Silty coasts are mainly composed of fine-grained silt. Its average particle size is only 0.01-0.001mm. my country's muddy coasts are distributed in Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay, Laizhou Bay in the Bohai Sea and the coast of the North Jiangsu Plain in the Yellow Sea. Silty coasts are closely related to rivers, and rivers are the life source of silty coasts. Where rivers exist, silt coasts thrive; without rivers, silt coasts shrink and recede. The above-mentioned silty coasts in my country are related to the Liaohe River, Yellow River, Haihe River, etc. that enter the sea here. The Yellow River, in particular, transports huge amounts of sediment into the sea, forming a vast and flat silt coast along the coast.
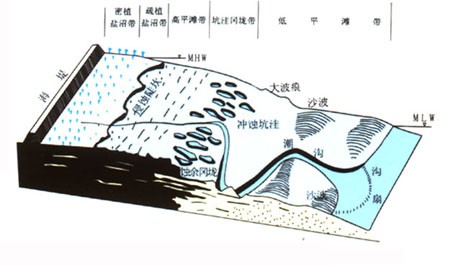
Schematic diagram of tidal flat landform zoning

Haizhou Bay is located at the junction of Shandong and Jiangsu. The southern part is affected by sediment, and the coastal sea area is lighter in color.

Laizhou Bay on the south coast of the Bohai Sea faces Liaodong Bay. It opens to the northeast and is located at the mouth of the Yellow River on the left.
my country's muddy coast is vast and vast, with a slope of about 0.5‰. The width of the tidal flat between the high and low tide lines is generally 3-5 kilometers, and can be more than 10 kilometers wide. The muddy beach near the high tide line is called high tide beach. It is the highest point of the entire tidal flat and the place farthest from the sea. Generally, the seawater cannot rise to this area during high tide. Only when a spring tide or storm surge occurs, the tide can submerge it. The exposed beach surface here is affected by strong evaporation, and the surface layer dehydrates and shrinks, forming many irregular cracks. These cracks resemble the patterns on turtle shells and are called turtle cracks. The longer the beach surface is separated from the sea water, the more obvious the cracking phenomenon will be, and the width of the cracking zone can reach several hundred meters. When a spring tide occurs, the seawater reaches the high tide beach, the turtle cracks disappear, and the beach surface returns to a moist and smooth appearance.

Tidal hooks are well developed off the east coast of Jiangsu, which is a major feature of tidal flats on muddy coasts.

The unique landscape on the tidal flats of the muddy coast
This change is sometimes very rapid. On the silty coast on the west coast of Bohai Bay, when northerly winds blow on the sea surface and the tide coincides with the high tide, the seawater floods the beach and the cracks there disappear. When you wake up overnight and go to the shore again, the surface of the beach there has changed drastically, and there are no traces of turtle cracks anymore. However, when the spring tide passes and the sea water recedes, the high tide beach near the coast will not see sea water for many days, and turtle cracks will form on the beach surface.

Broad, flat plain coastal tidal flats
Tides are the main force shaping muddy coasts. The current flowing into the bay from the vast sea brings sediment to the bottom of the bay. At low tide, the current carries some sediment into the sea. In the process of the tide flowing in and out of the silt beach, strong currents wash away the coast and beach surface, while weak currents deposit sediment, heighten the beach surface and widen the beach surface. The effect of waves plays a secondary role. It can cause erosion on the coast and beach surface in local areas, causing the coast to recede and forming many potholes on the beach surface.

Zhejiang muddy coast

Hebei muddy coast
There is another interesting phenomenon near the silty coastline, which is the accumulation of countless large and small mud pellets. The mud balls are like round mud balls made by children with their hands. The small ones are 3 centimeters in diameter and the large ones are 6 centimeters in diameter. Some mud balls also contain shell fragments. These clay balls are not the work of children, but the work of waves. In summer and autumn, spring tides constantly wash away the cracked beach surface. The peeled off clay blocks of different sizes rolled back and forth up and down the coastline with the ensuing waves, and occasionally adhered to some shell fragments. The clay lumps rolled rounder and rounder, and finally became mud balls. After the tide recedes, the mud balls quietly pile up one by one near the high tide line. Tides in winter are smaller than in summer, and there are generally few large tides like seawater floodplains. The seawater that comes in along the tidal gully deposits the sediment it carries, burying the mud pellets formed in summer and autumn. In winter and spring, the mud balls near the muddy coast seem to have been buried, and none of them can be seen. Through field observations, scientists have revealed the secret of the mud balls - the children who make the mud balls and bury them are the familiar waves.

The muddy coast at low tide
On the vast tidal flats of the silty coast, there are some tidal gullies crisscrossed. They are channels through which the tide flows in and out. During high tide, seawater first flows toward the shore through these tidal gullies, and at low tide, the seawater in the tidal gullies drains last. The tidal gullies on the beach are like river channels on the Great Plains, cutting the beach surface. There are fishing boats entering and exiting the wider and deeper tidal troughs. The silt layer in the tidal ditch has extremely high water content and very little bearing capacity. When people walk on silt flats and pass through tidal ditches, they are in danger of falling into the silt and being drowned. The tidal ditch became an obstacle for people walking on the silt flats. Because walking on the silt beach is difficult and life-threatening, there are few people on the silt beach.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.