The fascinating world of dinosaurs contains an endless variety of remarkable species, each with its own adaptations and evolutionary strategies. Among them, one of the largest and most diverse groups was undoubtedly the herbivorous dinosaurs. These plant-eating giants roamed the Earth throughout the Mesozoic Era, feeding on a wide variety of leaves and plants, and developing unique anatomical features to survive in a world full of dangerous predators.

Thanks to decades of paleontological research—studying fossilized bones, footprints, and even eggs—we now have a detailed understanding of the names, physical traits, and lifestyles of these incredible creatures.
In this article, we will explore the main characteristics, diet, types, and representative species of herbivorous dinosaurs, along with some fascinating facts.

To survive alongside fierce carnivorous dinosaurs, plant-eaters evolved special physical structures and defense mechanisms:
Massive body size and weight – They ranged from smaller species of around 0.5 tons to colossal giants weighing up to 123 tons. Their large size often made them slow but gave them a natural deterrent against predators.
Neck structure – Long and strong necks allowed them to reach high treetops or low-growing vegetation.
Teeth and chewing ability – Teeth were typically broad and not sharp, designed for stripping leaves and crushing plant material. Many could not chew efficiently and swallowed leaves whole, relying on their stomachs for digestion.
Large stomach and digestion – Some could eat up to 200 kilograms (440 pounds) of plants per day. Many species swallowed small stones (gastroliths) to help grind tough plant fibers.
Time period – Herbivorous dinosaurs lived during the Mesozoic Era (about 252 to 66 million years ago), which included the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods—often called “The Age of Dinosaurs.”
Their diets consisted entirely of plant-based materials:
Tender leaves and shoots from tall trees (like conifers and cycads)
Low-lying shrubs and ferns
Ground-level vegetation
Harder plant parts, such as pine cones and needle-like leaves
Differences in neck length, beak shape, and tooth structure determined which plants each species could eat. For example, long-necked species fed on treetop foliage, while beaked species could pick fruits and soft shoots with precision.
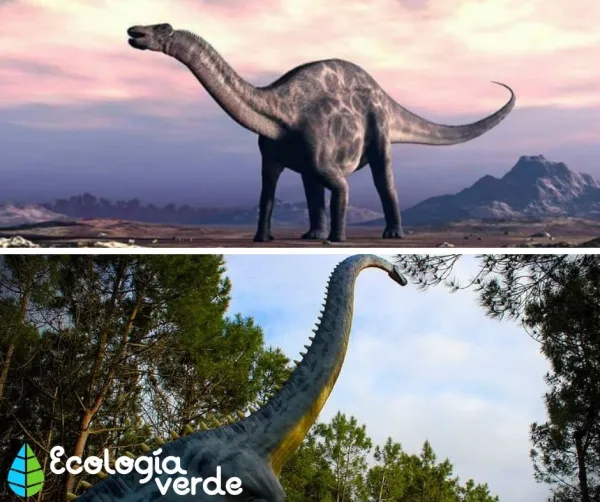
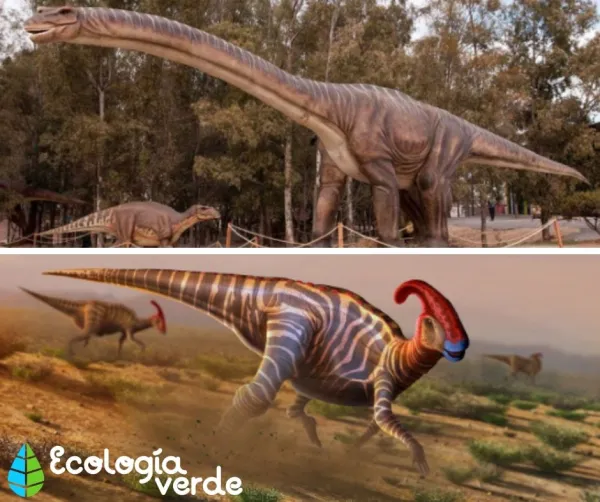
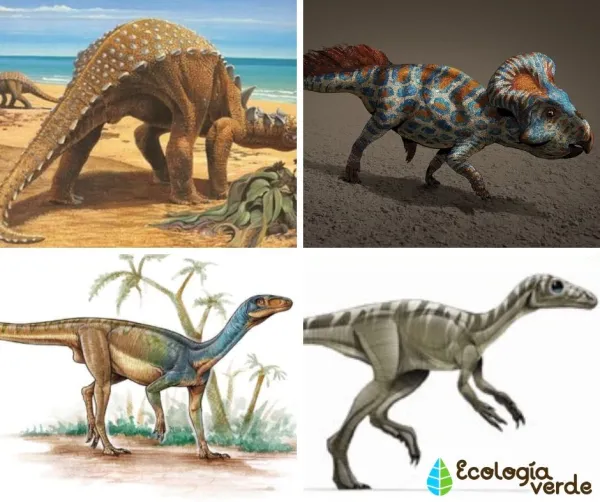
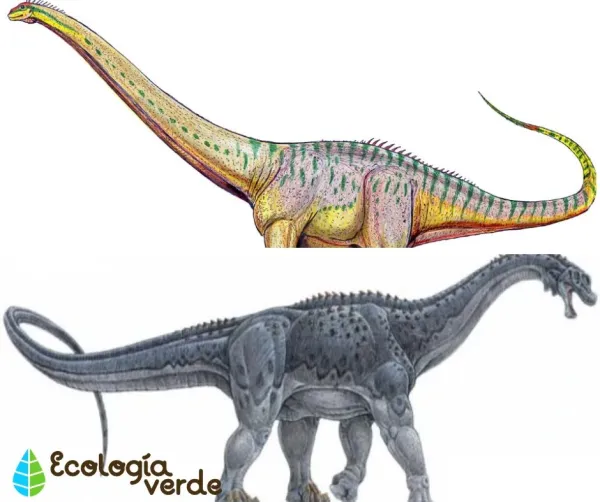
Sauropods
Walked on four legs, with hips similar to lizards.
Had long necks, long tails, and enormous bodies.
Teeth were adapted for stripping leaves rather than chewing.
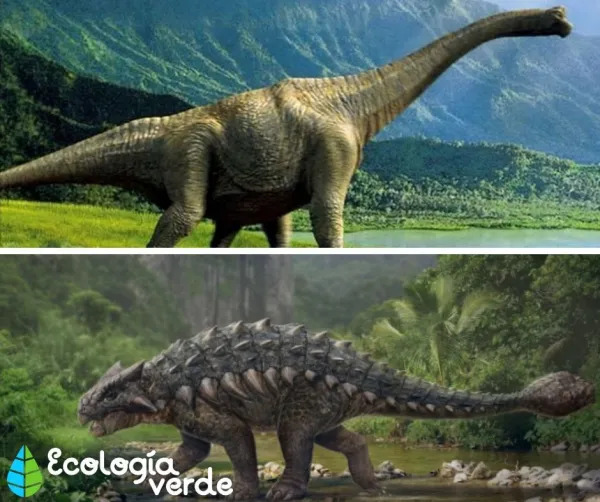
Examples: Diplodocus, Brachiosaurus, Argentinosaurus.
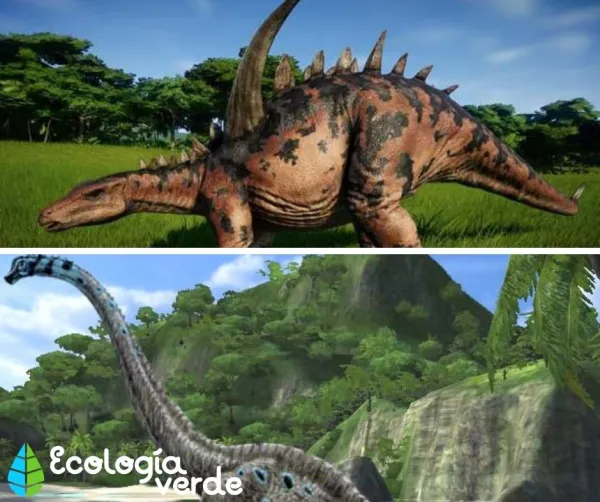
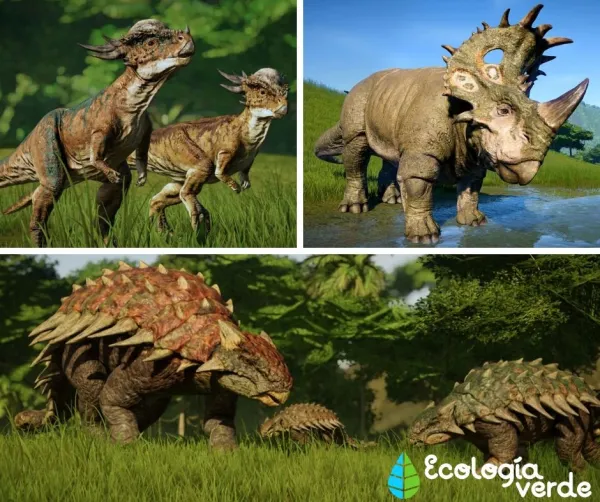
Ornithischians
Hip structure similar to modern birds; some could walk on two legs.
Many had beak-like mouths and specialized teeth for cutting and chewing.
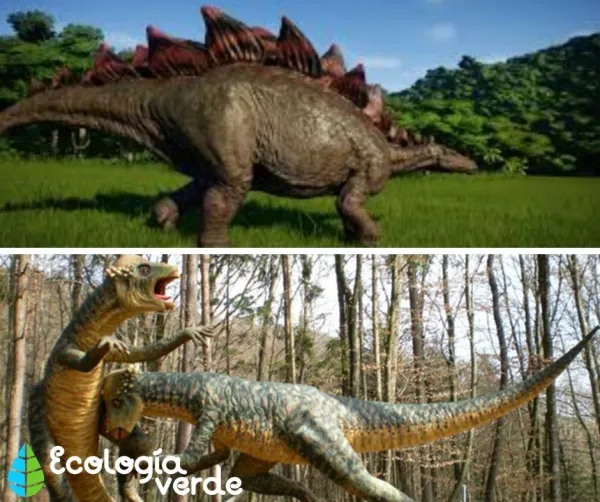
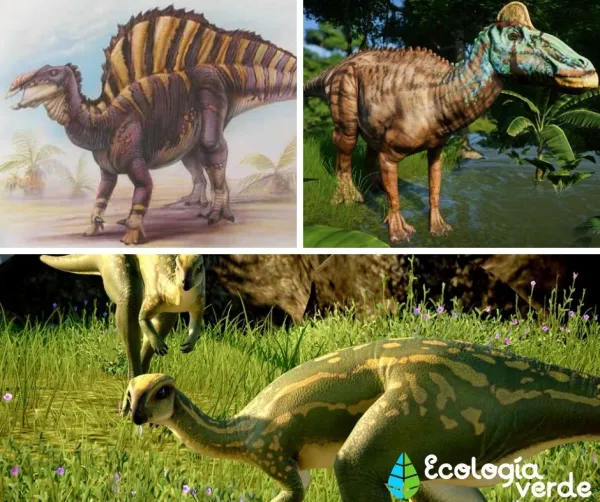
Examples: Triceratops, Stegosaurus, Parasaurolophus.
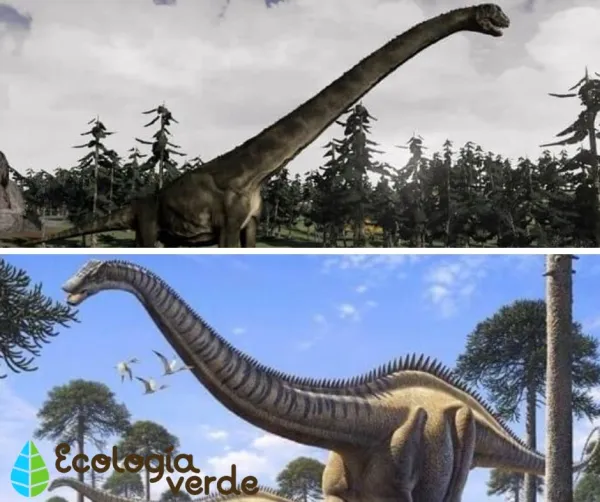
Diplodocus – Up to 36 m (118 ft) long, with a whip-like tail and long neck for reaching high leaves.
Brachiosaurus – Forelegs longer than hind legs, allowing it to browse at great heights.
Stegosaurus – Recognizable by two rows of bony plates along its back, possibly for defense or temperature regulation.
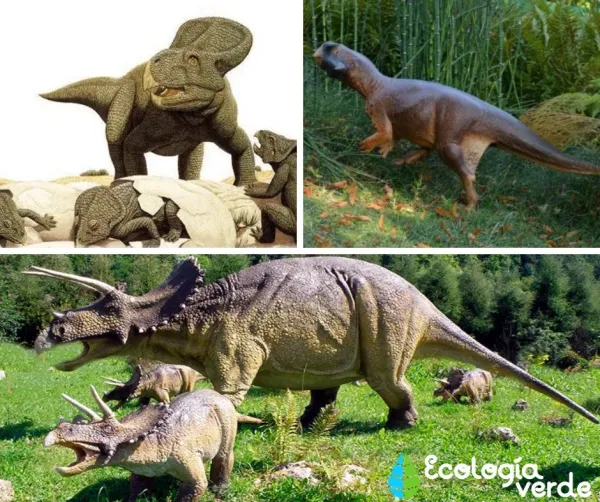
Protoceratops – Small-bodied (about 2 m), often lived in family groups, fed on low vegetation.
Triceratops – Had three horns on its head, likely used for defense and foraging.
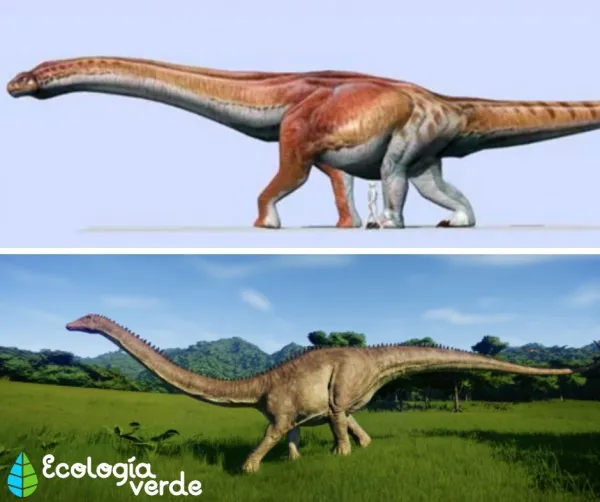
Patagotitan Mayorum – One of the largest known dinosaurs, about 37 m (121 ft) long.
Brontosaurus – Weighed about 30 tons, with a long tail used for defense.
Apatosaurus – Similar to Brontosaurus, used gastroliths to aid digestion.
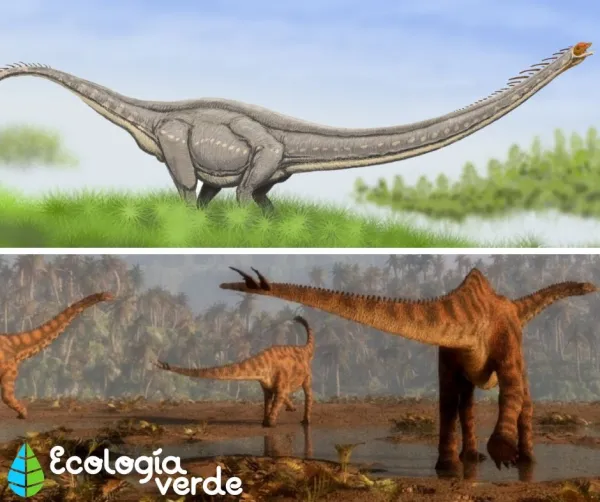









Largest herbivore – Amphicoelias (about 50 m / 164 ft long)
Smallest herbivore – Lagosuchus (about 60 cm / 2 ft long)




In the Jurassic Park and Jurassic World films, many herbivorous dinosaurs have appeared, including:
Brachiosaurus
Triceratops
Ankylosaurus
Stegosaurus
Parasaurolophus
These cinematic appearances help people visualize the grandeur of these prehistoric giants.

Herbivorous dinosaurs were essential to prehistoric ecosystems, shaping plant evolution and distribution. Their sheer variety and adaptability make them one of the most fascinating subjects in paleontology. Studying them not only reveals the glory of ancient life but also reminds us of the fragility of modern ecosystems.
Bibliography
Salgado, L. (2010) The Sauropod Dinosaurs of the Cretaceous of Patagonia: Evolution and Paleobiology. Biodiversity and Environment Research Institute (Argentina).
Norman, D. (1992) Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs: A Complete and Exciting Journey Through the World of Dinosaurs. Susaeta Publishing House, 50-92.
animal tags: herbivorous dinosaurs
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.