The Strait of Gibraltar is located between southernmost Spain and northwest Africa. It is an important gateway connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, with a total length of about 90 kilometers. The narrowest point of the gorge is only 14 kilometers, and the widest point where it enters the gorge in the west is 43 kilometers; the water depth is 301 meters at the shallowest point, 1181 meters at the deepest point, and the average depth is about 375 meters; the sea flows from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea through the Strait of Gibraltar. The flow speed is 4 kilometers per hour. In the early years, it was used by Atlantic navigators. Expedition fleets from countries along the Mediterranean Sea frequently passed here to reach the Atlantic Ocean to complete their expeditions. Today, the Strait of Gibraltar is still an important waterway from the Atlantic Ocean to southern Europe, North Africa and Western Asia.
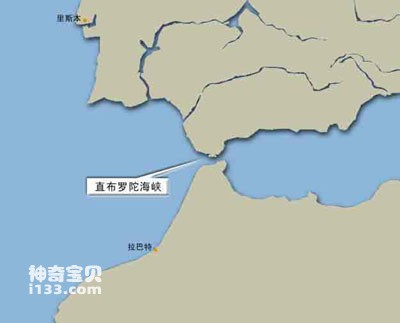
Geographic location map of the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is only 58 kilometers long, 43 kilometers wide between Cape Trafalgar and Cape Spartel, and only 13 kilometers wide between Marroquillo in Spain and Cape Sires in Morocco. . The average water depth is 310 meters.
In addition to connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, the Strait of Gibraltar is also the "source of life" of the Mediterranean Sea. It turns out that at a depth of 122 meters in the Mediterranean Sea, there is a heavier, colder and saltier ocean current that continuously flows westward out of the Mediterranean Sea. After reading this, you may ask, if this continues, won’t the Mediterranean Sea become dry? Indeed, it is. However, nature has its own laws, and the Mediterranean Sea will not dry up. The Strait of Gibraltar continuously replenishes the Mediterranean Sea with seawater. It turns out that the wind direction in the Strait is mostly easterly or westerly. The cold air mass entering the western Mediterranean from the north passes through here as a low-level, high-speed easterly wind. The locals call this easterly wind the Levant wind. Levantine winds drive the Atlantic surface current eastward through the Strait of Gibraltar and into the Mediterranean Sea, and the flow of this current is greater than the westward current in the Mediterranean Sea at a depth of 122 meters. Therefore, the existence of the Strait of Gibraltar has saved the Mediterranean from becoming a shrinking salt country, and its contribution is not small.
The name Gibraltar originates from Arabic and means "Taliq Mountain". According to legend, in 711 AD, Tariq, an officer of the Moorish dynasty, led a team of 7,000 people across the sea to attack Spain. After Tariq's army forcibly landed, Tariq stood on a giant rock in Gibraltar and commanded the battle, defeating 100,000 Spanish troops. Tariq then ordered the construction of Gibraltar Castle here. The name of the Strait of Gibraltar comes from the city of Gibraltar.
animal tags:
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a Animals Top editor.