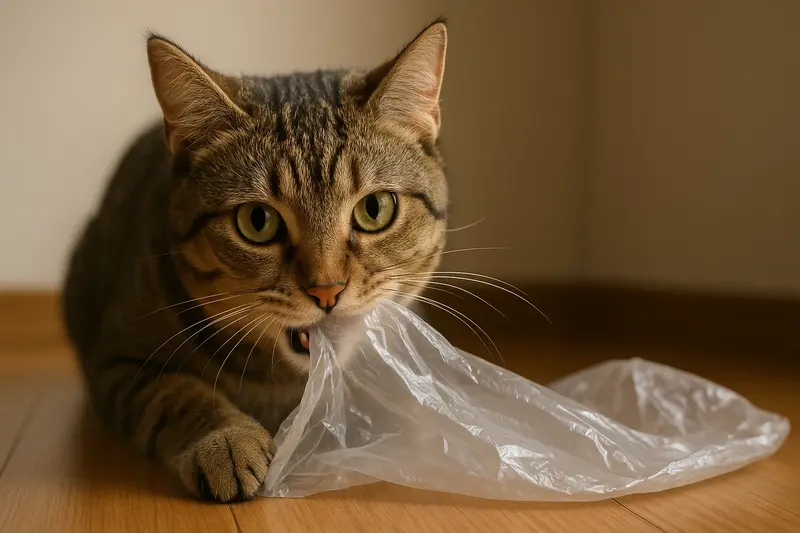

Many cat owners have been puzzled by a strange and potentially dangerous feline behavior: chewing or even swallowing plastic bags. While it might seem quirky or amusing at first, this habit can be a sign of underlying issues that deserve serious attention. In this article, we’ll explore from a prof...
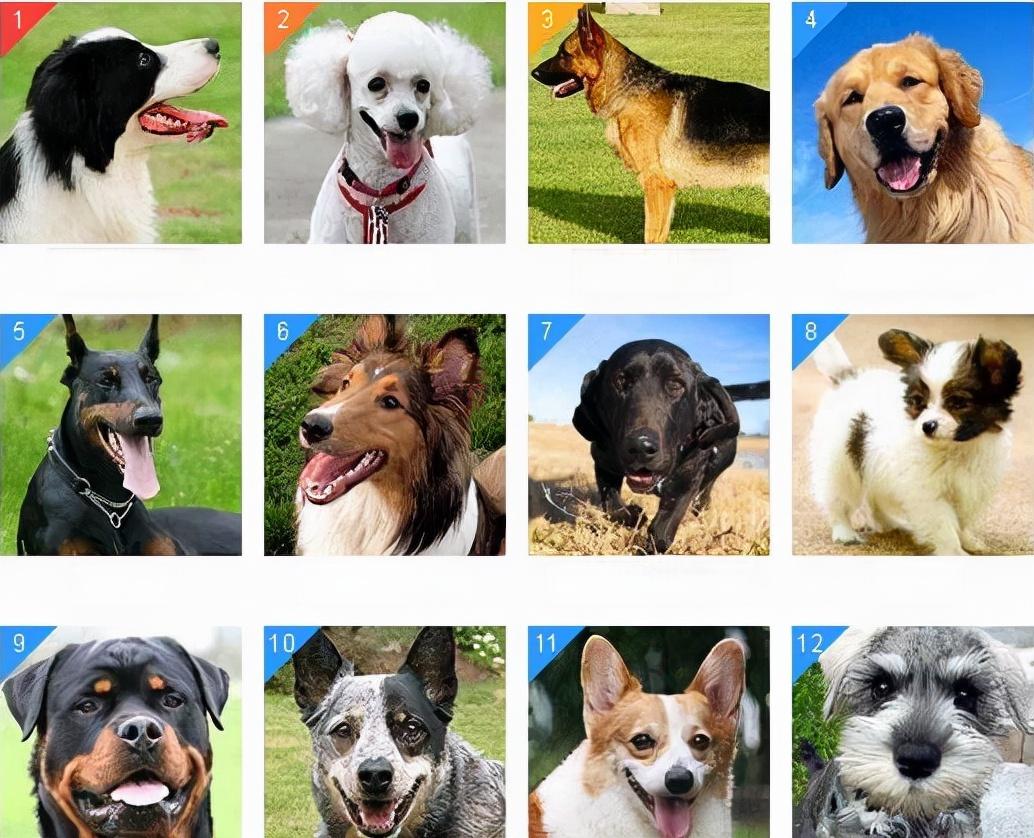

Dog intelligence refers to a dog’s ability to learn, solve problems, and follow commands. Different breeds exhibit varying levels of intelligence, with some excelling in quick learning and obedience, while others may require more time to understand instructions. Dog intelligence rankings classify d...
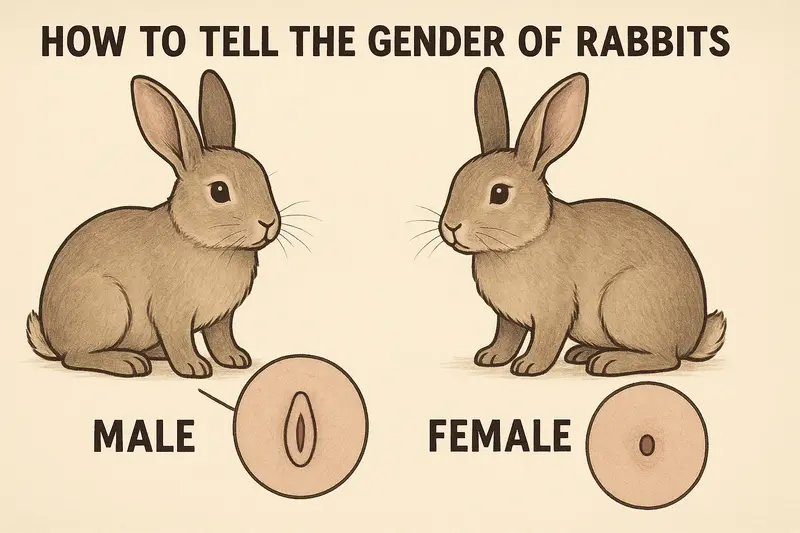
Knowing how to identify a rabbit's gender is essential for proper care, breeding management, and disease prevention. Compared to cats or dogs, rabbits are more challenging to sex, especially at a young age. This article offers a detailed guide from a zoological and anatomical perspective on how...
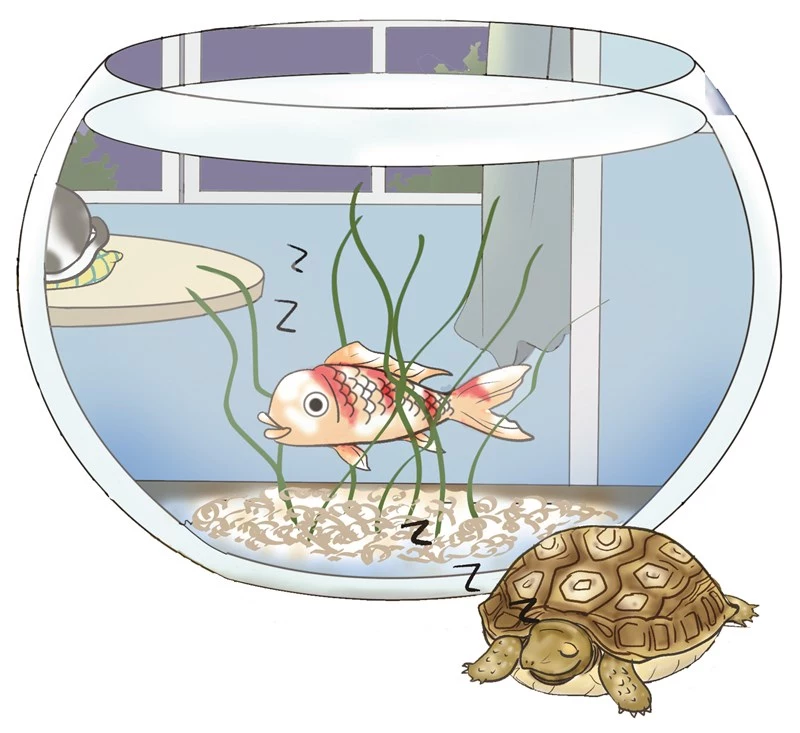
Fish are aquatic vertebrates, and their physiological characteristics and behaviors are very different from those of terrestrial animals such as mammals and birds. A common question is: Do fish sleep? If so, how do they sleep? Since fish do not have eyelids, they do not close their eyes when they s...
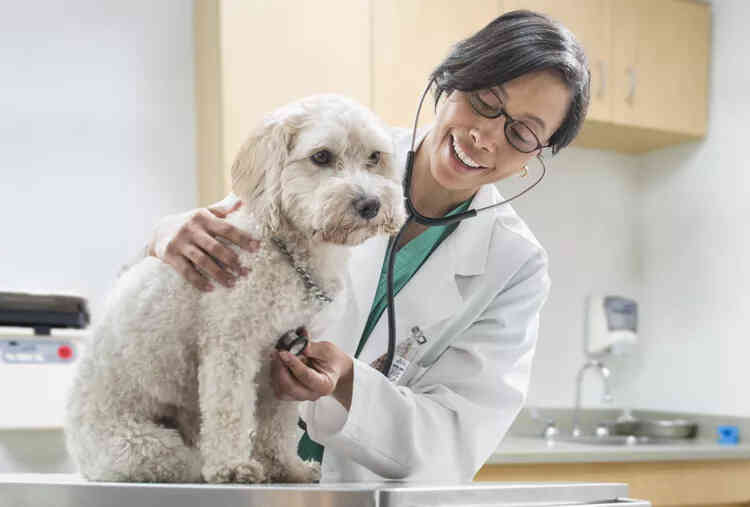

Any dog can develop a heart murmur, regardless of age, sex, size or breed. While heart murmurs are not always a problem, they can be a sign of other serious problems in the body and may indicate the presence of heart disease. Heart murmurs are detected by veterinarians as abnormal sounds duri...
Email: jsset668#gmail.com (change # to @) Please indicate your purpose of visit! Guangdong ICP No. 2022053326 XML| map| Chinese

