my country is rich in forestry resources and occupies a vast area. However, there are a large number of pests and diseases in the forest, with more than 8,000 different pests and diseases, of which about 100 have repeatedly caused serious damage. There are many insects that harm trees, including the following 10 forest pests, which pose a serious threat to the growth and development of forests: pine wood nematode, glabripennis, American white moth, powerful bark beetle, punctatus punctatus, spring looper, pine sawyer, etc. Let's learn about them together.
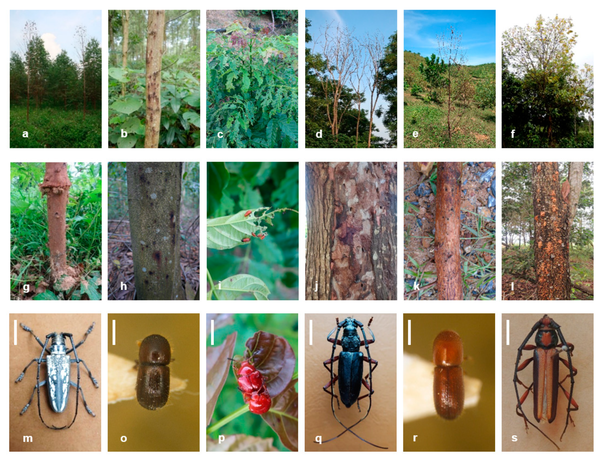

These forest pests are destructive and can cause serious waste and loss of forest resources. Timely discovery and effective prevention and control of these pests are crucial to maintaining and protecting forest health. Therefore, understanding these pests and implementing preventive measures play a key role in maintaining the sustainable development of national forest resources.
1. Pine wood nematode (first-level harmful forest pest/fast reproduction/withering and death of parasitic trees)
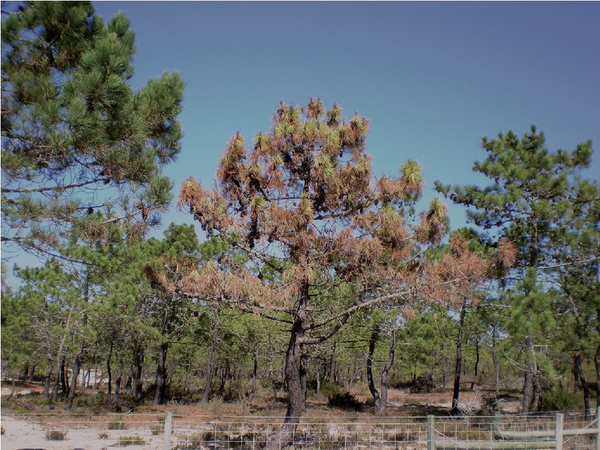

Pine trees with typical symptoms of pine wood nematode damage
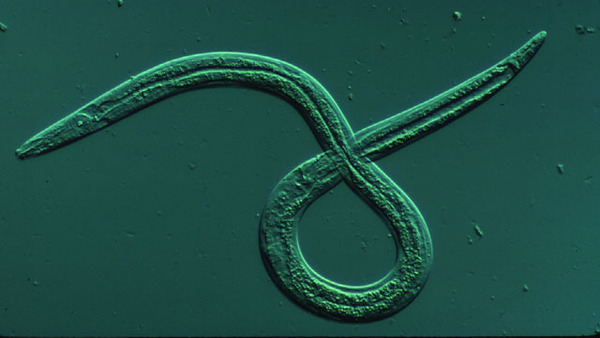
Among forest pests, pine wood nematodes are one of the most harmful. These pests are widely distributed in many countries, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, South Korea, Japan, Portugal, Spain, China, etc. Pine wood nematodes can parasitize more than 70 species of conifers. At a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius, the nematodes can complete a generation of life cycle in just 3 days. They can cause the entire host tree to die quickly, forming the so-called pine wood nematode disease. This disease spreads quickly and is extremely difficult to prevent and control. It has caused large-scale pine tree deaths in China, Japan and South Korea, causing serious impacts on local ecological security. At the same time, this has also had a huge impact on the market for pine wood panels and ornamental pine wood, and has become one of the important factors affecting global economic trade.
2. Longhorn beetle (secondary hazardous forest pest/causing the whole plant to die)
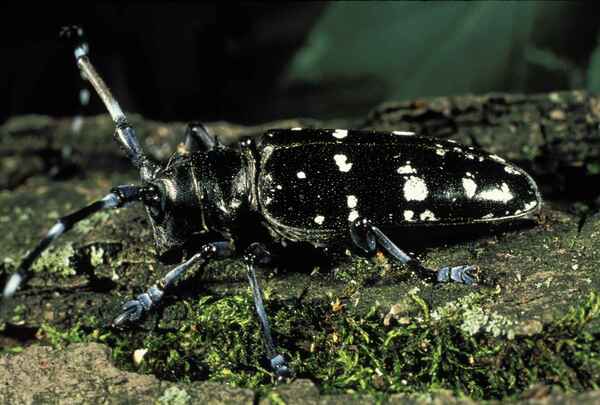

Longhorn beetles occupy an important position in the detection of common forest pests and diseases. Their adults usually have the habit of supplementing nutrition and like to gnaw on the tender branches and bark of trees, causing the death of branches and branches. Every year, the losses they bring to forestry far exceed fires. As an important member of the longhorn beetle family, the longhorn beetle undertakes important tasks in forestry. When the damage is relatively minor, it will lead to a decline in wood quality; when the damage is severe, it will cause tree tip death, which is easy to be broken by wind, leading to the death of young trees, affecting the overall tree vigor, and causing serious damage to the forest.
The glabripennis beetle mainly harms many tree species such as sycamore, willow, poplar, elm, maple, and maple. During the breeding season, the damage caused by these pests is particularly serious.
3. American white moth (secondary hazardous forest pest/worldwide quarantine pest "smokeless fire")
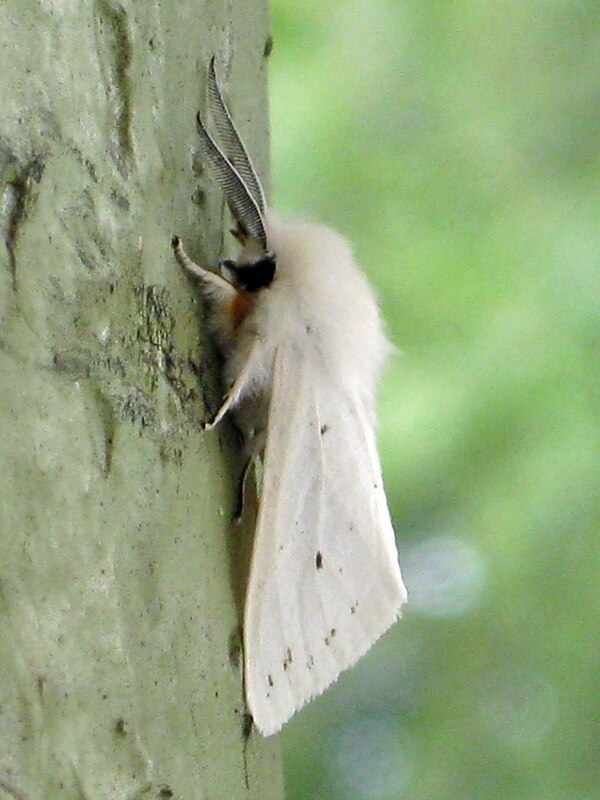

The American white moth is also a very harmful existence among common forest pests and diseases. This pest has extremely strong reproductive capacity, adaptability and transmission speed, especially after the female moth lays eggs in spring, the number of larvae can reach hundreds of millions by the time the third generation of larvae reproduces. In addition to using various means of transportation and logistics to spread, adults can also fly, and the speed of spread is astonishing.
The diet of the gypsy moth is very wide and amazing, with up to 636 host plants. Once serious damage occurs, it can completely eat the leaves of the host plants and even gnaw on the bark, thereby weakening the resistance and stress resistance of the trees and causing serious impact on the growth of forests. Sometimes it even invades farmland, causing serious consequences such as reduced production and even complete crop failure. Therefore, the gypsy moth is called "smokeless fire", which shows how great its harm is.
4. The powerful bark beetle (secondary hazardous forest pest/cause death of damaged trees)
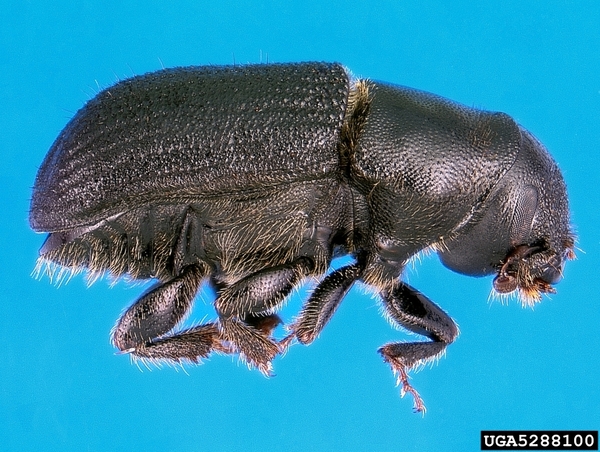

The powerful bark beetle (dù), also known as the red lip bark beetle, is listed as one of the top ten pests in forestry. Except for the wintering period, the activities of adults can be seen in the forest throughout the year. The locations where the adults and larvae of this bark beetle infringe on trees include the phloem tissue at the base of the trunk and the roots. When the damage is serious, the tunnels formed by the larvae will connect together and extend to the phloem tissue of the main lateral roots, causing the death of the damaged trees.
The powerful bark beetle causes damage to almost all pine species in North America, and occasionally to larch and fir species. It is speculated that the introduction of this pest may be related to the introduction of wood from the United States to Shanxi in the late 1980s. Unlike the situation in North America, in the affected areas, the powerful bark beetle not only targets weak trees, but also attacks healthy trees, resulting in the death of a large number of local host plants.
5. Dendrolimus punctatus (Historical forest pest in my country/induces pine caterpillar disease)

Pine caterpillars are one of the most notorious and long-standing pests in the world, especially in China, where millions of hectares of pine forests are attacked every year, causing huge losses to the economy and the ecological environment. Among them, Dendrolimus punctatus is one of the most destructive species, also known as hairy insects or caterpillars, which mainly harms Pinus punctatus, but also affects Pinus thunbergii, Pinus elliottii and Pinus taeda. As one of the most serious forest pests in China's history, the pine caterpillar is mainly characterized by eating pine needles. When it breaks out on a large scale, the entire pine forest may be completely destroyed by the pest in just a few days. From a distance, the forest area appears to be withered and burnt, as if it has been burned by fire.
The growth of pine forests damaged by pine caterpillars may be affected at the least, and the pine trees may die completely at the worst. In addition, after the pine caterpillars damage, it is easy to attract other harmful insects such as pine sawyer beetles, pine longitudinal pit cutter beetles, and pine white star beetles to further invade, causing a large area of pine trees to die.
6. Spring looper (Second-level hazardous forest pest/overeating)

The common forest pest, spring looper, commonly known as walking song, hanging ghost, hanging nematode, etc., has a wide distribution range. Its larvae mainly feed on the young shoots, young leaves and flower buds of the host plant. They have a huge appetite and can cause disasters in large-scale outbreaks. In addition to the damage to fruit trees such as apples, sand apples, and pears, the damage to trees such as sedge, elm, sand date, poplar, poplar, and willow is more serious. In the year of large outbreaks, spring loopers not only harm fruit trees around fruit trees, but also damage the leaves of nearby plants such as wheat, corn, alfalfa, grapes, and walnuts.
In Xinjiang, large-scale prevention and control by aircraft is required every year. For example, in 1976, the spring looper broke out in the Manas Plain Forest Farm in Xinjiang, causing the leaves of 10,000 mu of elm forest to be completely devoured in early May, leaving them bare and leafless. The larvae spun silk and made webs to hang in the forest, making it impossible for pedestrians to pass through.
7. Monochamus alternatus (Secondary Harmful Forestry Pests/Forestry Quarantine Pests)
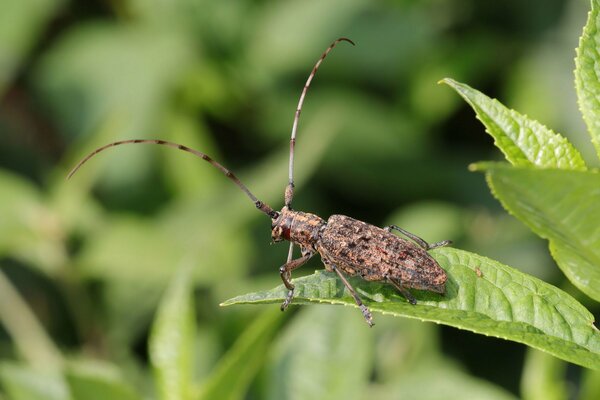

Monochamus alternatus is one of the common forest pests and is considered an important forestry quarantine pest. Its larvae attack the phloem and xylem of pine trees, destroy the conductive tissues, hinder the normal transportation of water and nutrients, and cause the wood to die. In the process of feeding and obtaining nutrition, the adults gnaw on tender branches and may carry pine wood nematodes in their bodies. These nematodes further damage the pine trees and infect the wounds, resulting in stunted growth and eventually large-scale death.
If infected trees are cut down but not moved out of the forest area in time, and if they are not debarked in the summer, they will soon be attacked again by pine beetles. The migration distance of adult pine beetles is generally between 1.0 and 2.4 kilometers.
8. Pine scale (Secondary Harmful Forestry Pest/Forestry Quarantine Pest)

In China, scale insects pose a serious threat to garden plants, with more than 600 species of scale insects harming these plants. These pests are covered in a thick wax layer, making prevention and control extremely difficult, so they are regarded as the top problem among the "five small pests" in the garden industry. Among them, pine scale is an important scale insect that mainly harms the needles, twigs and cones of pine trees.
Pine scale insects suck sap from the leaf sheaths or needles, twigs, and cones of the host plant, which inhibits the growth of needles and twigs and seriously affects the lipid-forming organ function of the pine tree and the photosynthesis of the needles. The affected parts will show symptoms such as discoloration, blackening, shrinkage and rot, and the needles will fall off and turn yellow. In severe cases, the new branches of the pine tree will become shorter and yellow, and may even cause the entire pine tree to die.
9. Plane tree square-winged web bug (secondary hazardous forestry pest/strong vitality)

Pests that damage trees are really a headache. I would like to nominate the plane tree square-winged web bug, which is a very serious pest to trees. It can cause trees to shed leaves prematurely, interrupt growth, and even weaken the tree to death. Worse still, the sycamore bug also carries dangerous pathogens, indirectly causing greater potential harm to trees.
The adult lifespan is only about one month, but their reproductive capacity is amazing. Each adult can lay 200 to 300 eggs, and 4 to 5 generations can occur each year. Moreover, this insect is relatively cold-resistant, with a minimum survival temperature of minus 12.2 degrees Celsius. They often hide under the bark of the host tree or in the cracks of the bark during the winter, and can also spread over short distances with the help of wind or flying, or even over long distances with seedlings or logs with bark. In addition, the sycamore bug will invade indoors in groups, causing trouble to the normal lives of residents.
10. Lishan Longhorn Beetle (Secondary Harmful Forestry Pest)
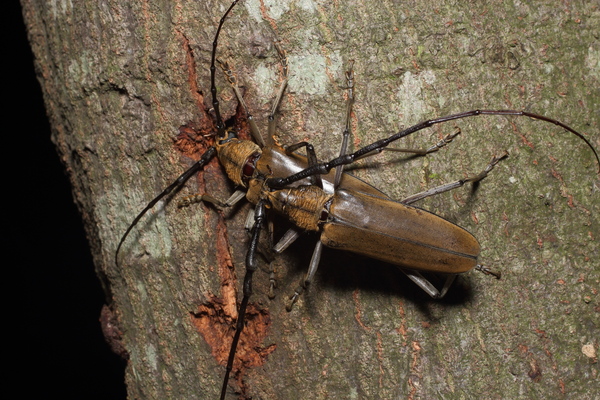

Lishan Longhorn Beetle, also known as Alpine Longhorn Beetle, is one of the common insect pests of trees in my country. It is widely distributed in more than 20 provinces including Taiwan, especially in Jilin, Liaoning Province and Inner Mongolia. These pests mainly damage the host wood by larvae boring into it, and the degree of damage is very serious.
When slightly infected, Lishan Longhorn Beetle will cause a large amount of wood to lose its craft value, causing heavy losses to the economy. In severely affected forests, most of the branches of the host tree crown will die, and the trunks will be full of holes. The overall tree is weak and easily broken by the wind, causing a large number of fallen trees. Severely affected trees can only be used as low-quality firewood or charcoal, and the loss is extremely serious.
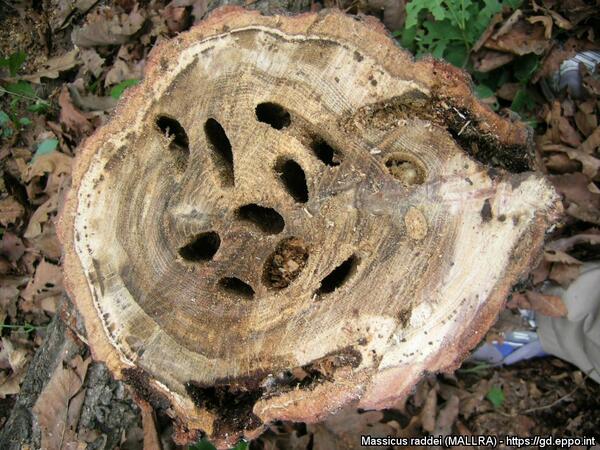

The chestnut mountain longhorn beetle mainly harms 30-year-old oak trees, especially those in the high growth period and the largest diameter growth stage. The trunks of the affected oak trees are full of longhorn beetle tunnels, the branches of the affected trees are withered, and fallen trees can be seen everywhere.
Other common forest pests:
Apple moth, mulberry longhorn beetle, vertical pit cutting tip borer, red pine tip moth, double hooked heteropterygium long borer, hibiscus cotton mealybug, small round-breasted mealybug, poplar wedge longhorn beetle, pine bee, big bag moth, brown-edged green spiny moth, Sophora japonica looper, tea bag moth, clouded longhorn beetle, elm blue leaf beetle, white wax scale, Korean hairy ball scale, round shield scale, water wood scale, Cole's white shield scale, mulberry white shield scale, red spider, spotted wax cicada, boxwood silk borer, wetland pine mealybug, yellow-spine bamboo locust, Yunnan pine caterpillar, gypsy moth, larch caterpillar, Japanese pine stem scale, wetland pine mealybug, poplar fan boat moth, elm purple leaf beetle, yellow-brown tent caterpillar, larch aphid, etc. ……

Spotted Lanternfly
animal tags: Pests
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.