In 1980, Academician Cao Wenxuan questioned the concept of fauna complex at the annual academic meeting of the Chinese Ichthyology Society, believing that it has no boundaries in time and space and should be abandoned. In 1998, Dr. Liu Huanzhang and others published the paper "Distribution Pattern of Freshwater Fishes in China and the Origin and Evolution of Freshwater Fishes in East Asia" in the Journal of Zoological Taxonomy. They pointed out: Chinese freshwater fishes are dominated by carps everywhere. Therefore, the origin and evolution rules of carp fishes reflect the origin and evolution rules of freshwater fishes in East Asia. It is proposed that except for schizothorax, the distribution of extant carp fish groups in China can be divided into 6 types:
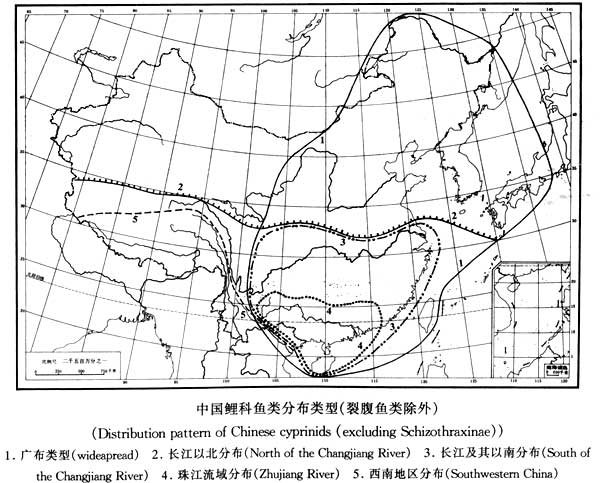
1. Widespread distribution: including Heilongjiang, Yangtze River, Pearl River and other water systems, some species even reach Japan and South Korea, such as Chinese crucian carp, bream, etc.
2. Distribution north of the Yangtze River: including the Heilongjiang, Yellow River, Irtysh River and other water systems, such as the genus Erythium and the genus Yaluo.
3. Distribution in and south of the Yangtze River: Mainly in the areas south of the Yangtze River and east of the Red River, such as the genus Barbelia and the genus Roundnose.
4. Distribution in the Pearl River Basin: including Zhejiang and Fujian areas, such as Yaoshan carp, Tang carp, etc.
5. Distribution in the southwest region: mainly the Red River and the water system west of it, such as some genera and species of the subfamily * and the subfamily Dauphinae.
6. Other regional distributions: The most important ones are the distribution in the Yunnan Plateau lakes and the Yangtze River Basin.
For freshwater fish in East Asia, the Red River is a very important water system. The westernmost limit of many East Asian species is in the Red River. The distribution pattern is the same whether at the genus level or the species level, but at the species level, the proportion of other regional distributions is higher, while at the genus level, the proportion of widespread types is much higher. After removing the widespread type, this distribution pattern shows a large difference between the north and south of the Yangtze River, and the number of species shows a gradual decreasing trend from south to north.
Although all components of the extant fish fauna appeared in the Pliocene, the glaciers of the Fourth Period had a greater impact on the formation of the distribution pattern of extant fish. Mainly manifested in two aspects:
1. During the Quaternary Ice Age, species as a whole retreated southward, and fish fauna exchanges occurred between different water systems; during the interglacial period, different species spread northward, resulting in the existence of widespread species and subrelict species, such as some widespread species. The distribution of the species in the Heilongjiang River Basin and the distribution of the species in the Yangtze River Basin;
2. Changes in glacial and interglacial periods have also caused the exchange of fish fauna among the upper, middle and lower tributaries of large rivers such as the Yangtze River, and contributed to the occurrence of species differentiation events in the upper, middle and lower reaches, forming many regional Distribution, such as the differentiation of species such as Protognathus bream in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.