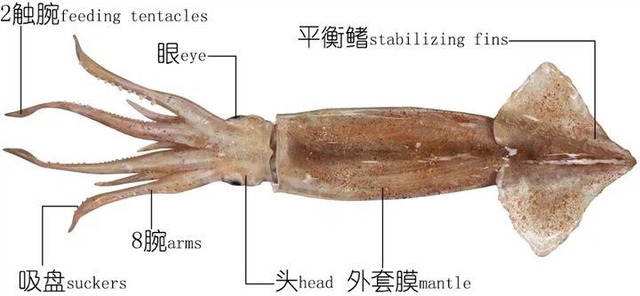
Tube squid(scientific name: Teuthida), also known asLancetorSquid<span style="color: #202122; Squids, commonly known as squids, are a class of animals belonging to the order Decapoda in the class Cephalopoda of the phylum Mollusca, including more than 300 species, and are distinctive for their elongated bodies and ten tentacles surrounding their mouths. Its meat is tender, soft and delicate, with an excellent taste, and is often processed into dried squid. It can be found in waters all over the world, both in shallow and deep seas. As a species, it is very prosperous and is also the staple food of various dolphins, whales, seals, seabirds. So what are the common types of squids in the world?
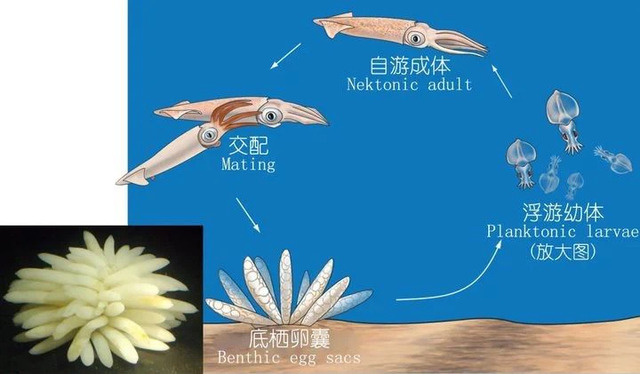
Today, the editor sorted out the top ten squid species, namely: Chinese squid, Japanese squid, American giant squid, Argentine squid, California squid, North Pacific squid, Long's mulberry squid, sword-pointed squid, firefly squid and firefly squid. Next, let's learn about these squids and their characteristics!

Little knowledge: Compared to the official name of "squid" is "Tubula", the official name of "cuttlefish" is "Cuttlefish", and the two add up to become "squid", and the official name of squid is "Decapoda".
In Taiwan, China, squid is further divided into "squid" (Occipital suborder), "big roll”,"Medium curl”,Small curl", but this classification method is not common in other Chinese-speaking regions. In other regions, "squid" is directly used, or even the larger "cuttlefish" is used as a vague substitute.
1. Chinese Squid
Features: Slender carcass/luminous
Habitat: South China Sea/Gulf of Thailand/Malay Archipelago

Chinese squid, also known as Hong Kong squid, Chinese squid or lock tube, is an important economic squid species, accounting for about 60% of the world's total squid production. It is slender and conical, with a pointed tail, no longitudinal vertebral midline on the ventral surface, two fins on the edge of the tube, and a diamond shape. The whole squid looks like a rocket. In addition, the Chinese squid can also glow. They are mainly distributed in the South China Sea, the Gulf of Thailand, the Malay Archipelago and the waters of Queensland, Australia. They are most common from May to June each year.
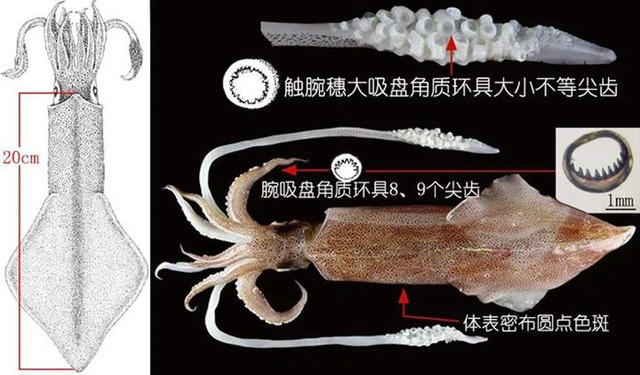
Although the name of this squid contains "China", the actual production is highest in Thailand, followed by the Philippines, China and Vietnam. The meat of Chinese squid is sweet and fresh, and is often used for stir-frying, cooking or as sashimi.
2. Japanese squid
Characteristics: Small/short and wide
Habitat: Western Pacific
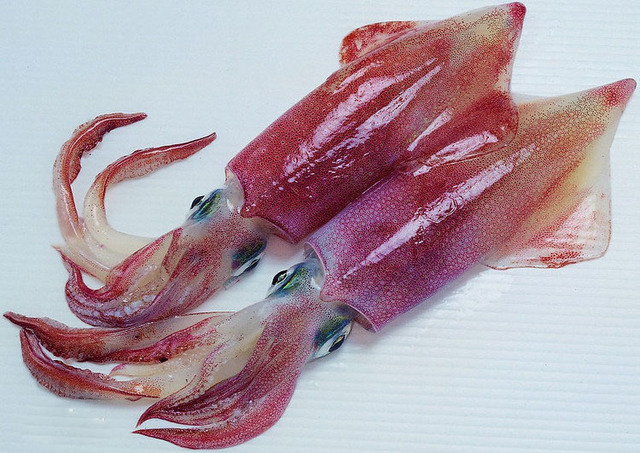

Japanese squid is one of the top ten common squids, mainly distributed in the waters of 21°N to 50°N in the western Pacific, including eastern China, Japan, Russia, Alaska and British Columbia, Canada. The main countries that catch this squid are Japan and South Korea. Compared with ordinary squid, Japanese squid is smaller, short and wide, with tentacles longer than the body, and a keratinous, thin and transparent inner shell. There are obvious purple spots on the back of its eyes. It has high protein and amino acid content and low crude fat content. It is a kind of squid with high nutritional value.
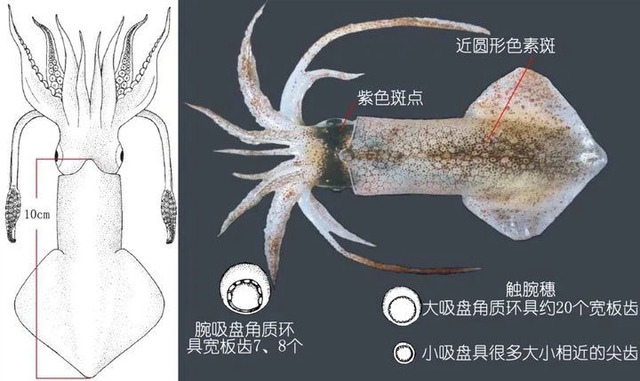
Japanese squid can be eaten fresh or processed into various dried or frozen products. Common cooking methods include blanching or stewing. It tastes sweet and refreshing, and is elastic, and is deeply loved by diners.
3. American giant squid
Characteristics: Large/long conical
Habitat: East of the central Pacific Ocean
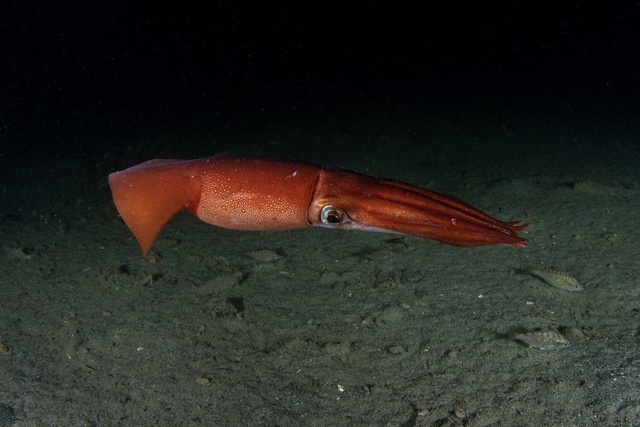

The American giant squid is named for its deep red appearance and is the largest of the squids. Its carcass is conical, with a slender rear and covered with nearly circular spots of varying sizes. The American giant squid can reach a length of 1.2 meters and a maximum weight of 50 kilograms. This type of squid is mainly distributed in the central to eastern Pacific Ocean, especially along the coasts of Peru and Chile in South America, as well as offshore areas, and is rich in resources.

Due to the large catch and relatively low price of the American giant squid, it has become the preferred raw material for many domestic squid shred processing factories. These squids are usually processed abroad, including squid heads, raw plates, cooked plates, raw ears, cooked ears and squid tentacles, and then imported into China for making various squid shred products.
4. Argentine squid
Characteristics: Brown skin/short and wide fins
Habitat: Southwest Atlantic
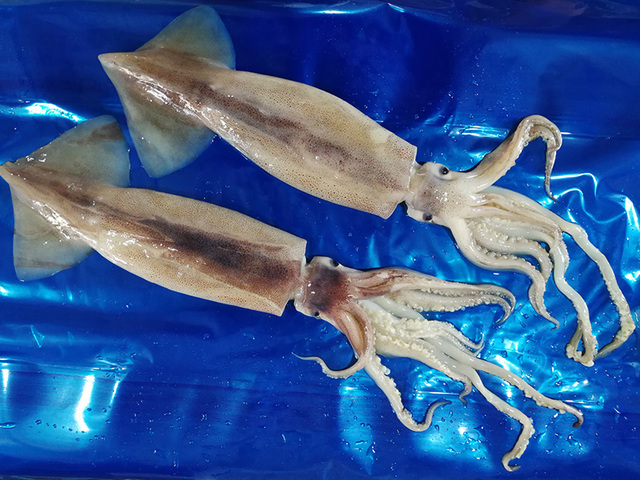

Argentine squid is a type of squid with a large catch at present, and is also one of the common squid species in China. Its carcass is conical, with a shallow hole in the front of the funnel, but no longitudinal wrinkles, no side capsules, and the overall surface is smooth. The fleshy fins of the Argentine squid are short and wide, with a fin angle of about 45 degrees, and the two fins are slightly rhombus-shaped. Its color is brownish yellow and white, and its skin is brown. It tastes chewy, has thick meat, and tastes delicious.

The Argentine squid is mainly distributed in the 22°S to 54°S area in the southwest Atlantic, including the continental shelf and slope near Uruguay, Argentina and the Falkland Islands.
5. California Squid
Features: Small-sized squid
Habitat: California Coastal Area

California squid, also known as California pen squid, is one of the ten most common squid species. Its main production area is in the eastern Pacific Ocean, covering the waters from Mexico to Alaska. Most of the catch comes from California, USA, especially the catch on the California coast, which accounts for 85% of the total catch in the United States.
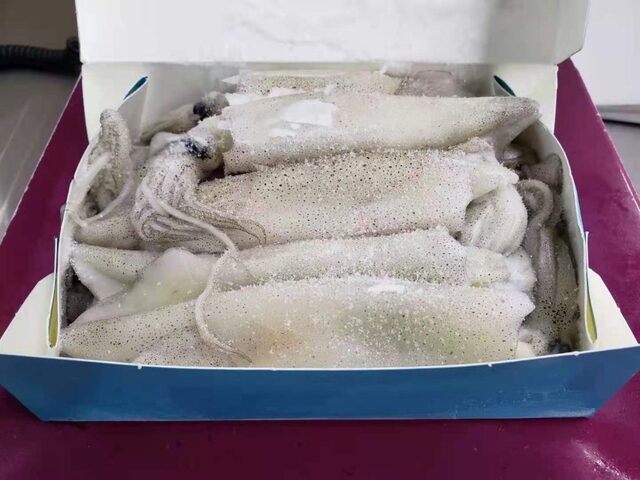

It is understood that California squid can be caught all year round, but its main fishing season is in winter in Southern California, starting in November or December each year and lasting until March of the following year. California squid is generally small in size, with an average weight of 45 to 165 grams. Common sizes are 8-9, 9-10, 10-11, 11-12 and 12-14 per pound. Usually, they are packaged in boxes of 25 pounds (about 11.4 kilograms) and exported in large quantities to the Chinese market.
6. Northern Pacific squid
Features: cylindrical front section/conical rear section
Habitat: North Pacific Ocean
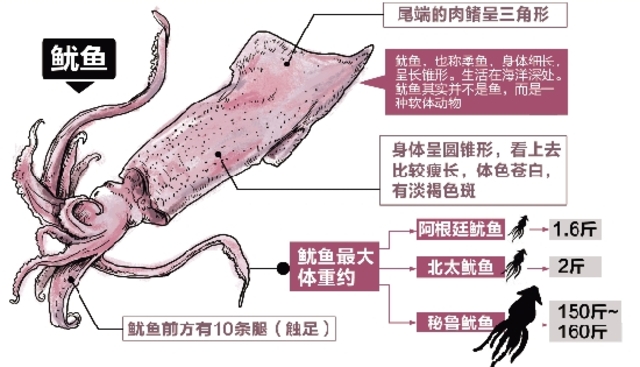
The North Pacific squid, also known as the North Pacific squid, is one of the important economic cephalopod resources in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It lives in subtropical and temperate marine waters, mainly distributed in the sea where the cold and warm currents of the North Pacific meet. The body shape of the North Pacific squid is characterized by a cylindrical front part, a gradually contracted cone at the back, a slightly thin and pointed tail, a blunt triangle at the front edge of the back, and a slightly concave front edge of the ventral side. The small sucker tooth ring from the base to the handle is smooth and has no sucking teeth. The male North Pacific squid can grow up to 45 cm, while the female can reach 60 cm.
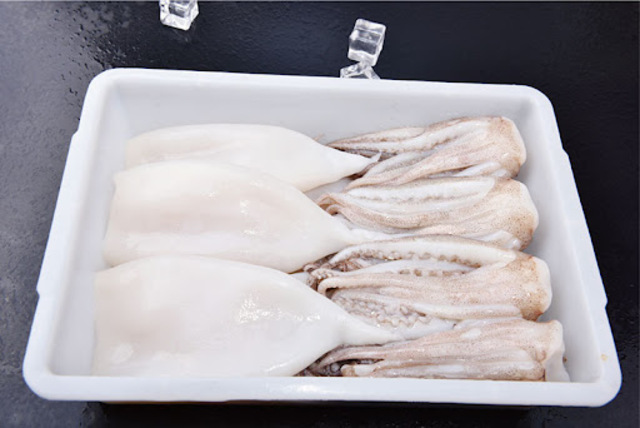

This squid is purple-red in color, thin in texture, slightly doughy in taste, and not very chewy. However, adding an appropriate amount of soy sauce, ginger slices or chopped green onions during processing can better highlight its delicious original flavor.
7. Long's mulberry squid
Features: Deep-sea squid
Habitat: Subtropical and tropical waters
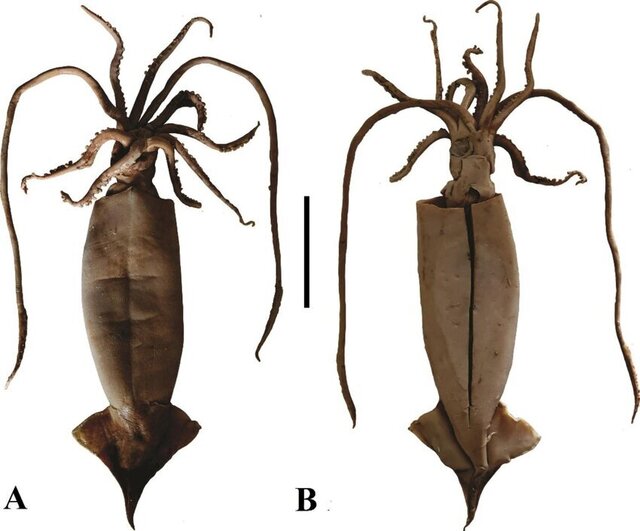

One of the common squid species on the market is Long's mulberry squid, which belongs to the lock tube family and mainly inhabits subtropical and tropical waters. It is widely distributed in the South my country Sea and the southern waters of the Japanese archipelago. As a deep-sea squid, Long's mulberry squid usually lives in waters 700 to 900 meters deep. The common frozen squid on the market is basically this variety, which is mainly caught by trawling.

The rear part of the fleshy fin of Long's mulberry squid is concave and the end is extended. The length of the fin exceeds half of the body length, and the junction of the two fins is slightly horizontal rhombus-shaped. Its meat is delicious and delicate in taste. It is a high-quality raw material for making sashimi and is widely loved by diners.
8. Sword-pointed squid
Characteristics: Shallow sea squid
Habitat: Southern Japan

Sword-pointed squid is mainly distributed in the waters south of Aomori Prefecture, Japan, as well as the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea and around the Philippine Islands. It is a common squid. Its maximum annual output can exceed 20,000 tons, which has high economic value and can be sold fresh or processed into dried products.
The body of the sword-pointed squid is conical, with a medium structure and a relatively straight rear. The male has longitudinal folds in the midline of its abdomen, long fleshy fins, and suction cups. It is a shallow-water squid that often lives in waters 30 to 170 meters deep. In winter, it migrates to deep waters to hibernate, and in spring and summer, it gathers and migrates to shallow waters near the coast. According to different growth cycles, the sword-pointed squid can be divided into spring-born groups, summer-born groups, and autumn-born groups.
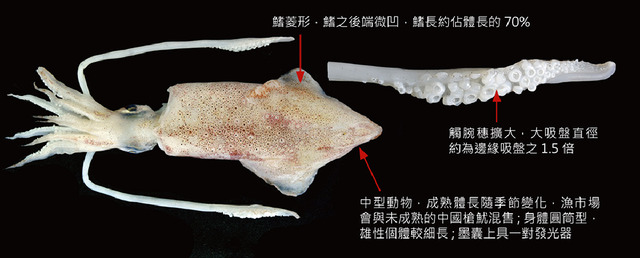
This type of squid is more active in feeding at night, especially in the middle of the night and before dawn, when the feeding intensity is the highest. Therefore, many squid anglers are accustomed to going out to sea at night and returning early in the morning.
9. Firefly Squid
Characteristics: Small/luminous
Habitat: Sea of Japan and north of Shikoku, Japan

Firefly squid, also known as firefly squid or firefly cuttlefish, is a small squid with luminous ability. It is usually only 7.6 cm long and has a standard 8 tentacles and 2 tentacles. Although the light organ of the firefly squid is located on the tentacles, its entire body can emit light, and these lights are mainly used to lure prey.
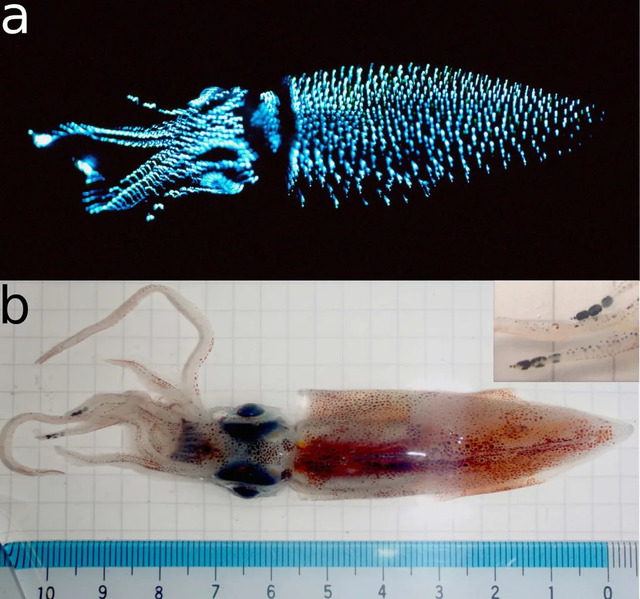

Firefly squid is widely distributed in the Sea of Japan and the Pacific coast north of Shikoku, Japan. Toyama Bay in Toyama Prefecture is one of the important fishing grounds for this squid. The deep waters here are rich in minerals and organic matter, and the V-shaped sea valley terrain pushes the firefly squid to the shore. Therefore, from March to June every year, the firefly squid will go to Toyama Bay to spawn.
10. Firefly squid
Features: Small size/purple spots on the body
Habitat: North and South China Coastal Areas
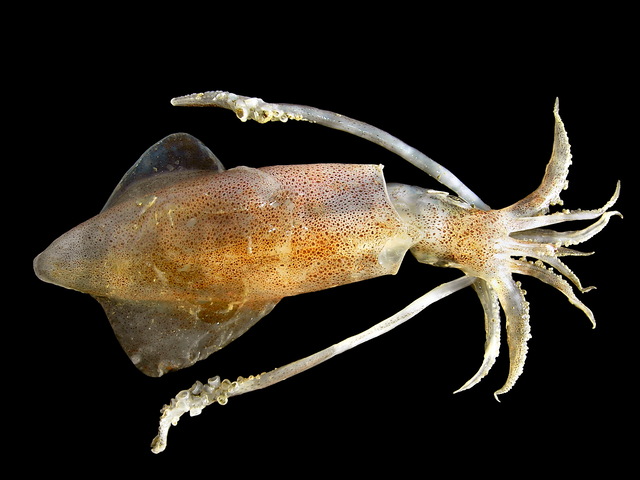

Firefly squid, also known as squid fry, is a common small coastal squid. It is widely distributed in the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea, the South China Sea, and the southern waters of the Japanese archipelago. It is also found in coastal waters such as North Korea and Indonesia. This squid lives around offshore islands and reefs and mainly preys on small shrimps. Egg-bearing individuals of musketeers can be found almost all year round, but they are more common in spring and summer. The peak season is usually from August to September, and the fishing season is from May to September every year.
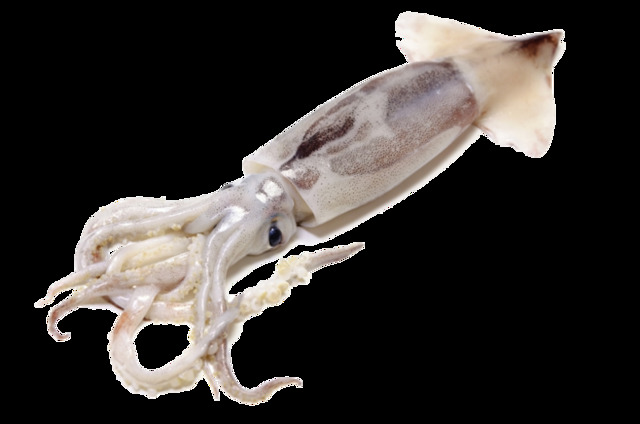

The carcass of musketeers is conical, with a slightly straightened back. The length of the fins exceeds half of the carcass. The fins on both sides are connected, and the shape is slightly longitudinally diamond-shaped. The outer edge of its gelatinous ring has small sharp teeth, the length of the tentacles exceeds the carcass, the inner shell is horny, thin and transparent, and the back is covered with dense purple spots.
The top ten squid species are based on the characteristics and quality of common squids, and refer to the public popularity of squid species and other related information, and then combined with other related rankings/lists on the Internet for comprehensive ranking recommendations. The list is for reference only. If you have any questions, please comment/communicate at the end.
More other squid species: Giant squid, European squid, New Zealand squid, Australian squid, tiger squid, Lai's squid...
animal tags: squid
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.