When it comes to the animal kingdom, no two noses are quite the same. Some animals have evolved extraordinary noses to help them thrive in their specific environments. From long and slender snouts to highly specialized nasal features, these creatures demonstrate just how diverse nature’s adaptations can be. In this article, we’ll explore 10 animals with unique noses that play a crucial role in their survival, from hunting prey to sensing their surroundings.
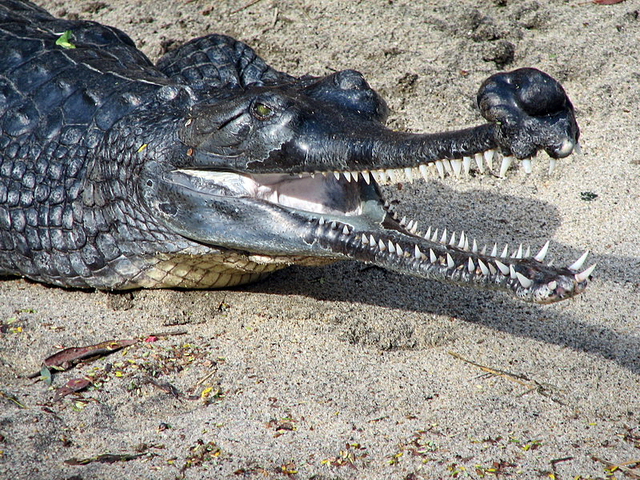

The Gharial, a crocodilian native to South Asia, is instantly recognizable due to its long, thin snout. This adaptation makes it an efficient underwater hunter, particularly skilled at catching fish.
Streamlined Snout: Reduces water resistance and allows for rapid movement, aiding in catching fast-swimming prey.
Highly Sensitive Nostrils: Positioned on top of the snout, enabling the Gharial to breathe while staying mostly submerged.
Specialized Jaws: Filled with sharp teeth, perfect for gripping slippery fish.
As a top predator in freshwater ecosystems, the Gharial helps maintain ecological balance. Unfortunately, habitat destruction has placed it on the endangered species list.
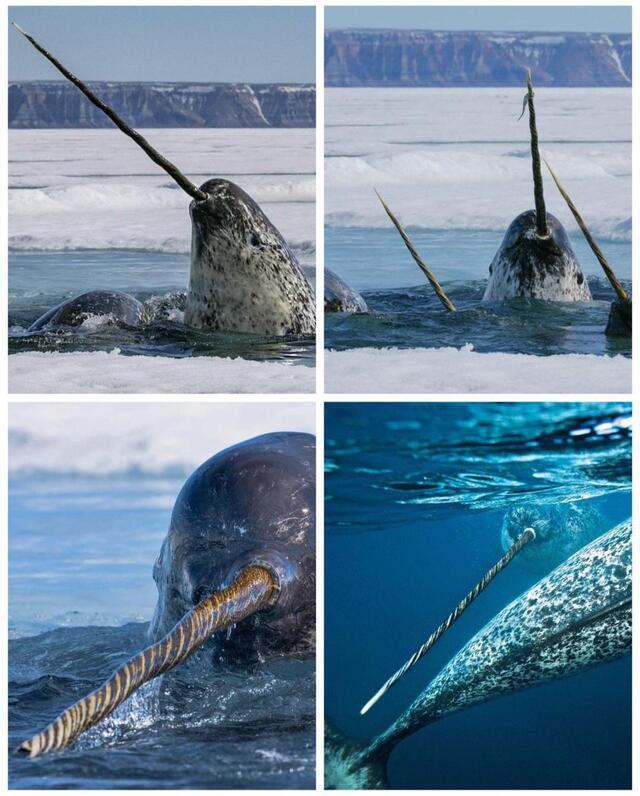

The Narwhal, often called the "unicorn of the sea," has a long, spiral tusk that is actually an extended tooth, growing up to 10 feet (3 meters) long. Scientists believe this unique feature serves multiple functions.
Environmental Sensor: The tusk contains millions of nerve endings, allowing Narwhals to detect changes in temperature, salinity, and water pressure.
Mating Signal: Males with larger tusks may have an advantage in attracting mates, making the tusk a possible sexual selection trait.
Hunting Assistance: While not directly used to spear fish, the tusk may help in disturbing prey or navigating icy waters.
Narwhals primarily hunt squid, fish, and shrimp, playing a key role in the Arctic marine food web.
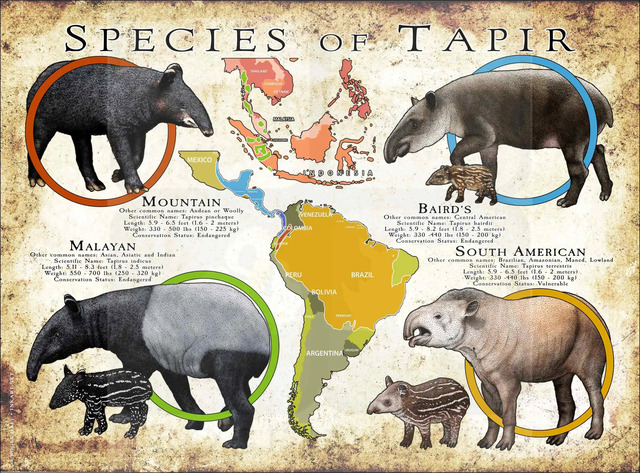

Tapirs resemble a mix between a pig and an elephant, with a short, prehensile nose that helps them grasp leaves, fruits, and aquatic plants.
Flexible Trunk-Like Structure: Allows them to grab and pull food toward their mouths.
Highly Developed Sense of Smell: Essential for navigating dense forests and avoiding predators.
Adapted for Both Land and Water: Their nostrils close when submerged, enabling them to forage in water.
As seed dispersers, tapirs play a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of rainforests.

The Star-Nosed Mole has one of the most bizarre noses in the animal kingdom—its snout is covered with 22 fleshy, tentacle-like appendages, making it the world’s most sensitive touch organ.
Extreme Sensory Perception: Contains over 100,000 nerve fibers, allowing it to detect and identify prey within milliseconds.
Rapid Foraging: It can touch and analyze up to 12 objects per second, making it the fastest-eating mammal.
Navigation in Darkness: The star-shaped nose compensates for poor eyesight, helping the mole find food underground.
Star-Nosed Moles contribute to soil aeration by tunneling and help control insect populations.
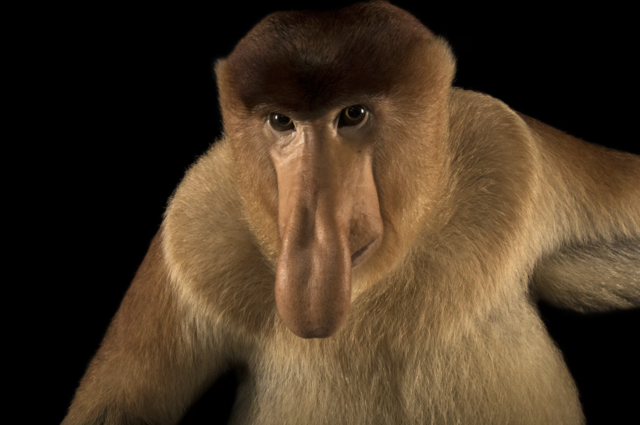

The Proboscis Monkey is famous for its large, bulbous nose, particularly in males. Scientists believe this exaggerated feature plays a key role in reproduction and communication.
Sexual Selection: Females prefer males with larger noses, possibly as a sign of good health and genetics.
Amplifying Calls: The large nose enhances vocal resonance, making the male's calls louder and more attractive to females.
Temperature Regulation: The oversized nose may help with heat dissipation in humid environments.
Proboscis Monkeys live in mangrove forests, where they help disperse seeds and maintain ecosystem balance.
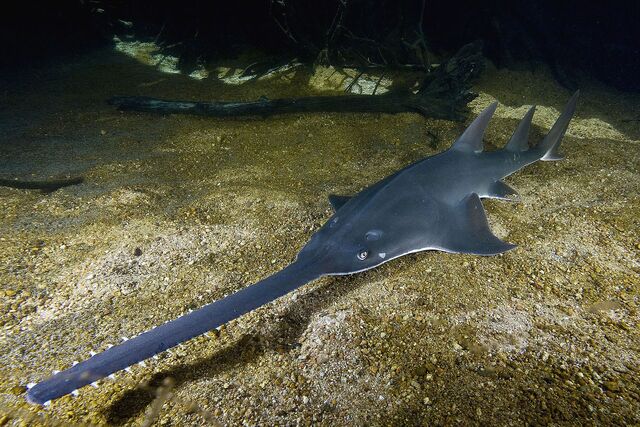

The Sawshark has an elongated snout lined with sharp, tooth-like structures, resembling a chainsaw. This deadly adaptation makes it a formidable hunter.
Electroreception: Detects the weak electric fields emitted by hidden prey, even in murky waters.
Slashing Attack: Uses its saw-like snout to strike and incapacitate fish before eating them.
Efficient Digging: Can use its nose to stir up sand and reveal buried prey.
Sawsharks help regulate fish populations, contributing to healthy marine ecosystems.
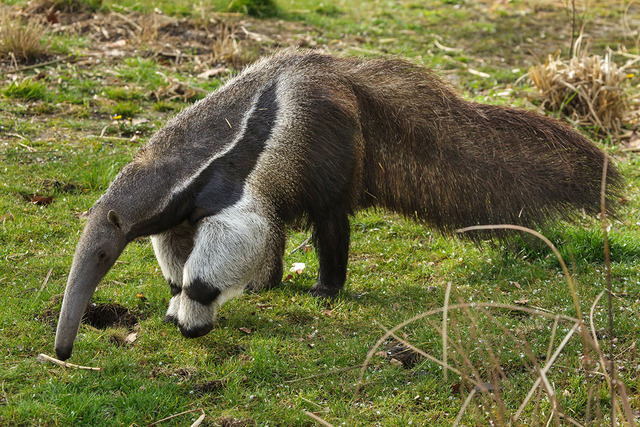

The Giant Anteater uses its elongated, toothless snout to feed on ants and termites, consuming thousands in a single day.
Extended Snout: Allows access to deep insect tunnels.
Superb Sense of Smell: Can detect food up to 30 feet (9 meters) away.
Sticky Tongue: Can extend up to 2 feet (60 cm), coated with a sticky substance to trap insects efficiently.
Giant Anteaters help control insect populations, preventing outbreaks of ants and termites.
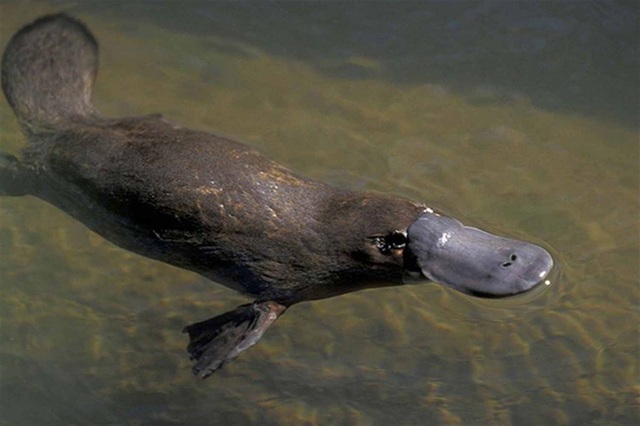

The Platypus has a flat, duck-like bill that functions as an advanced sensory tool for underwater hunting.
Electroreception: Can detect the electric fields of prey, allowing it to hunt in total darkness.
Filter-Feeding Adaptation: Uses its bill to sift through mud for insects and crustaceans.
Waterproof Design: The bill works efficiently even when submerged.
Platypuses play a key role in river ecosystems by controlling populations of small aquatic invertebrates.
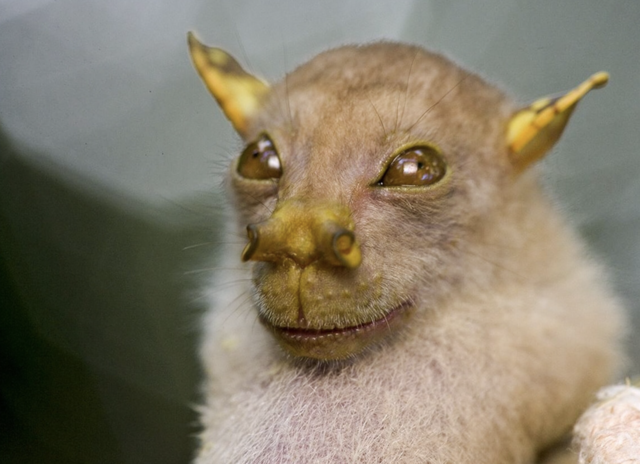

The Tube-Nosed Fruit Bat is a fascinating species known for its unique tubular nostrils, which are thought to enhance its olfactory abilities. As a nocturnal frugivore, this adaptation plays a crucial role in locating ripe fruit in dense tropical forests.
Tubular Nostril Structure: Unlike most bats, the nostrils of these bats extend outward like small tubes, potentially increasing scent detection range and accuracy.
Acute Sense of Smell: Their heightened olfactory ability allows them to locate fruit in complete darkness, even from a considerable distance.
Foraging Efficiency: The combination of keen smell and echolocation helps them efficiently navigate dense canopies and find food sources.
Tube-Nosed Fruit Bats play a vital role in seed dispersal, helping maintain the biodiversity of tropical rainforests. Their feeding habits contribute to the regeneration of plant species, making them crucial to ecosystem balance.

The Saiga Antelope is an ancient species found in the dry grasslands and deserts of Central Asia. Its strangely large, downward-facing nose serves as a multi-functional adaptation for extreme environmental conditions.
Natural Air Filter: The nasal structure helps filter out dust and sand, which is essential for survival in the arid, windy steppes.
Climate Control: In summer, the large nose helps cool down inhaled air before it reaches the lungs, while in winter, it warms and humidifies cold air to conserve body heat.
Enhanced Smell for Migration: The species migrates long distances, and its strong sense of smell helps detect water sources and vegetation.
Saiga Antelopes play a key role in the steppe ecosystem by controlling plant growth and serving as prey for large predators. However, their populations have declined due to poaching and habitat loss, making conservation efforts critical.
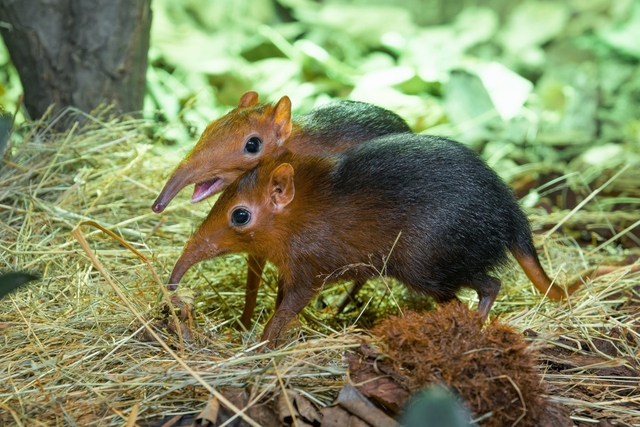

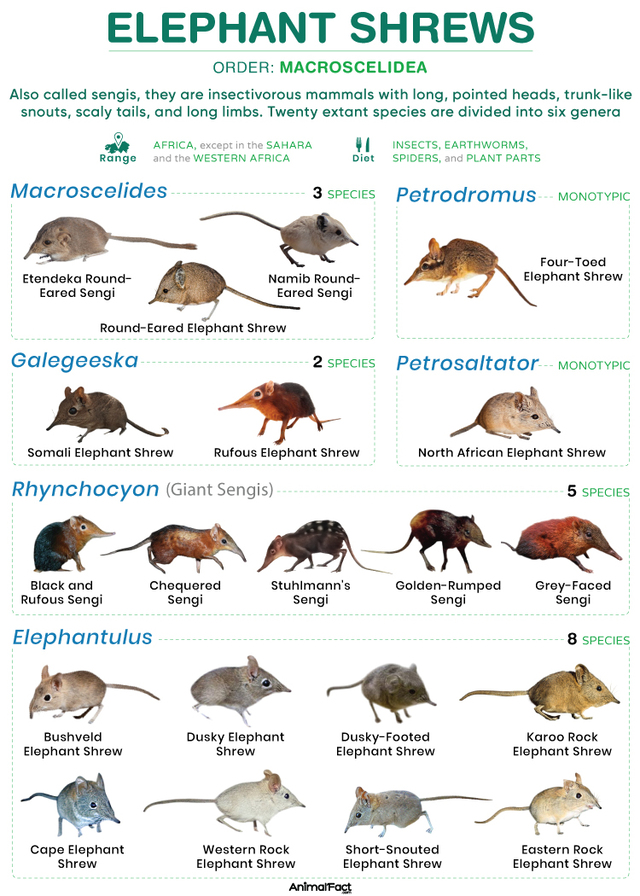
Despite its name, the Elephant Shrew is not related to Elephants-Are-Endangered.html">elephants but shares a similar elongated, flexible nose. These small, fast-moving mammals use their highly mobile snouts to forage for food in their natural habitats, ranging from forests to savannas.
Highly Flexible Structure: The snout is extremely mobile, allowing it to scan the ground and probe into crevices for insects.
Keen Sense of Smell: Essential for locating food and avoiding predators.
Rapid Foraging Ability: The combination of a sensitive nose and quick reflexes helps it efficiently find and consume small invertebrates.
Elephant Shrews help control insect populations and are prey for many predators, contributing to the balance of their ecosystems.
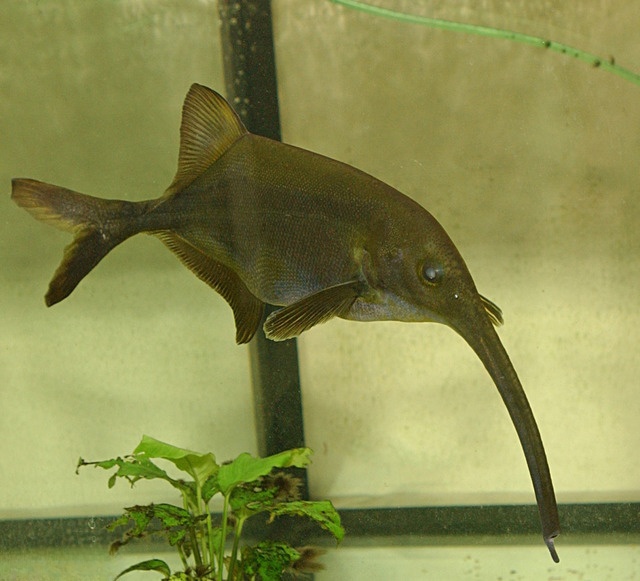

The Elephantnose Fish is a fascinating freshwater species native to African rivers, known for its elongated, trunk-like snout. This peculiar feature is not just for show—it serves as a highly specialized sensory organ that helps the fish navigate and hunt in murky waters.
Flexible, Trunk-Like Snout: The fish's elongated "nose" is an extension of its lower jaw, densely packed with electroreceptors.
Electroreception: Elephantnose fish use their snout to detect weak electric fields in the water, helping them locate prey, avoid obstacles, and communicate with other fish.
Hunting and Communication: This sensitive organ allows them to find small invertebrates hidden in the riverbed, even in complete darkness.
Elephantnose fish play a crucial role in controlling populations of small aquatic invertebrates, maintaining the balance of freshwater ecosystems. Additionally, their unique electric-sensing ability has made them a subject of scientific research in neurology and bioelectrics.

The Hammerhead Shark is one of the most distinctive sharks in the ocean, easily recognizable by its T-shaped head, known as a "cephalofoil." This unusual head structure is not just for appearance—it provides significant evolutionary advantages in hunting and navigation.
Hammer-Shaped Head: This flattened, extended head structure increases sensory perception and enhances maneuverability.
Superior Olfactory Ability: The widely spaced nostrils allow hammerhead sharks to detect even faint traces of chemicals in the water, making them highly efficient hunters.
Electroreception: Like other sharks, hammerheads possess ampullae of Lorenzini—specialized electroreceptors that help them sense the electric fields produced by prey, even if the prey is buried under sand.
Enhanced Vision: The lateral placement of the eyes gives hammerhead sharks an almost 360-degree field of vision, allowing them to scan vast oceanic areas while searching for food.
As apex predators, hammerhead sharks help regulate marine ecosystems by preying on fish, squid, and crustaceans. Their role in ocean food chains is vital for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
From the narwhal’s tusk to the star-nosed mole’s tentacles, animals with specialized noses have adapted to their environments in remarkable ways. Their noses help them survive, thrive, and perform essential tasks like hunting, feeding, mating, and navigating. In many cases, these adaptations have allowed them to occupy ecological niches that other animals cannot.
Animals with unique noses
Long-nosed crocodile
Narwhal tusk
Tapir’s flexible nose
Star-nosed mole
Proboscis monkey nose
Sawfish saw-shaped nose
Anteater’s long snout
Platypus bill
Tube-nosed bat
High-nosed antelope
These fascinating creatures serve as a reminder of the complexity and beauty of evolution, where even the smallest features can play a significant role in survival. Whether it’s for detecting prey, finding mates, or navigating harsh environments, the noses of these animals are a testament to the wonders of nature.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.