Someone has made statistics and found that there are more than 500,000 species of living things on the earth. Living things can be divided into three categories: animals, plants and microorganisms. According to some statistics, there are more than 180,000 kinds of animals and 20,000 kinds of plants in the ocean, totaling more than 200,000 kinds. There seems to be less variety of life in the ocean than on land. However, until today, we still know very little about the biological world in the vast ocean, and we cannot accurately count the number of marine life species at all. However, we can say with certainty that most species of life on land appear to be found in the ocean. Another interesting fact is that there are more plant species than animal species on land, while the opposite is true in the ocean, where there are more animal species than plant species.
1. The three-round fish of crawling, swimming and flying is a leopard bream

Leopard bream
Fish cannot live without water. This sentence shows that fish spend their whole lives in water, so swimming in water is their instinct. However, in addition to swimming in the water, some fish can also "fly" in the air, such as aquarium/flying-fish.html">flying fish; some can also jump on the beach, such as mudskippers. Able to "fly" and jump, these fish only have two abilities. The leopard bream has three abilities: crawling, swimming, and flying. It can be said to have the ability to move in three dimensions: "sea, land, and air."
The three rays of the leopard bream's pectoral fin are independent and can move freely. It uses these three fins to crawl freely on the vast seabed. At the same time, these independent fins are also the tactile organs of the leopard bream, and they can be used to sense the surrounding environment on the seabed. Due to the special functions of these three independent fins, the muscles that drive these fins are particularly developed. This is the result of natural selection and natural selection - organs are used and discarded.
When the leopard bream changes from crawling on the seabed to swimming in the water, the pectoral fins and the three independent fins in front of the fins are folded in close to the side of the body to reduce resistance in the water. When the leopard bream's swimming excitement reaches its climax, it rushes out of the water at a very fast speed, then spreads its "double wings" - pectoral fins, and flies in the air. In fact, the "flying" of the leopard bream and the "flying" of the aquarium/flying-fish.html">flying fish are not true wing-beating flights, but only rely on the force of the wind.
2. Fish that can climb trees

Mudskipper
The main respiratory organ of fish living in water is gills. When the fish leaves the water, the gill filaments dry out and stick to each other, preventing breathing, and life ceases. However, there is a kind of mudskipper that can adapt to amphibious life living along the coast of my country.
The body of the mudskipper is about 10 centimeters long. It is slightly sideways and has two eyes above its head, like frog eyes, with a wide field of vision. Its gill cavity is large and its gill cover is sealed to store a large amount of air. The epidermis in the cavity is covered with a network of blood vessels, which plays a role in breathing. Its skin is also covered with blood vessels. Blood passes through the extremely thin skin and can directly exchange gases with the air. In addition to functioning as a fin in the water, its tail fin is also an auxiliary respiratory organ. These unique physiological phenomena enable them to leave water and live in the air for a longer period of time. In addition, the left and right pelvic fins of the mudskipper merge into a suction cup shape, which can be attached to other objects. The well-developed pectoral fins are arm-like, much like the appendages of higher animals. When encountering enemies, it can move faster than a human walking. Mudskippers, which live in tropical areas, often jump around on the beach to catch food at low tide. They prefer to climb on the roots of mangroves to catch insects. Therefore, people call it "the fish that can climb trees".
3. Fish that can make sounds

The touching whale song
Most people think that all fish are mute, which is obviously not true. Many fish make a variety of surprising sounds. For example: Kangji carp can make a "bark" sound; the electric catfish's call is like an angry cat; the box fish can make a dog bark; the gill sound of the bream is sometimes like a pig's bark, sometimes like a moan, and sometimes like a snoring; seahorses can It makes a monotonous sound like a drum. Totoabas are known for their calls, which include sounds like rolling, drumming, hummingbirds flying, meowing and whistling. Their calls are particularly common during the reproductive period, for the purpose of swarming.

box fish
Most of the sounds made by fish are caused by bone friction and swim bladder contraction, and some are caused by breathing or anal exhaust. Experienced fishermen can judge the size of the fish school based on the sound made by the fish so that they can lower their nets to catch fish.
4. Double sawfish and large anemone
Neither benefit nor harm, this phenomenon is called commensalism. In the coral reefs of the South my country Sea and the tropical oceans of the world, there is a kind of small fish with bright body colors. Their body surface has bright red and snow-white color bands, which are clear, beautiful and very eye-catching. This kind of small fish is called double sawfish, commonly known as clownfish.

Double sawfish and large anemone
The sawfish often lives together with large anemones and is a typical example of marine animal symbiosis.
Under normal circumstances, any animal that encounters a large anemone will be anesthetized or killed by the poisonous stinging cells in the petal-shaped tentacles of the anemone. But the two sawfishes are an exception. Not only can they move around the large anemone, but they can also shuttle back and forth between the tentacles of the large anemone unscrupulously. The brightly colored sawfish will attract many ferocious carnivorous fish to chase it. At this time, the double sawfish fled and hid among the tentacles of the sea anemone to avoid predators. However, the ferocious fish approaching the anemone's tentacles are anesthetized to death by the stinging cells shot by the anemone's tentacles, and become a delicious meal of the anemone.
On the other hand, because the sawfish moves around the large anemone and between its tentacles, it strengthens the flow of water around the large anemone, allowing the large anemone to obtain sufficient oxygen.
If people take away the anemone, the anemone will be eaten by other fish. The large anemone protects the giant sawfish, and the double sawfish attracts food and brings sufficient oxygen to the large anemone. This pair of mutually beneficial partners is truly an ingenious arrangement by nature.
5. Animals with legs on their heads - cephalopods
Cephalopod is a comprehensive term for many animals, which includes more than 400 kinds of molluscs existing in the world, such as squid, soft fish, octopus, octopus and the less common nautilus. Cephalopods, as the name suggests, are a group of molluscs with legs attached to their heads.

Nautilus
The nautilus is the oldest living cephalopod. The ancient ocean was once its world. During the long evolutionary process of hundreds of millions of years, the nautilus was very conservative and stayed still. It still maintained the appearance of its ancient ancestors and survives to this day. Therefore, it is recorded in the history of zoology as a "living fossil".
Cephalopods are widely distributed in the world's oceans, from shallow seas to deep seas of 3,500 meters, from the surface, middle, bottom to the bottom of the sea, and in cold, tropical and temperate oceans. They can be found everywhere.

The nautilus crawls on the bottom of shallow water about a hundred meters away, while the octopus lives in underwater caves, rock gaps or rocks, and can use the "eight legs" on its head to hold shrimps and crabs with hard shells tightly Cover it and then eat it. Squid and soft fish can use the "funnel" in their abdomen to swim quickly using the recoil force obtained by spraying water, so they are called "undersea rockets". They swim quickly to hunt for food and escape predators. The giant squid living in the deep sea is 18 meters long and weighs about 30 tons. One of its "legs" is 25 centimeters in diameter, as thick as a telephone pole. There are hundreds of suckers on its "legs", and the largest sucker is as big as a dish.
The king squid is not only the "biggest" among cephalopods, but also the largest among all invertebrates. It dares to fight to the death with the largest toothed whale, the sperm whale!
The "dwarf" in the squid family is the fluorescent squid that can glow on the seabed. Its length is only 5 centimeters. The glow squid is small. But he is not the youngest member of the family. The smallest squid is the microfin squid, which is only 1.5 centimeters, as big as a small peanut, and weighs only 0.1 grams. There are suction cups on its back, and the microfin squid uses the suction cups to attach its body to the seaweed to rest. Not only does the octopus have a strange shape, but what’s even more strange is that there are huge differences between male and female individuals. The male is so small that when attached to the female, people often mistake it for a parasite on the female.
6. The mysterious seahorse

Seahorses are fish. They are called seahorses because they have a head that is very similar to a horse's head. It is mysterious because their habits and movements are very strange. Seahorses swim upright, with their heads perpendicular to their bodies and pointing forward. The back of the body, which is very similar to a horse, drags a tapering tail. When eating and resting, the tail can be wrapped around coral or seaweed branches to support the body. The way seahorses reproduce is also unusual. The female seahorse lays her eggs in the male seahorse's pouch, where they are fertilized and hatch into young seahorses.
7. Glowing fish
existIn the ocean world, whether it is the vast sea surface or the bottom of the 10,000-meter-deep abyss, there are all kinds of strange and luminous creatures living there, just like a wonderful "undersea dragon palace", with fish lights and shrimps brightly lit all night long. It is they that bring light to the sunless deep sea and the sea shrouded in darkness. In fact, at least 44% of fish in the dark layer have the ability to emit their own light, so that they can see other objects during the long night, facilitate hunting, and find companions and mates.

Glowing anglerfish
Some fishes emit light, such as the hairtail fish and dragonhead fish in the southeastern coast of my country. The light is emitted by the luminescent bacteria attached to their bodies, while the light emitted by more fishes is emitted by the light-emitting organs of the fish itself.
The Candlelight Fish has multiple rows of light-emitting devices on its abdomen and ventral side, just like rows of candles, hence the name Candlelight Fish. The back of the head of the deep-sea bald fish is flat and covered by a pair of large light-emitting devices, which may play a role in vision.
The luminescence of fish is a biochemical reaction caused by the catalysis of a special enzyme. The luminescent luciferin is catalyzed by luciferase. The luciferin absorbs energy and turns into oxidized luciferin, which releases photons and emits light. This is a special case of chemiluminescence, which only emits light but does not generate heat. Some fish can emit white and blue light, others can emit red, yellow, green and will-o'-the-wisp light, and some fish can emit several different colors of light at the same time. For example, a deep-sea fish has large luminous cheek organs that emit blue and reddish light, while other tiny luminescent spots throughout its body emit yellow light.
The biological significance of fish luminescence has four points: first, to trap food, second, to attract the opposite sex, third, to connect populations, and fourth, to confuse enemies.
8. Electric sea animals

electric ray
We must deal with electricity in our daily lives, but have you heard that some fish also have specialized power-generating organs? At present, there are more than 500 kinds of fish in the world that are known to be able to generate electricity, but only 20 kinds have been studied by humans. Take the electric ray, for example. The electric ray is a fish in the ocean that can generate electricity. It is a common cartilaginous fish along the coast. The electric stingray's power-generating organs are on both sides of the body's midline, and it can emit a voltage of 80 volts, up to 200 volts. Many of the power-generating organs on the electric ray are evolved from muscle fibers into electric plates. There are 2 million electric plates in the electric ray. Although the voltage of a single electric plate is not high, when they are connected in series, a very high voltage will be generated. .
The special abilities of electric fish have long attracted people’s attention. As early as the ancient Greek and Roman times, people used the electricity of electric rays to treat diseases. In the 19th century, the Italian physicist Volta designed the earliest voltaic battery using the electric stingray's power-generating organ as a model. Because this kind of battery is designed based on the natural power-generating organ of electric fish, it is also called an "artificial electric wonder". The voltaic cell was the world's first direct current power source. In recent years, people have imitated the power-generating organs of discharge fish to create "electronic hands" and "electronic legs".
These electronic products manufactured by imitation organisms are used in industrial production and medical rescue, which greatly reduces human labor intensity and improves labor productivity.
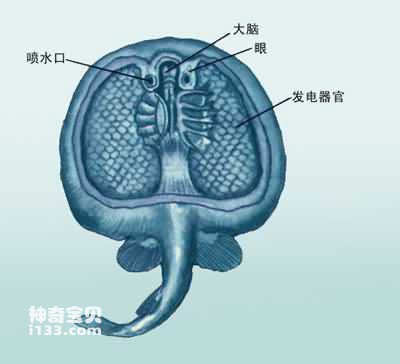
Schematic diagram of electric stingray’s power-generating organ

Schematic diagram of electric ray generating electricity in the sea
9. Be wary of poisonous aquarium/52-marine-animals.html">marine animals

Scorpionfish
There are several kinds of poisonous fish in the ocean: one is a fish with special poison glands in the body, which can produce venom and transport it to the teeth and spines; other fish do not have poison glands, but in the meat, eggs or internal organs Contains toxins; some fish have both toxins. These venoms and toxins can have different consequences: convulsions, damage to the nervous system, brain damage or heart paralysis. In mild cases, there may be a slight burning sensation, while in severe cases, it may be life-threatening.

sculpin
Among all the underwater killers, the most dangerous one is the "stone fish" that lives among coral reefs. Its scientific name is the poisonous scorpionfish. It has an extremely ugly appearance. It is covered with dark brown or grayish-yellow skin and has 12 dorsal fins. Poisonous spines with thick roots often live among rocks in shallow water. When they encounter danger or find prey, they will immediately open all the poisonous spines on their bodies and stab the opponent. These sharp spines can pierce a person's heel, and the victim will soon lose consciousness. If a major blood vessel is punctured, the person will die within two or three hours. Venomous scorpionfish are widely distributed and can be found along the coasts of the Red Sea, the Indian Ocean, and the coastal waters of Australia, Indonesia, and the Philippines. There are also some species of venomous fish in the South my country Sea and the East China Sea.

pufferfish
The lionfish, a close relative of the poisonous scorpionfish, is also a poisonous fish, but it is different from the poisonous scorpionfish in that it looks bright and pretty, has a graceful body, and has 18 poisonous spines on its body. The venomous sting of a lionfish is very powerful. Even a slight sting by it will cause excruciating pain and may even cause you to lose consciousness quickly. If you do not take timely measures, you may die.

man-of-war jellyfish
The angler that inhabits the coast of America is also venomous. There are hollow tubes connected to the venom glands on the two large spines of the dorsal fin and one spine on the gill cover. If you are accidentally hit by these thorns, it will cause pain, vomiting, convulsions, and even loss of consciousness, but the toxin is not fatal.
Finally, let’s talk about the stingray class. The stingray looks strange, with a flat body and a long and slender tail. It has a large stinger that can secrete venom. This is its deterrent weapon. Most stingrays live in shallow waters and often bury their bodies in the sand, so they pose the greatest threat to swimmers and fishermen. If people step on it without paying attention, the fish spines will suddenly pierce into people's feet. The toxin will immediately spread throughout the body, and in severe cases, life may be in danger.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.