
Alias Bahaba taipingensis,Chinese Bahaba,Golden money sturgeon, golden money croaker, golden money fierce fish, fish high, big gull, white flower fish, yellow sweet
length 100-150 cm, up to 180 cm
Chinese Bahaba (scientific name: Bahaba taipingensis) is called Chinese Bahaba in foreign language. It has no subspecies and belongs to the family Sciaenidae and the genus Bahaba.
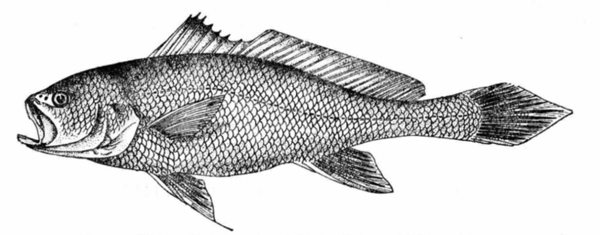
Chinese Bahaba gathers in clear water and disperses in turbid water. Juvenile fish live in estuaries and nearby coasts. During the lowest tide, flat water and easterly wind from the 23rd to the 26th day of the lunar calendar, yellow croaker fry will float to the surface in groups; when the tide starts to rise, the water flows and the wind is not blowing from the east, the yellow croaker fry will sink in groups.
Yellow croaker is a carnivorous fish that feeds on small fish and large crustaceans such as shrimp and crabs, while young fish feed on shrimp. Yellow croaker in Dongguan waters mainly eat shrimp from December to May of the following year, mainly eat mudskippers from June to August, and mainly eat mullet from September to November.
According to statistics on the gonadal development of captured wild yellow croaker, the naturally grown yellow croaker in Dongguan waters, China, only has fully mature eggs when the weight reaches more than 15 kilograms. The weight of the ovaries can reach 20% of the fish's body weight. The size of the eggs is similar to that of carp eggs. After absorbing water, they are 30-50% larger than before. They are estimated to be sticky eggs. The yellow croaker lays eggs around Qingming to Guyu. The spawning ground in the waters of Dongguan, China, is in the Shiziyang area from Longxue to Dahu. After spawning, the abdominal scales of female yellow croakers are rough, which is suspected to be caused by friction with hard objects during spawning.

The shape of the swim bladder of the yellow lip fish has degenerated, and the end of the swim bladder extends to both sides in a long tubular shape, forming a unique type. In terms of phylogeny, it has become a small branch of the Sciaenidae family and has important academic value in the phylogeny of the Sciaenidae family.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the annual production of yellow croaker in the Pearl River Estuary in China was about 180 tons, the highest in China, and a record of 1.5 tons of yellow croaker was set in one net. In the early 1980s, yellow croaker was still the dominant species of fish in the Humen Sea area, ranking sixth in terms of resource volume and frequency of occurrence, accounting for 9.0% of the total catch. After the reform and opening up, with the environmental pollution caused by overfishing and rapid economic development, the resources of yellow croaker have dropped sharply, and it is rarely seen. It is on the verge of extinction, and only a few hundred young fish are recorded as being caught by mistake every year.
In order to effectively protect the precious resource of yellow lip croaker and promote its recovery, proliferation and rational development and utilization, in 2005, Dongguan City, China established the Dongguan Yellow Lip Croaker Municipal Nature Reserve in the Humen Sea Area of the Pearl River Estuary, the only remaining spawning ground for yellow lip croaker. This is the only nature reserve in China that mainly protects yellow lip croaker. Dongguan Yellow Lip Croaker Nature Reserve is a marine nature reserve for wild animals. It is located in the central and southern part of Guangdong Province, on the east side of the Pearl River Delta, and at the Humen Gate, the largest of the eight estuaries of the Pearl River. The Yellow Lip Croaker Nature Reserve is divided into a core area, a buffer zone, and an experimental area. It starts from the west bank of Weiyuan Island in the east, borders Guangzhou in the west, starts from the southern estuary of Taiping Waterway in the south, and ends at the northern estuary of Taiping Waterway in the north, covering an area of 686 hectares. The geographical coordinates are: 113°39′16″ east, 113°36′26″ west, 22°45′48″ south, and 22°48′41″ north. On July 22, 2022, the artificial breeding of the globally endangered species yellow lip croaker was successful in Huidong County, Huizhou City, Guangdong Province, and the results of the "2022 Yellow Lip Croaker Artificial Breeding Technology Research" were accepted by the expert group.
Listed in the first level of the "List of National Key Protected Wildlife in China".
Protect wildlife and eliminate game.
Maintaining ecological balance is everyone's responsibility!