Owstoni's sharpnose shark (scientific name: Mitsukurinidae owstoni), also known as Owstoni's sharpnose shark, Owstoni's sharpnose shark, sharpnose shark, goblin shark (goblin is an ugly monster in Western folklore that likes to play pranks), is the only species under the family of sharpnose sharks (also known as sharpnose sharks or Mitsukurinidae), and is a deep-sea shark. They were first discovered in the waters of Japan.
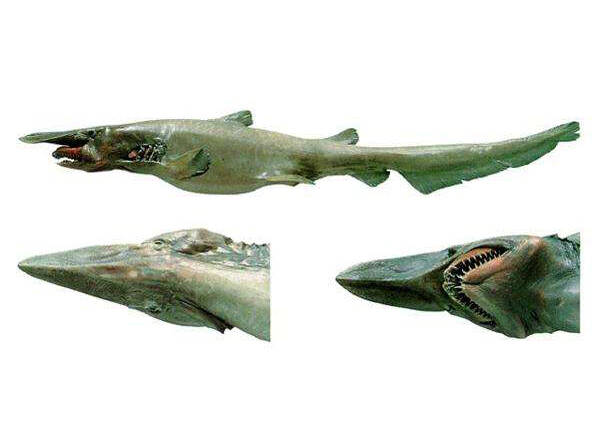
Generally, sharks have well-developed muscles, move quickly, agilely, and are extremely ferocious. However, the muscles of the European sharpnose shark are soft and weak, and other characteristics of its body also indicate that it moves slowly. Such sharks will not pose a threat to humans, and it is also difficult to chase prey. Of course, the European sharpnose shark is not a vegetarian. Checking its stomach content shows that it feeds on bony fish, squid, and crustaceans. It swims slowly on the seabed, using its long snout like a metal detector to search for prey. It scans the seabed and when it detects a small fish, crab, or squid, it suddenly extends its jaws and bites the prey. Its teeth are very sharp, and it can swallow the prey whole after biting it.
The European sharpnose shark preys on different species of creatures in the deep sea. They mainly feed on squid, crabs, and deep-sea fish. Little is known about their life and reproductive habits, and they have few enemies. Therefore, the World Conservation Union does not classify them as endangered species.
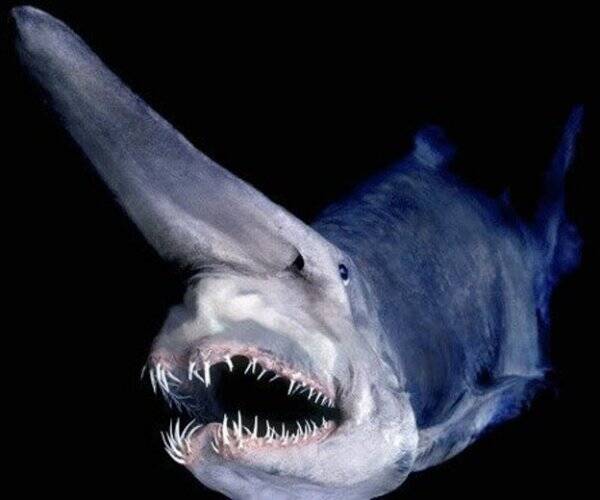

The liver of the European sharpnose shark can account for 25% of its body weight. It is still unknown why their liver is so large. When it is trapped in a fishing net and struggles to get out, it will swell up through the changes in its own body pressure similar to that of a fish bladder, and finally explode into large and small pieces. Until now, no country in the world has caught a complete European sharpnose shark. What people usually see are only fragments of the body of the European sharpnose shark, with jagged edges, very much like the appearance of broken bricks or porcelain. Their thick skin and flesh are rarely tough and elastic, especially the fish skin, which is as hard as ceramic products. The pieces of devil shark after the explosion are like a piece of porcelain that we usually break, and the broken edges can be pieced together exactly.
At present, nothing is known about the reproduction of the European sharpnose shark. Although no pregnant European sharpnose shark has ever been caught, as a member of the order Porphyria, it is estimated that they are also ovoviviparous. Their fertilized eggs will hatch in the mother's body, and they are already a baby shark when they are born.
The European sharpnose shark is a high-level carnivorous creature. It also has different parasites both outside and inside the body. Two new roundworms, called Litobothrium amsichensis and Marsupiobothrium gobelinus, were found in specimens of European sharpnose sharks in Australia.
The World Conservation Union lists them as "low risk" species.
Protect wildlife and eliminate game.
Maintaining ecological balance is everyone's responsibility!