Yellow anglerfish, whose scientific name is Lophius litulon, is a deep-sea benthic fish.
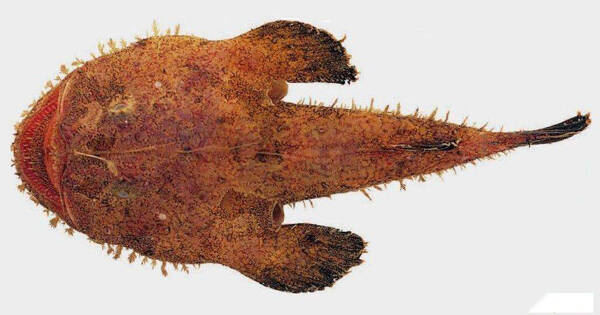
Yellow anglerfish usually lures prey with its snout tentacles and bait balls, sucks the prey in one gulp, and feeds on fish and crustaceans. The main prey of yellow anglerfish in the southern Yellow Sea are small yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena polyactis), lancetail goby (Chaeturichthysstigmatias), fine-striped cardinalfish (Apogonichthys lineatus), hairtail fish (Trichiurus shaumela), dragonhead fish (Harpadonne hereus), hawk claw shrimp (Trachypenaeus curvirostris), anchovy (Engraulis japonicus), etc. Fish is the main feeding group of yellow anglerfish, accounting for 83.44% of the total weight percentage in the food. The feeding intensity of yellow anglerfish has obvious seasonal and body length changes, with the highest in winter and the lowest in spring; the highest in the group with a body length of less than 100 mm and the lowest in the group with a body length of more than 500 mm. In the four seasons and six body length groups, small yellow croaker is the prey with the highest weight percentage in the stomach of yellow anglerfish. The proportion of goby and cardinalfish in the stomach contents of juvenile yellow anglerfish was high, but the proportion in the stomach contents of adult fish was low. The results of cluster analysis showed that the yellow anglerfish had a diet change when its body length reached 100 mm. The trophic level of yellow anglerfish was 3.66, indicating that it was in a high position in the food web of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea.
The length of female yellow anglerfish at first sexual maturity was 293 mm, and the age of first sexual maturity was 1.5 years old. The breeding season was from February to May, with April to May as the peak period. The maturity coefficient of female fish reached the maximum in April, followed by May, and the maturity coefficient of male fish reached the maximum in May. The absolute fecundity ranged from (3.11 to 14.1)×105 eggs, with an average of (6.74±2.87)×105 eggs. The relative fecundity (F/L) ranged from 883 to 2153 eggs/mm, with an average of (1521±581) eggs/mm. The relative fecundity (F/W) ranged from 181 to 426 eggs/g, with an average of (264±76) eggs/g. The diameter measurement results of 132 oocytes in stage IV ovaries showed that the egg diameter ranged from 1.30 to 1.76 mm, with an average of (1.59±0.19) mm. An obvious peak appeared at 1.575 to 1.625 mm, accounting for 33.3% of the total number of eggs. The egg diameter distribution was uneven, which should belong to the one-time spawning type.
There is a kind of glandular cell secretion in the body of the anglerfish, which contains a kind of phospholipid. This phospholipid is called fluorescein. Then, under the action of the catalyst luciferase, the fluorescein will combine with oxygen in the blood to emit a kind of fluorescence, also called cold light. The secretion of the glandular cells of the anglerfish contains a kind of phospholipid. It has a dorsal fin in its body. Its first dorsal fin spine grows a fishing rod. There is a fleshy spike on the top of the fishing rod, which can emit various colors of light. And this fleshy spike floats in the water. Uninformed small fish think it is a small insect and come to eat it. It doesn’t matter if it comes to eat. It will open its mouth wide and all the small fish and shrimps will flow into its mouth. If a big fish comes, it will immediately remove the light color. After extinguishing it, other fish can’t see that it is here, so it protects it.
Fish meat is rich in vitamins A and C. Its tail muscles can be eaten fresh or processed into fish paste, etc. Its fish maw and fish roe are both highly nutritious foods, its skin can be used to make glue, its liver can be extracted from liver oil, and its bones are good raw materials for processing boneless fish meal. Yellow anglerfish is an export variety, its English name is Angler, and it is exported to the country and region: France. The export ports are: Shandong, Liaoning, Hebei, Tianjin, and Jiangsu.
Protect wild animals and eliminate game.
Maintaining ecological balance is everyone's responsibility!