Hamsters are among the most beloved small pets in the world due to their compact size, easy care, and adorable appearance. However, “hamster” is not a single species—there are many hamster breeds, each with its own traits, size, temperament, and lifespan. In this article, we explore the 10 most common types of pet hamsters to help you choose the perfect furry friend!
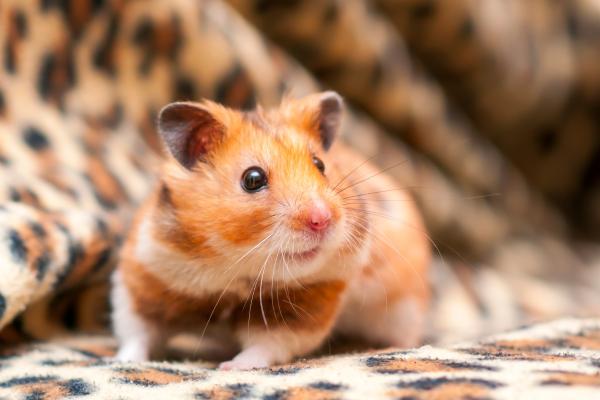


The largest and most common pet hamster, Syrian hamsters can grow up to 19 cm and weigh between 110–140 grams. Females are typically larger. They come in various colors, but golden is the most popular. Solitary by nature, they must be housed alone. Average lifespan: up to 4 years.
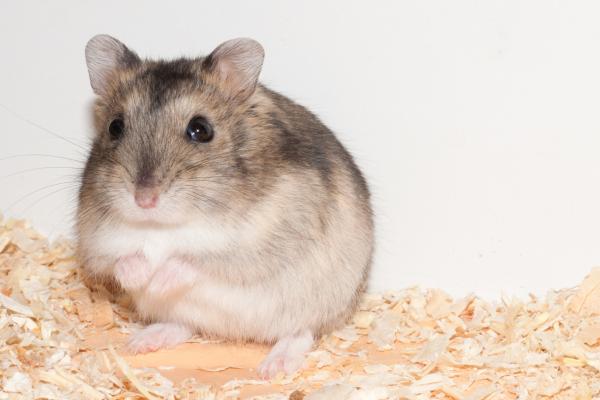

Small and agile, measuring 8–10 cm and weighing 35–50 grams. Known for their sociable temperament and ability to live in pairs if introduced early. Typical gray fur with a dark dorsal stripe. Handle with care due to their delicate size.
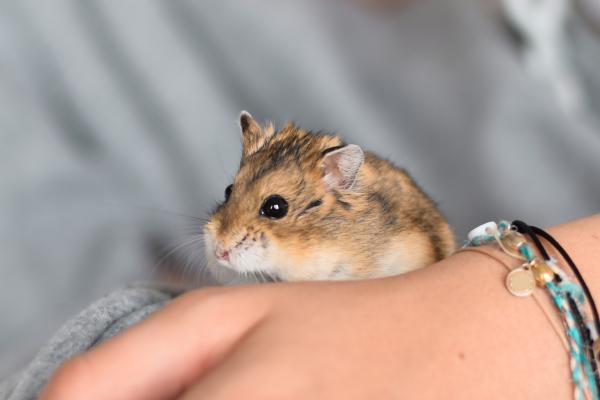

The tiniest domestic hamster at just 4–5 cm and 20 grams. Originating from Central Asian deserts, it is fast, shy, and difficult to handle, but highly entertaining to watch. Lifespan: 2–4 years.
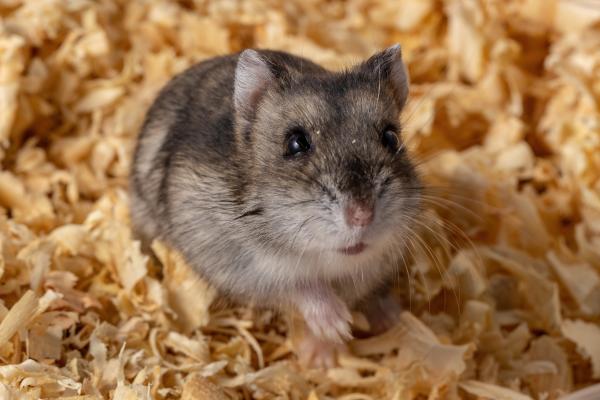

Looks similar to the Russian dwarf but is more territorial and may bite if provoked. Found in central Asia's steppes and semi-arid regions. Comes in a wide range of colors. Lifespan: 1.5–3 years.
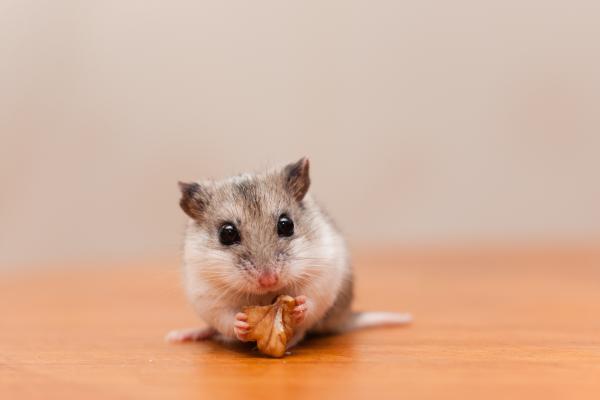

Native to China and Mongolia, this breed is slim and mouse-like, measuring 8–13 cm. Gentle and docile, it makes a great companion pet. Features a small prehensile tail. Lifespan: 2–4 years with proper care.
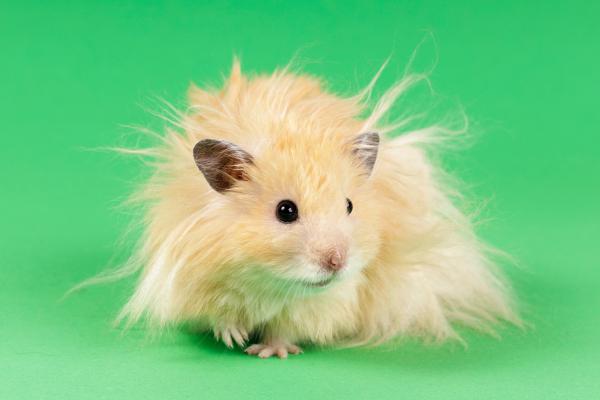

A variation of the Syrian hamster known for its long, silky fur, especially in males. Requires regular grooming and is often seen in pet shows or exhibitions.
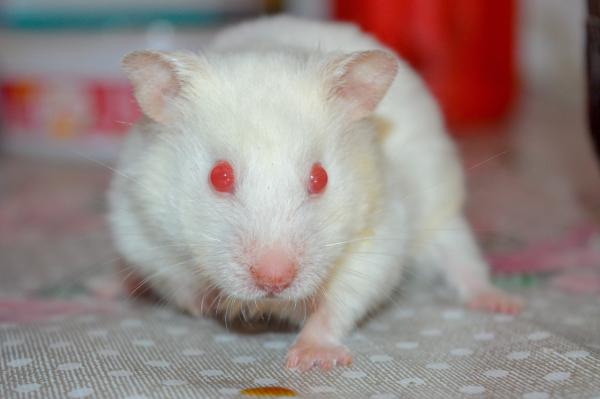
Not a separate breed, but a genetic mutation causing white fur and red eyes due to lack of melanin. Found in several hamster species. Behavior and care needs are similar to standard hamsters.

A color morph of the Syrian hamster with distinct black and white patterns resembling a panda. Black on the head and ends, white in the middle. Calm and easy to tame when handled from a young age.
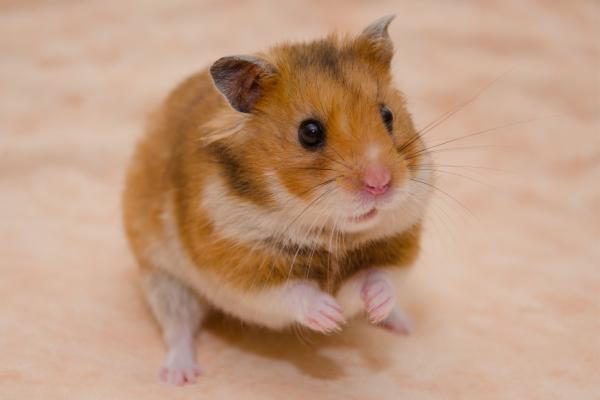

Known for its shiny, silky coat caused by a “satin” gene mutation. Found in both long and short-haired varieties, commonly among Syrian hamsters. Grooming is necessary to keep their coat glossy.
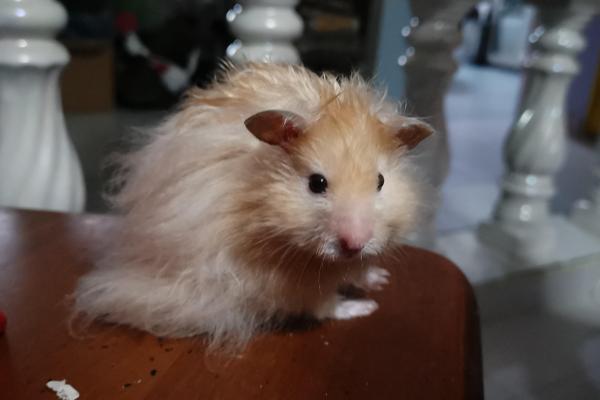

Features curly, coarse fur and whiskers due to a unique genetic mutation. Seen in both Syrian and dwarf hamsters. Highly valued for their unique appearance.
Want more pet guides and hamster care tips? Bookmark our website for the latest animal encyclopedia updates!
animal tags: types hamsters
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.